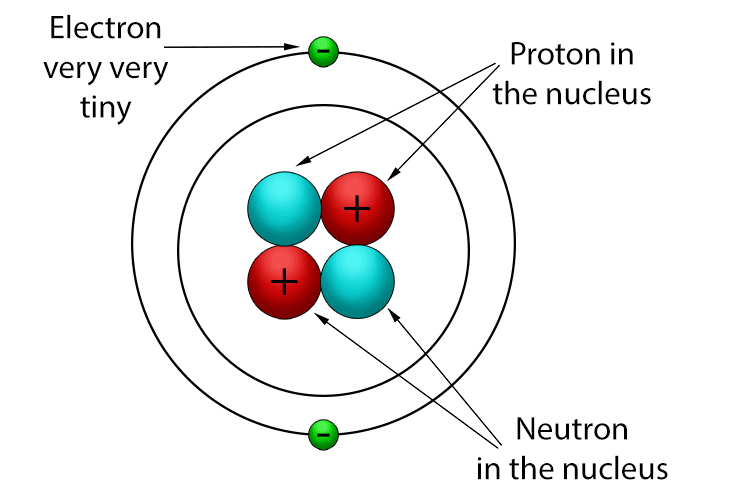
protons – are positively charged subatomic particles
(pronounced proh-ton)
It's also vital to remember that the number of protons never changes. In any atom it is the number of protons that define an atom.
We know atoms can lose or gain electrons.
We know that atoms can have isotopes meaning that an atom can lose or gain neutrons.
A proton, however, always remain unchanged.
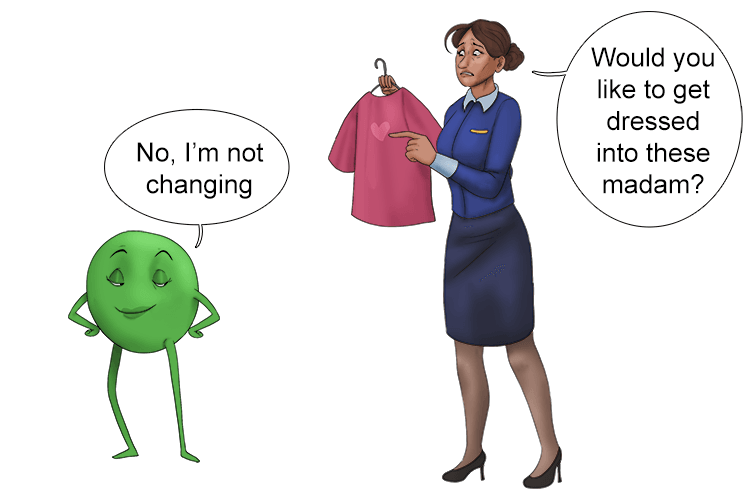
To remember that a proton is +ve and the number of protons remain unchanged, use the following mnemonic:
The pea (proton) was very +ve (positive) and when it was asked if it would like to get changed, she said "no, I always remain the same."
Another way to remember that protons never change and the number of protons define the atom, consider hydrogen on the periodic table.

This shows that the atomic number and the mass number are the same. If the atomic number is 1 then the number of protons is 1. If the mass number is the number of protons and neutrons then there are no neutrons in a hydrogen atom. The hydrogen atom has one proton which defines it as a hydrogen atom.
Every, and we mean every proton and neutron weighs =1
6 x 1023 grams
This is so tiny that chemists wanted to make this easy for themselves and decided to call this a "relative mass of 1."
1
6 x 1023 grams = Relative mass of one.
Electrons have a mass so much smaller than a proton or neutron.
Electron =1
1840th of a proton's or neutron's mass
Chemists decided to describe this as so small that even compared to the relative mass of a proton or neutron i.e. 1, that an electrons relative weight is described as zero.
Proton relative weight = 1
Neutron relative weight = 1
Electron relative weight = 0
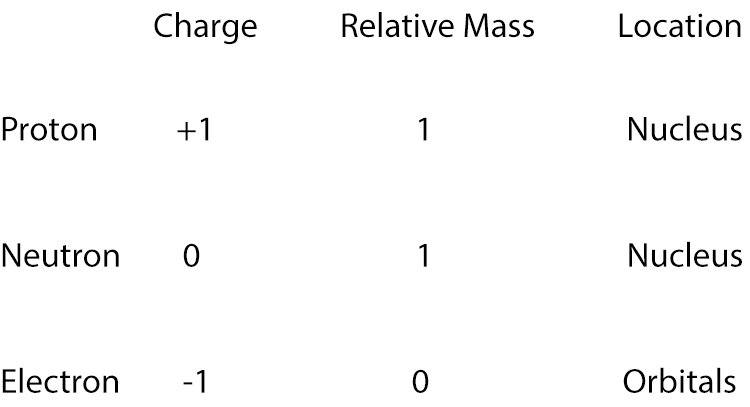
Here below is a helium atom that has two protons.