Using the quadratic formula to find `n^(th)` term of a sequence - consistent difference between differences
Method 1
This is the easiest to remember but takes the most time to work out an answer.
We know (from the last section) that:
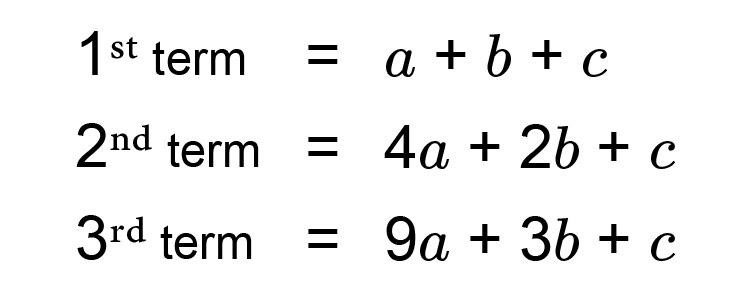
Once you have found `a,b,\ &\ c` you can slot these figures in the following formula.
`an^2+bn+c`
Example 1
Square numbers
We know the following sequence is a quadratic sequence but what is the formula for the `n^(th)` term and what is the `14^(th)` term?
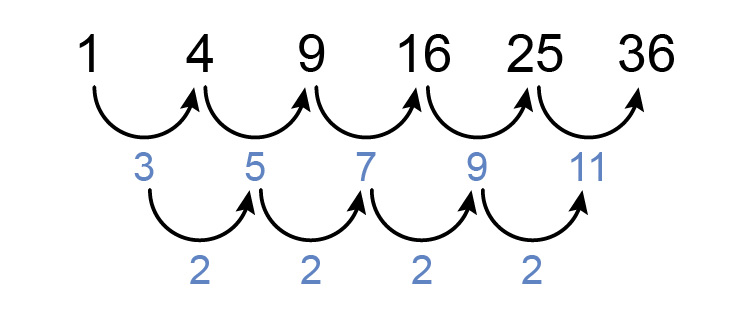
The 1st term `=a+b+c`
so `1=a+b+c`
The 2nd term `=4a+2b+c`
so `4=4a+2b+c`
The 3rd term `=9a+3b+c`
so `9=9a+3b+c`
Now you have 3 simultaneous equations.
`1=a+b+c` .................... (1)
`4=4a+2b+c` ................ (2)
`9=9a+3b+c` ................ (3)
Now solve for one letter at a time
`1=a+b+c`
therefore `c=1-a-b`
Substitute this into equations (2) and (3).
`4=4a+2b+1-a-b`
`9=9a+3b+1-a-b`
These two simultaneous equations become
`4-1=4a-a+2b-b`
and `9-1=9a-a+3b-b`
Which simplify to
`3=3a+b` ........... (i)
and `8=8a+2b` .......... (ii)
Now we can solve these two simultaneous equations
`3=3a+b`
is the same as `b=3-3a`
substitute this into (ii)
`8=8a+2(3-3a)`
which is `8=8a+6-6a`
which is `8-6=8a-6a`
becomes `2=2a`
therefore `a=1`
Sustitute `a=1` into (i)
and `3=3a+b`
becomes `3=3times1+b`
`b=3-3=0`
Now substitute `a=1` and `b=0` into equation (1)
`1=a+b+c`
`1=1+0+c`
`c=1-1=0`
Summary `a=1` `b=0` and `c=0`
therefore the formula for the `n^(th)` term in this sequence is
`an^2+bn+c`
or `1n^2+0n+0`
which is `n^2`
Now we need to check the formula is correct.
Try different values of `n` in the formula `n^2`
If `n=1` term `=1^2=1`
If `n=2` term `=2^2=4`
If `n=3` term `=3^2=9`
If `n=4` term `=4^2=16`
This is correct
The 14th term would be
If `n=14` then `n^2=14^2=196`
The 14th term `=196`
Example 2
We know the following sequence is a quadratic sequence but what is the formula of the `n^(th)` term and what is the 16th term?
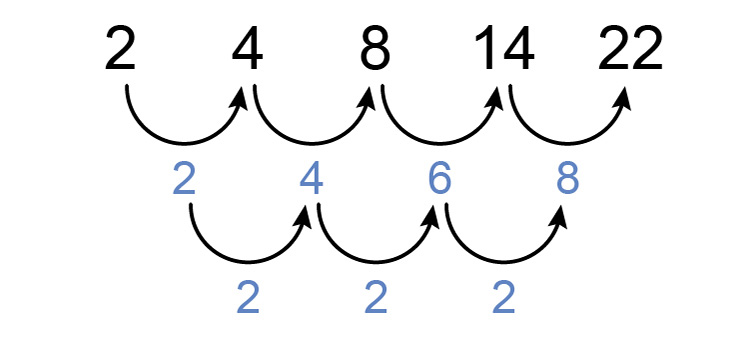
The 1st term `=a+b+c`
so `2=a+b+c`
The 2nd term `=4a+2b+c`
so `4=4a+2b+c`
The 3rd term `=9a+3b+c`
so `8=9a+3b+c`
Now you have 3 simultaneous equations.
`2=a+b+c` .................... (1)
`4=4a+2b+c` ................ (2)
`8=9a+3b+c` ................ (3)
Now solve for one letter at a time
`2=a+b+c`
therefore `c=2-a-b`
Substitute this into equations (2) and (3).
`4=4a+2b+(2-a-b)`
`8=9a+3b+(2-a-b)`
These two simultaneous equations become
`4-2=4a-a+2b-b`
and `8-2=9a-a+3b-b`
Which simplify to
`2=3a+b` ............ (i)
and `6=8a+2b` .......... (ii)
Now we can solve these two simultaneous equations
`2=3a+b`
is the same as `b=2-3a`
substitute this into (ii)
`6=8a+2(2-3a)`
which is `6=8a+4-6a`
which is `6-4=8a-6a`
becomes `2=2a`
therefore `a=1`
Sustitute `a=1` into (i)
and `2=3a+b`
becomes `2=3times1+b`
`b=2-3=-1`
Now substitute `a=1` and `b=-1` into equation 1
`2=a+b+c`
`2=1-1+c`
`c=2`
Summary `a=1` `b=-1` and `c=2`
therefore the formula for the `n^(th)` term in this sequence is
`an^2+bn+c`
or `1n^2+(-1)n+2`
which is `n^2-n+2`
Now we need to check the formula is correct.
Try different values of `n` in the formula `n^2-n+2`
If `n=1` term `=1^2-1+2=2`
If `n=2` term `=2^2-2+2=4-2+2=4`
If `n=3` term `=3^2-3+2=9-3+2=8`
If `n=4` term `=4^2-4+2=16-4+2=14`
This is correct
The 16th term would be
If `n=16` then `n^2-n+2=16^2-16+2=256-16+2=242`
The 16th term `=242`
Example 3
We know the following sequence is a quadratic sequence but what is the formula of the `n^(th)` term and what is the 12th term?
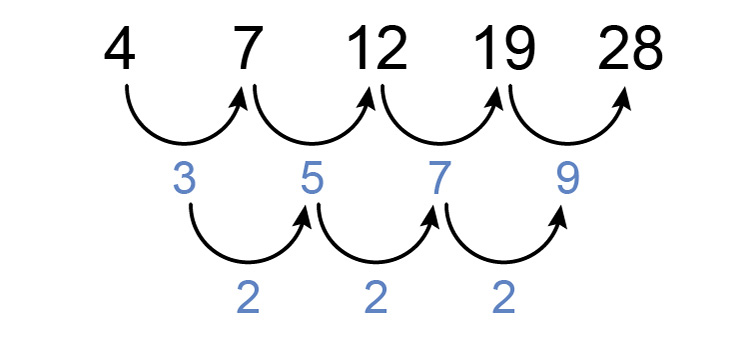
The 1st term `=a+b+c`
so `4=a+b+c`
The 2nd term `=4a+2b+c`
so `7=4a+2b+c`
The 3rd term `=9a+3b+c`
so `12=9a+3b+c`
Now you have 3 simultaneous equations.
`4=a+b+c` ..................... (1)
`7=4a+2b+c` ................ (2)
`12=9a+3b+c` ................ (3)
Now solve for one letter at a time
`4=a+b+c`
therefore `c=4-a-b`
Substitute this into equations (2) and (3).
`7=4a+2b+(4-a-b)`
`12=9a+3b+(4-a-b)`
These two simultaneous equations become
`7-4=4a-a+2b-b`
and `12-4=9a-a+3b-b`
Which simplify to
`3=3a+b` ........... (i)
and `8=8a+2b` .......... (ii)
Now we can solve these two simultaneous equations
`3=3a+b`
is the same as `b=3-3a`
substitute this into (ii)
`8=8a+2(3-3a)`
which is `8=8a+6-6a`
which is `8-6=8a-6a`
becomes `2=2a`
therefore `a=2/2=1`
Sustitute `a=1` into (i)
and `3=3a+b`
becomes `3=3times1+b`
`b=3-3=0`
Now substitute `a=1` and `b=0` into equation (1)
`4=a+b+c`
`4=1+0+c`
`c=4-1`
`c=3`
Summary `a=1` `b=0` and `c=3`
therefore the formula for the `n^(th)` term in this sequence is
`an^2+bn+c`
or `1n^2+0n+3`
which is `n^2+3`
Now we need to check the formula is correct.
Try different values of `n` in the formula `n^2+3`
If `n=1` term `=1^2+3=1+3=4`
If `n=2` term `=2^2+3=4+3=7`
If `n=3` term `=3^2+3=9+3=12`
If `n=4` term `=4^2+3=16+3=19`
This is correct
The 12th term would be
If `n=12` then `n^2+3=12^2+3`
`=144+3`
`=147`
The 12th term `=147`
Example 4
We know the following sequence is a quadratic sequence but what is the formula of the `n^(th)` term and what is the 11th term?
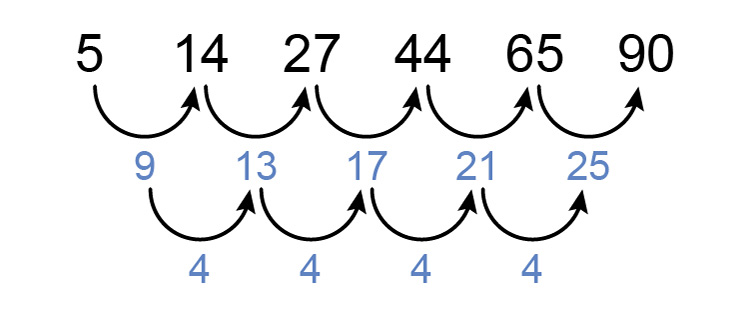
The 1st term `=a+b+c`
so `5=a+b+c`
The 2nd term `=4a+2b+c`
so `14=4a+2b+c`
The 3rd term `=9a+3b+c`
so `27=9a+3b+c`
Now you have 3 simultaneous equations.
`5=a+b+c` .................... (1)
`14=4a+2b+c` ................ (2)
`27=9a+3b+c` ................ (3)
Now solve for one letter at a time
`5=a+b+c`
therefore `c=5-a-b`
Substitute this into equations (2) and (3).
`14=4a+2b+5-a-b`
`27=9a+3b+5-a-b`
These two simultaneous equations become
`14-5=4a-a+2b-b`
and `27-5=9a-a+3b-b`
Which simplify to
`9=3a+b` ............ (i)
and `22=8a+2b` .......... (ii)
Now we can solve these two simultaneous equations
`9=3a+b`
is the same as `b=9-3a`
substitute this into (ii)
`22=8a+2(9-3a)`
which is `22=8a+18-6a`
which is `22-18=8a-6a`
becomes `4=2a`
therefore `a=4/2=2`
Sustitute `a=2` into (i)
and `9=3a+b`
becomes `9=3times2+b`
`b=9-6=3`
Now substitute `a=2` and `b=3` into equation (1)
`5=a+b+c`
`5=2+3+c`
`c=0`
Summary `a=2` `b=3` and `c=0`
therefore the formula for the `n^(th)` term in this sequence is
`an^2+bn+c`
or `2n^2+3n+0`
which is `2n^2+3n`
Now we need to check the formula is correct
Try different values of `n` in the formula `2n^2+3n`
If `n=1` term `=2times1^2+3times1=2+3=5`
If `n=2` term `=2times2^2+3times2=8+6=14`
If `n=3` term `=2times3^2+3times3=18+9=27`
If `n=4` term `=2times4^2+3times4=32+12=44`
This is correct
The 11th term would be
If `n=11` then `2n^2+3n=2times11^2+3times11=242+33=275`
The 11th term `=275`




