Atom – the smallest part of an element that can exist and is made up of protons, neutrons and electrons
(pronounced at-uhm)
To remember the meaning of Atom, use the following mnemonic:
The atom bomb was being carried by the newt (neutrons), the electronic robot (electron) and the pea (p for proton).
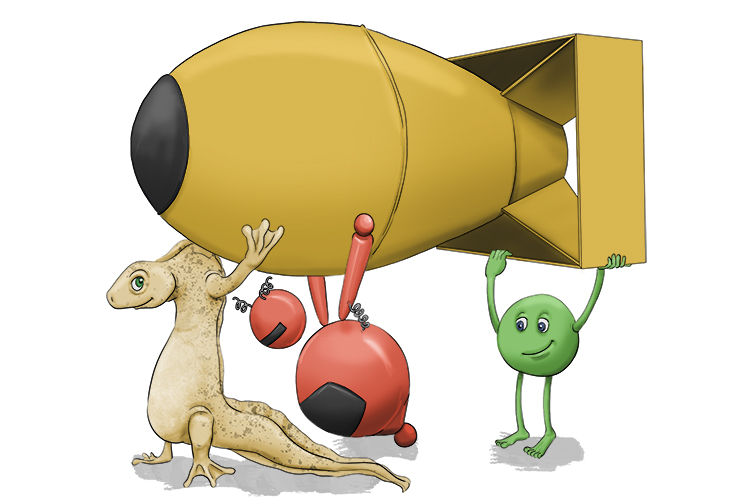
An atom is the basic unit of a chemical element consisting of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by a cloud of orbiting electrons. It is the fundemental building block of all matter. At the centre of an atom is a dense, positively charged nucleus, which contains positively charged protons and neutral neutrons. Negatively charged electrons orbit this nucleus.
A neutral atom has an equal number of protons and electrons which balances the positive and negative charges.
The number of protons determines the type of element or atom, it's the only thing that remains constant, everything else can change.
Hydrogen atom
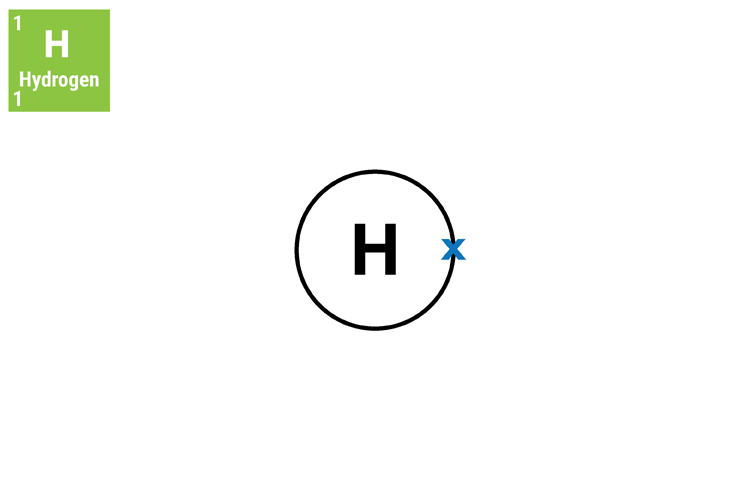
The hydrogen atom has no neutrons and therefore must be defined by the number of protons because electrons can leave the atom.
Helium atom
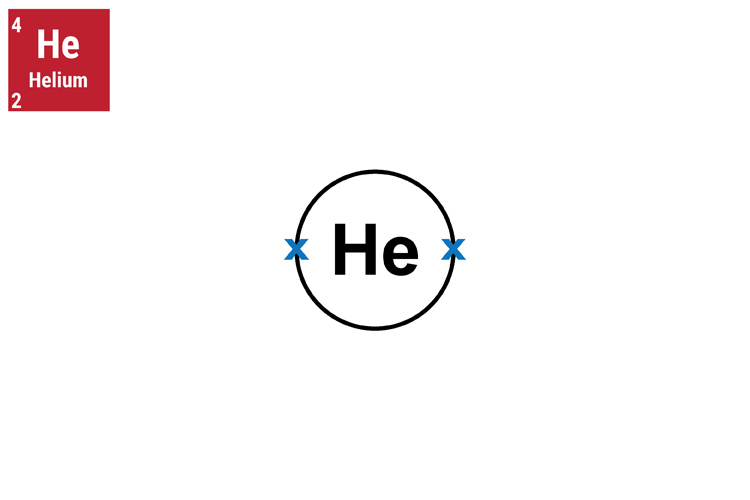
The helium atom here has 2 protons, 2 electrons and 2 neutrons.




