Examples of Vertebrates
Red squirrel (mammal)

1. Breathing system: lungs
2. Skin covering: fur
3. Thermoregulation: can regulate body temperature – animals that do this are called homeotherms, or “warm-blooded”.
4. Reproduction: internal fertilisation; gives birth to live young – animals that do this are viviparous
European robin (bird)

1. Breathing system: lungs
2. Skin covering: feathers
3. Thermoregulation: can regulate body temperature (homeotherm)
4. Reproduction: internal fertilisation; lays eggs – animals that do this are oviparous – link to oviparous below)
Adder (reptile)
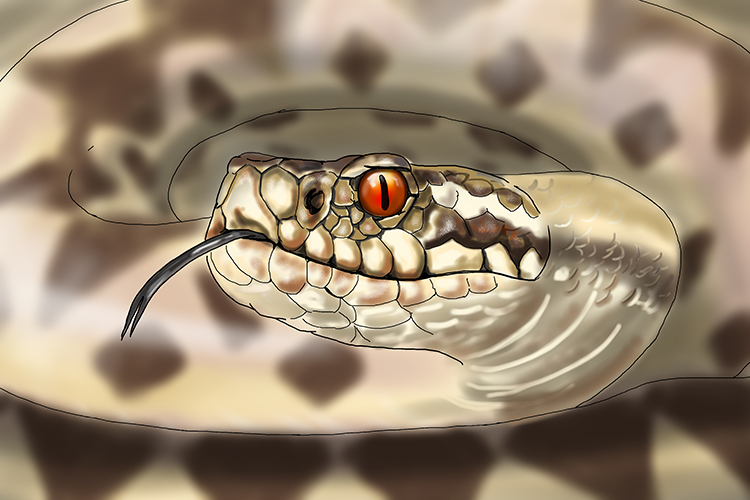
1. Breathing system: lungs
2. Skin covering: dry scales
3. Thermoregulation: cannot regulate its own body temperature – animals like this are called poikilotherms, or cold-blooded
4. Reproduction: gives birth to live young (but the babies actually develop within eggs inside the female)
Common frog (amphibian)

1. Breathing system: has lungs, but can also absorb oxygen through skin
2. Skin covering: none
3. Thermoregulation: cannot regulate own body temperature (poikilotherm)
4. Reproduction: external fertilisation; lays eggs (oviparous)
Pike (bony fish)
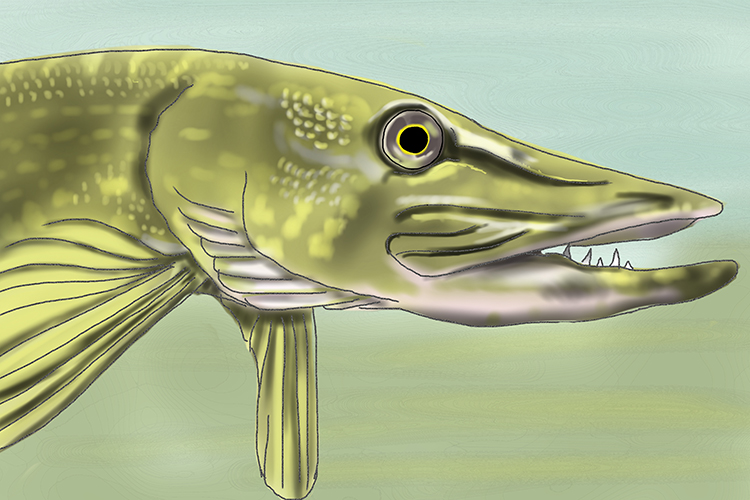
1. Breathing system: absorbs oxygen through gills
2. Skin covering: wet scales
3. Thermoregulation: cannot regulate its own body temperature (poikilotherm)
4. Reproduction: external fertilisation; lays eggs (oviparous)




