Step-up and step-down transformers
What are step-up transformers and step-down transformers? It is easy to remember by visualising the following diagrams:
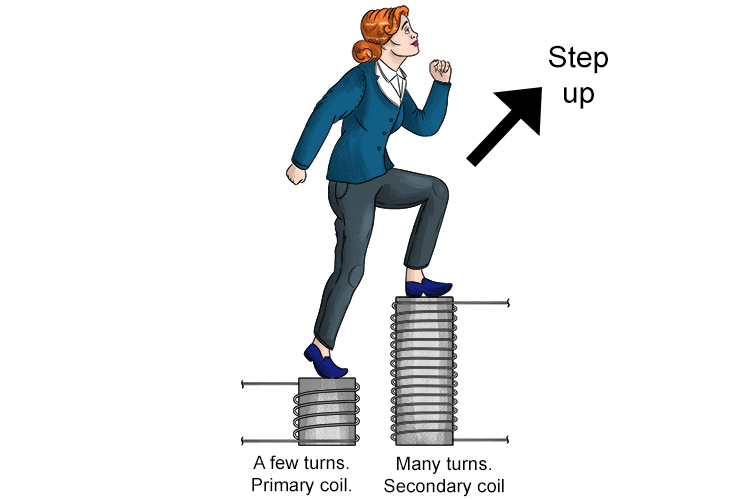
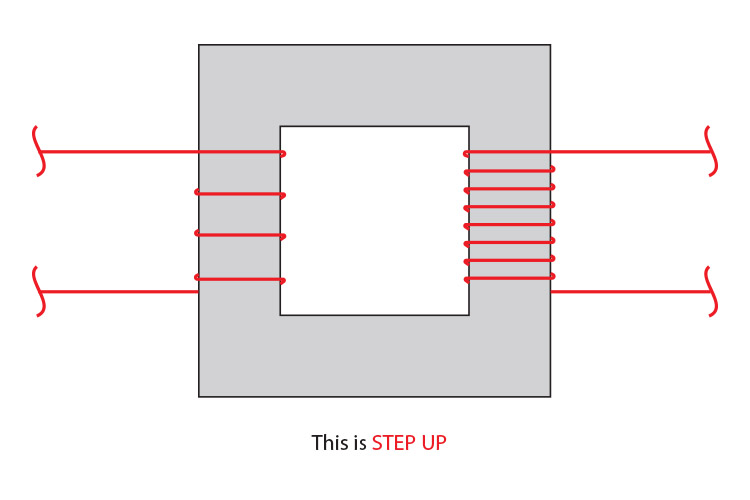
A step-up transformer has more turns on the secondary coil than the primary coil.
To work out what impact this has on voltage or current, rather than remember what the impact is, Mammoth Memory suggests that you try some basic numbers into the formulas you have learnt. It is easier than remembering the results.
The impact of a step-up transformer on voltage can be very quickly worked out by using:
`V_1/V_2=N_1/N_2`
Plug some imaginary numbers in.
`(15\ \v\o\l\t\s)/V_2=(10\ \turns)/(100\ \turns)`
`V_2=(15xx100)/10`
`V_2=150\ \v\o\l\t\s`
STEP-UP IS AN INCREASE IN VOLTAGE
The impact of this on current can be very quickly worked out by using:
`V_1\ \I_1=V_2\ \I_2`
Using
`V_1=15\ \v\o\l\t\s` and `V_2=150\ \v\o\l\t\s`
and an imaginary current of 5 amps for `I_1`
We get:
`15xx5=150xxI_2`
`I_2=(15xx5)/150`
`I_2=0.5\ \amps`
STEP-UP IS A DECREASE IN CURRENT
:
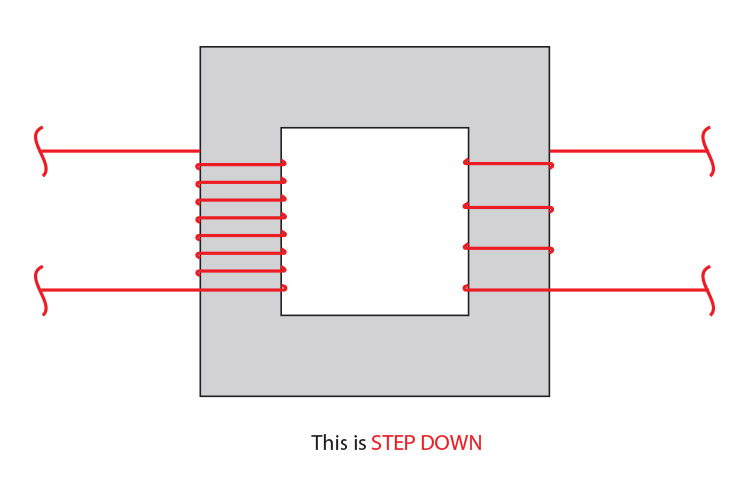
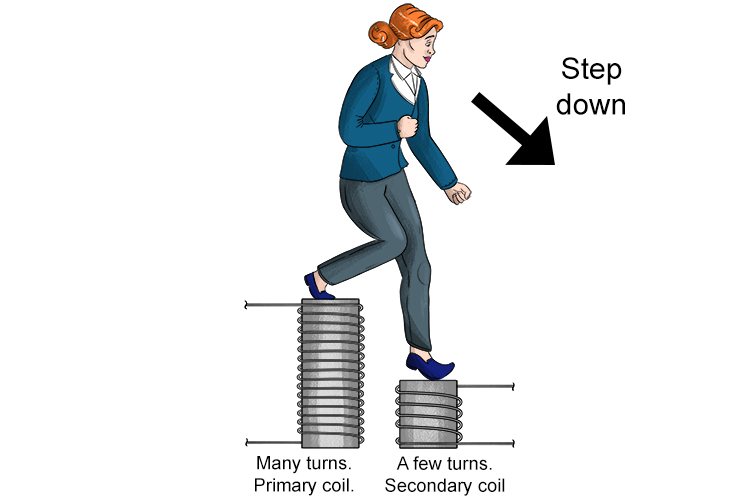
A step-down transformer has fewer turns on the secondary coil than the primary coil.
The impact of this on voltage can be very quickly worked out by using:
`V_1/V_2=N_1/N_2`
Plug some imaginary numbers in.
`(150\ \v\o\l\t\s)/V_2=(100\ \turns)/(10\ \turns)`
`V_2=(150xx10)/100`
`V_2=15\ \v\o\l\t\s`
STEP-DOWN IS A DECREASE IN VOLTAGE
The impact of this on current can be very quickly worked out by using:
`V_1\ \I_1=V_2\ \I_2`
Using
`V_1=150\ \v\o\l\t\s` and `V_2=15\ \v\o\l\t\s`
and an imaginary current of 5 amps for `I_1`
`5xx150=15xxI_2`
`I_2=(5xx150)/15`
`I_2=50\ \amps`
STEP-DOWN IS AN INCREASE IN CURRENT
Conclusion
A step-up transformer increases voltage.
That is, the voltage at the secondary coil is more than the voltage of the primary coil. Although the voltage increases, the current is reduced.
A step-down transformer does the opposite.




