DNA Hybridisation
DNA hybridisation is used to see how similar DNA is without sequencing it. DNA from different species is collected, separated into single strands and mixed together. Where the base sequences of the DNA are the same, hydrogen bonds form between the base pairs.
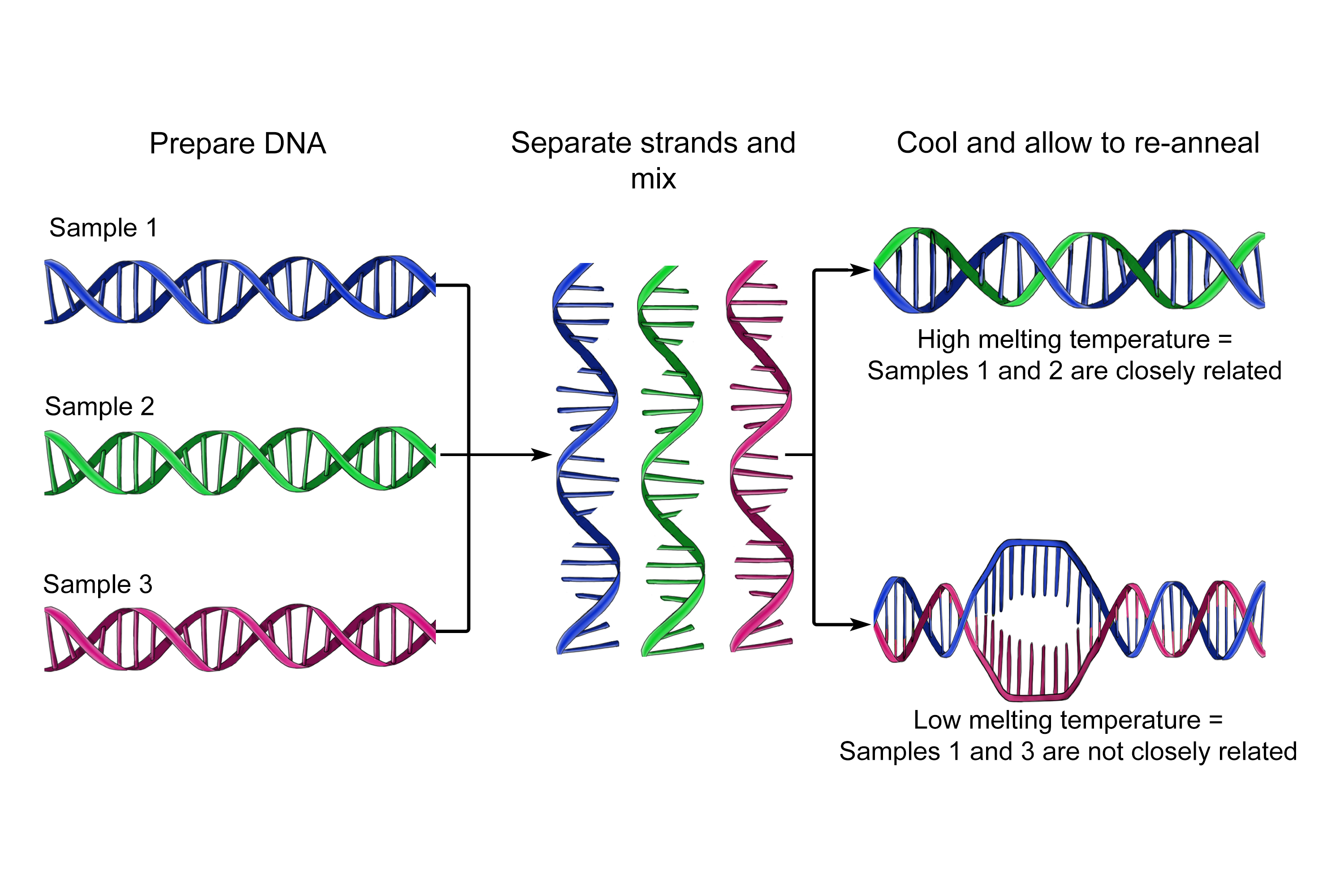
The DNA is then heated to separate the strands again. Similar DNA will have more hydrogen bonds holding the two strands together so a higher temperature is needed to separate the strands. Species that are more closely related will have higher separation temperatures.
To remember that hybridisation is a kind of soup heated up think of the following image. Note, the high bridge shoe refers to "Taxonomy based on DNA".

Jumping off the high bridge, shaped as a shoe (hybridisation) into a boiling hot soup.




