Mitosis
Mitosis is cell division which produces two identical cells used for growth and repair.
Starts with one human cell containing 46 chromosomes
Ends up with
2 cells each containing 46 chromosomes
When growth or replacement cells are required for the body, mitosis occurs.
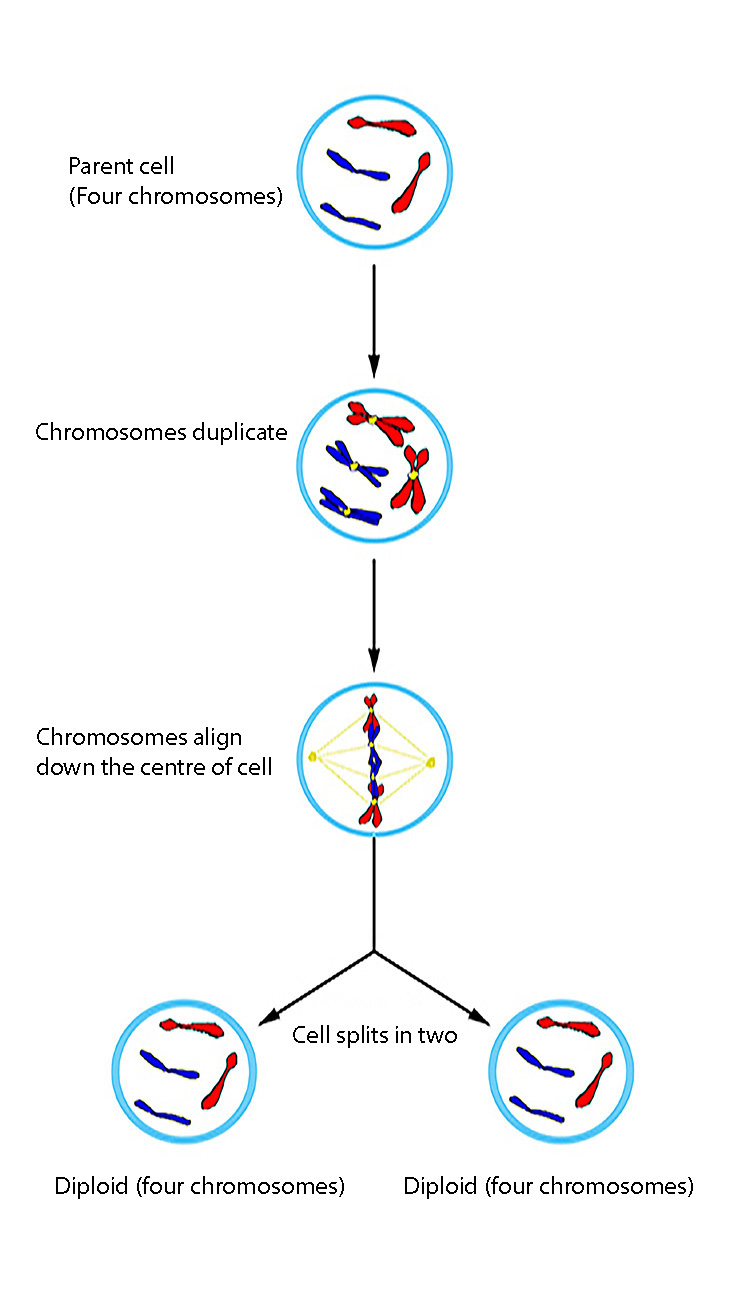
Mitosis starts with a cell. This is a normal cell (called a diploid cell) containing 46 chromosomes.
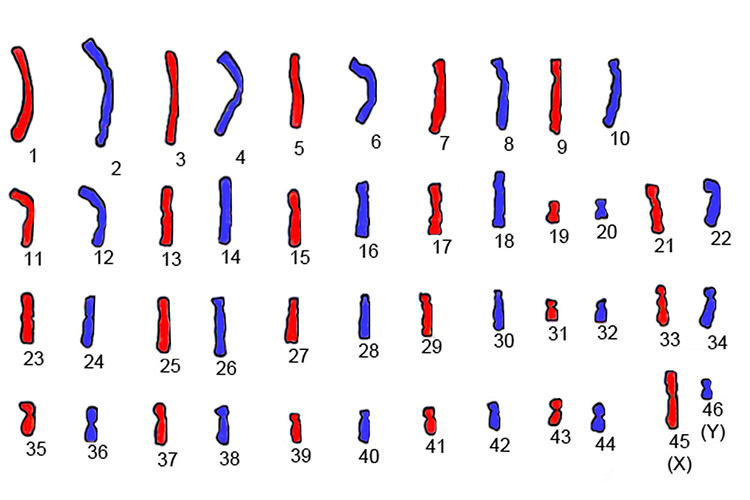
The chromosomes copy themselves and remain attached to the original.
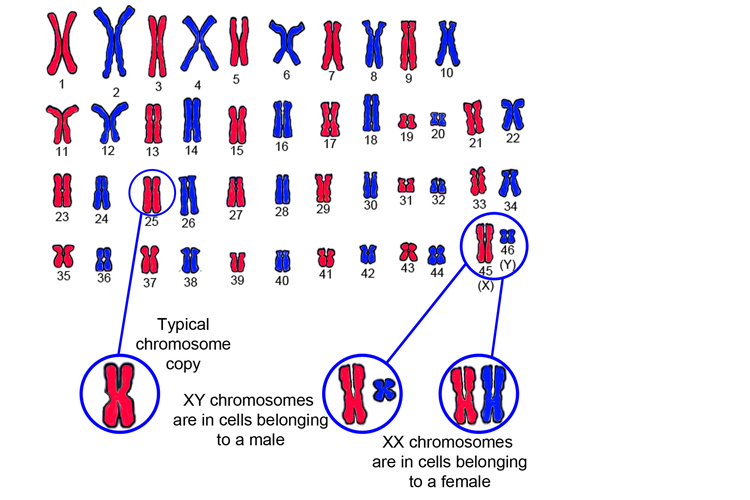
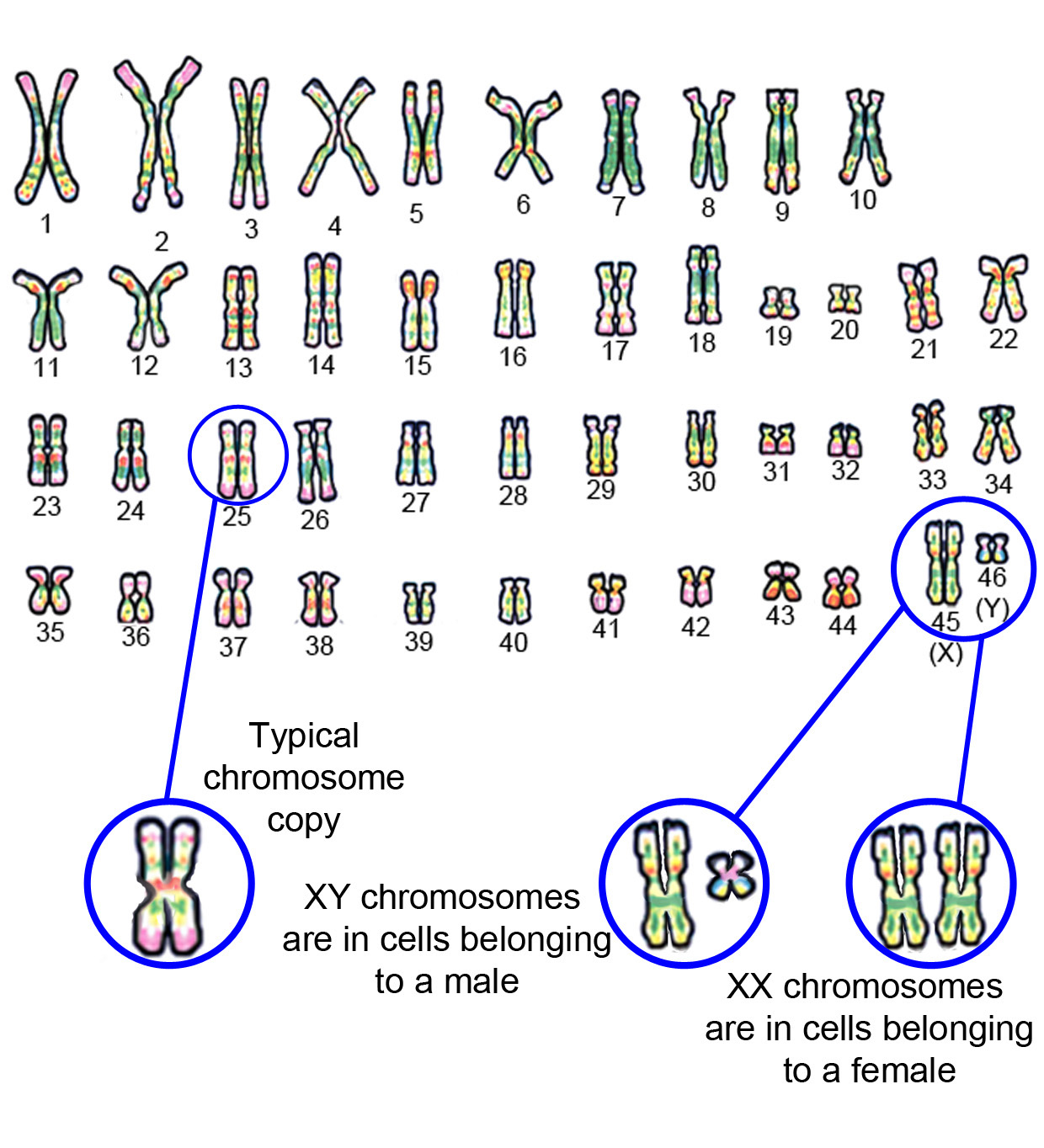
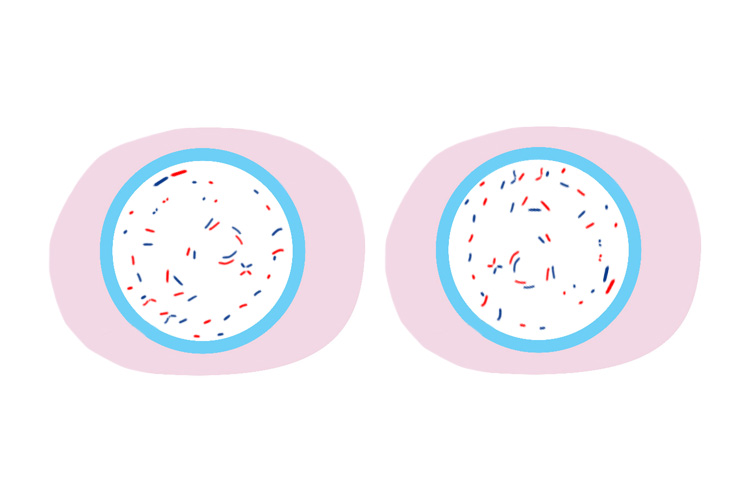
Below is an enlarged version of what the real paired chromosomes look like under a microscope.
All these chromosomes then line themselves up.
See 46 paired chromosomes lined up
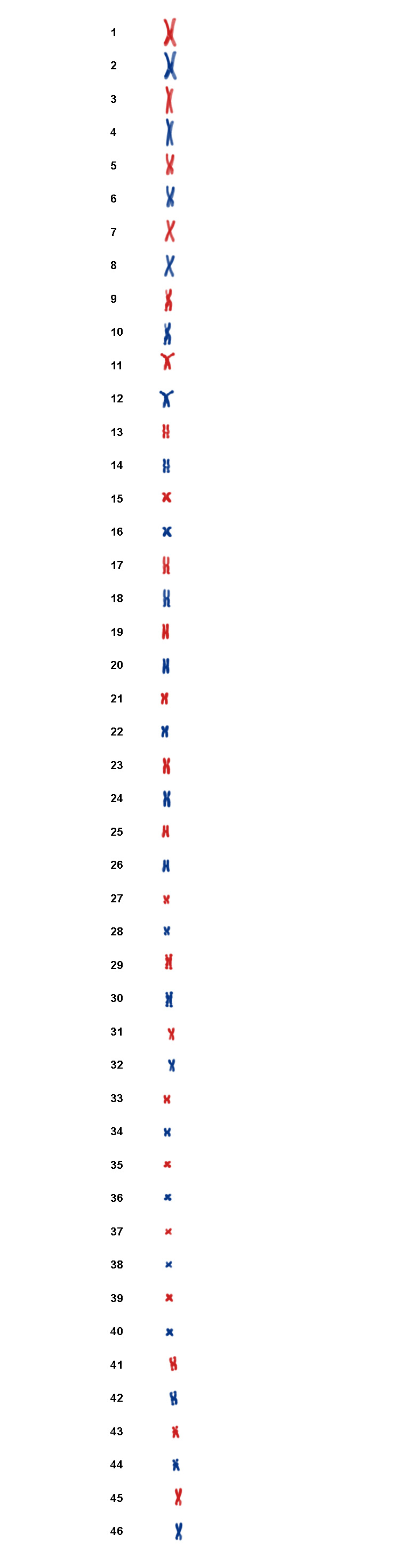
They then split down the middle to form a duplicate of each other as the cell divides.
Cell splits into two, each with 46 chromosomes.

Simplified, mitosis in a nucleus with just four chromosomes would be as follows:
Mitosis produces two identical cells.




