Cell division
Inside a living cell (plant and animal) is a nucleus which contains chromosomes.
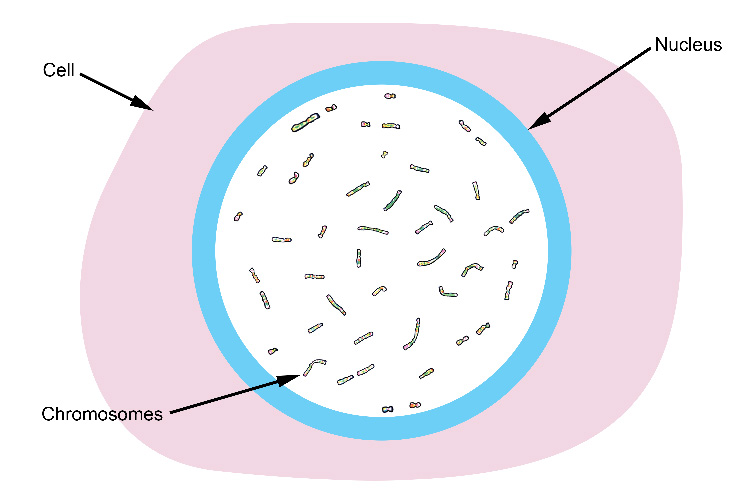
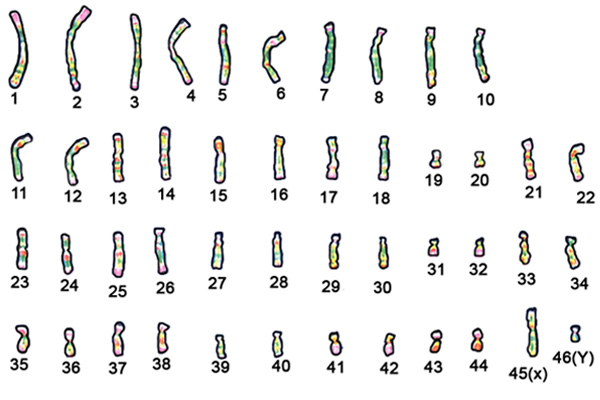
There are 46 chromosomes in human body cells, spread out randomly within the nucleus.
Lined up in order of size, these chromosomes look like this although chromosome 46 changes depending on whether the cell is from a female or a male.
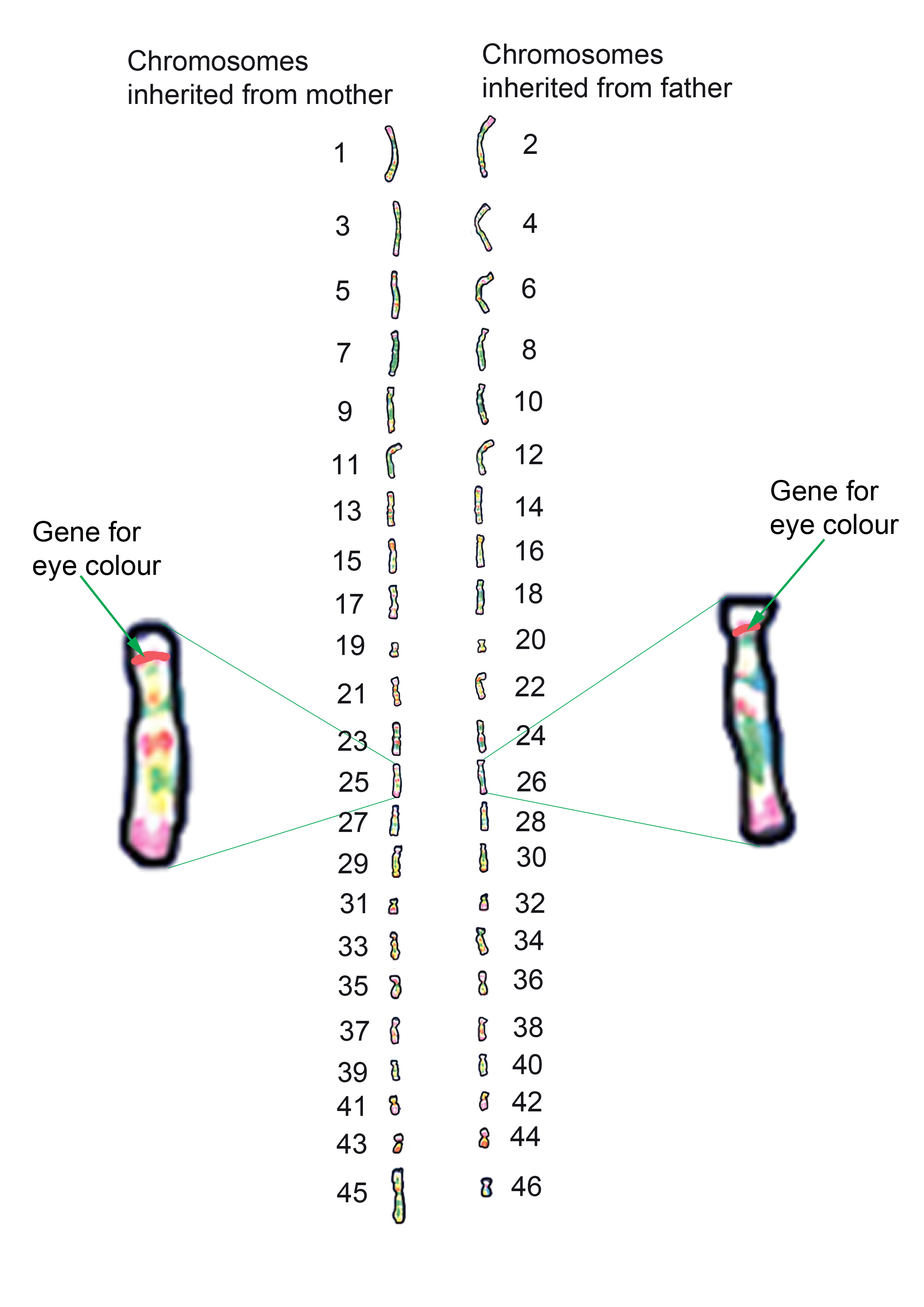
You will notice that every second chromosome is similar. The pairs carry the same type of genes along their length. Within each pair you inherit one chromosome from your mother and one from your father.
NOTE:
If this cell was from a male, the 45th chromosome would be ![]() called an X chromosome and the 46th chromosome would be
called an X chromosome and the 46th chromosome would be ![]() called a Y chromosome.
called a Y chromosome.
If this cell was from a female, the 45th chromosome would be ![]() called an X chromosome and the 46th chromosome would be
called an X chromosome and the 46th chromosome would be ![]() called X chromosome too.
called X chromosome too.
From this one cell there are two types of cell division.
Meiosis or Mitosis
Meiosis - Produces either sperm, eggs or pollen
Starts with one human cell containing 46 chromosomes
Ends up with
4 cells each containing 23 chromosomes
These 4 cells are either
4 eggs of animal or plants
or
4 sperm of animal or pollen for plants
NOTE:
After Meiosis
- If 4 sperm are produced one may join with a human egg
- If pollen are produced they may join with plant eggs
- If 4 human eggs are produced one may join with a sperm
- If plant eggs are produced they may join with pollen
Mitosis - Is cell division which produces two identical cells used for growth and repair.
Starts with one human cell containing 46 chromosomes
Ends up with
2 cells each containing 46 chromosomes




