atomic number – the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
(pronounced uh-tom-ik)
To remember the meaning of atomic number, use the following mnemonic:
If you can think of peas as positive protons, then think of the following.
A tom cat was stick (atomic number) thin because all it ate was one pea (pea for protons) a day.

The atomic number of an atom is the number of protons in its nucleus.
The periodic table shows the unique symbol of every element, together with its mass number and atomic number. For example, Lithium (Li) has a mass number of 7 and an atomic number of 3. This would be shown in the periodic table as:
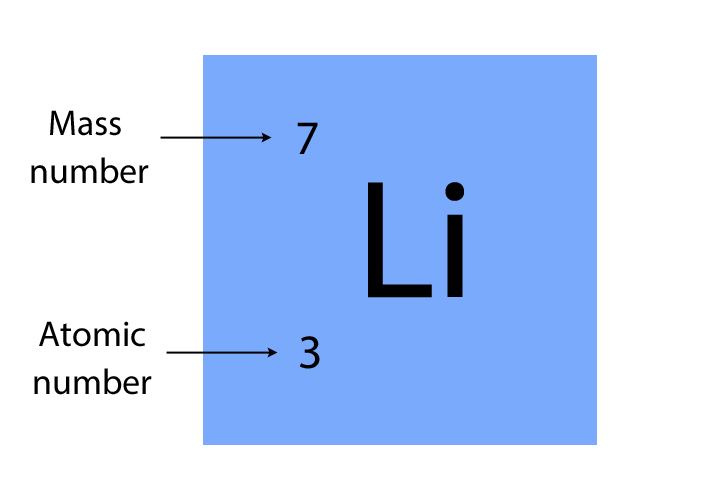
The number of protons determines the type of element or atom, it's the only thing that remains constant, the number of neutrons and electrons can change.
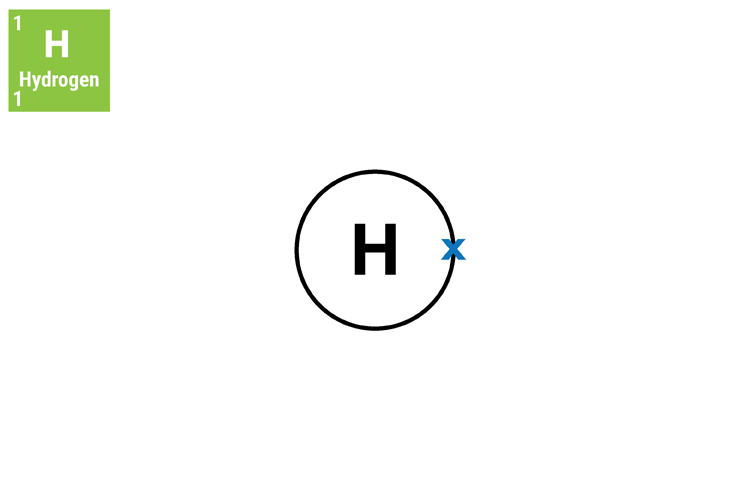
The hydrogen atom has no neutrons and therefore must be defined by the number of protons because electrons can leave the atom.
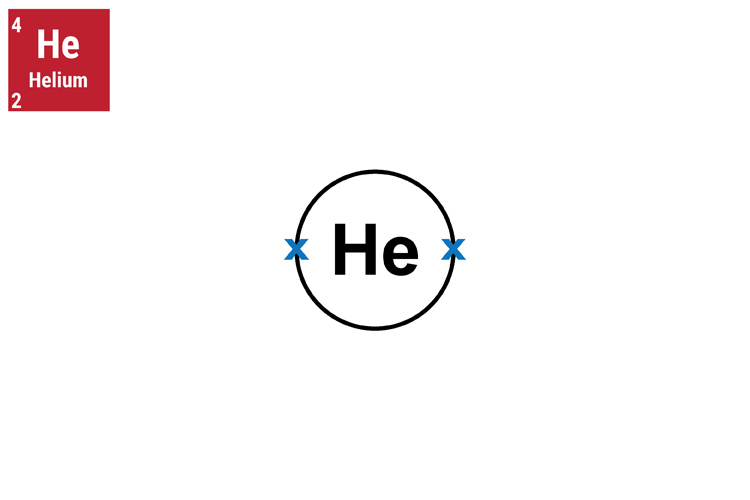
The atomic number is always the smallest number because the bigger number the mastiff (mass) will always be bigger that the tom cat who was stick (atomic) thin.





