Charles' Law In Use
We know that in Charles' law
`V_1/T_1=V_2/T_2`
NOTE: Pressure remains constant
Also, if you put a balloon inside a bucket and pour cold liquid nitrogen over the balloon, you can watch it shrink.
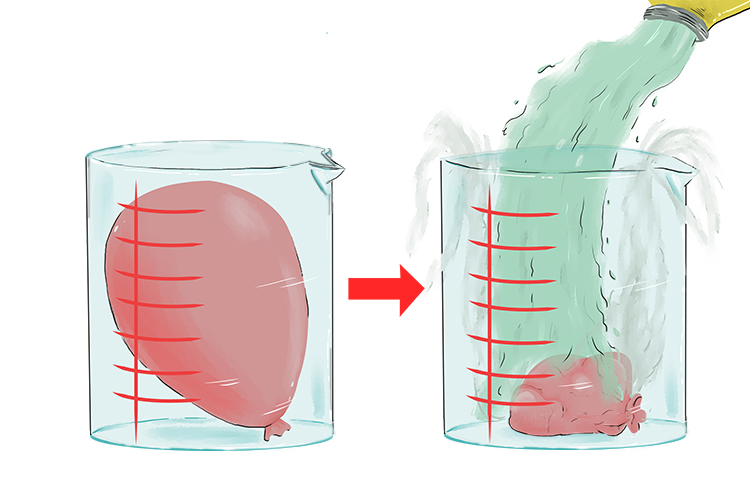
This is Charles' Law
`V_1` and `T_1` refer to the volume and temperature before you pour the liquid nitrogen on the balloon and `V_2` and `T_2` refer to the volume and temperature after you pour the liquid nitrogen on the balloon.
Reduce the temperature of the gas and the volume of the gas reduces too.
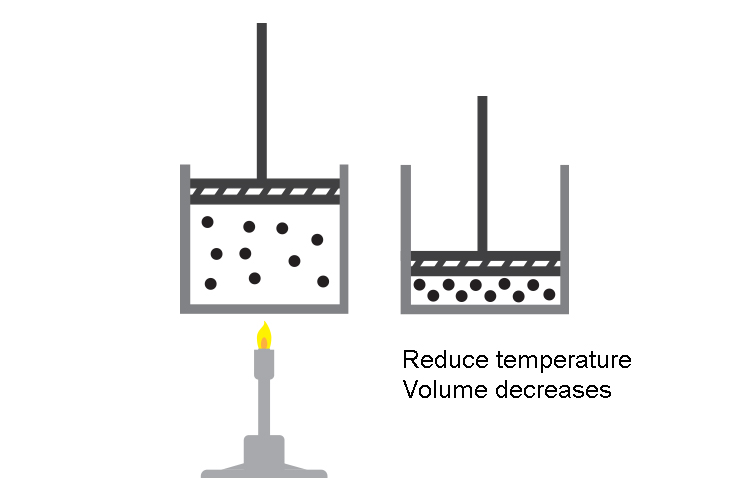
Reducing the temperature of a gas slows down the molecules and they have less energy (kinetic energy) to hit and push the sides of the balloon. The molecules will exert less force and so the external atmospheric pressure will collapse the balloon.
NOTE 1:
The standard unit used to measure volume is `m^3` (metre cubed)
The standard unit used to measure temperature is `K` (Kelvin)
NOTE 2:
You can use other units for volume such as `m^3` or `ml` as long as you use the same units either side of the equation but you must use Kelvin for temperature.
NOTE 3:
Never forget to convert temperature to Kelvin
Temperature in Kelvin `=` temperature in degrees Celsius `(\ ^(circ)C)+273`
You must always use temperature measured in Kelvin in any gas law equation.
Examples
1. A container holds `50.0\ \ml` of nitrogen at `25^circC` and a pressure of `736\ \mm\ \Hg`. What will be its volume if the temperature increases by `35^circC` ?
`V_1/T_1=V_2/T_2`
Therefore `V_2=(V_1xxT_2)/T_1`
`V_1=50\ \ml`
`V_2=?`
`T_1=25^circC+273=298K`
`T_2=25^circC+35^circC+273=333K`
Therefore `V_2=(50xx333)/298`
`V_2=55.9\ \ml`
2. `568\ \cm^3` of chlorine at `25^circC` will occupy what volume at `-25^circC` while the pressure remains constant?
`V_1/T_1=V_2/T_2`
`V_1=568\ \cm^3`
`V_2=?`
`T_1=25^circC+273=298K`
`T_2=-25^circC+273=248K`
Therefore `V_2=(V_1xxT_2)/T_1`
`V_2=(568xx248)/298`
`V_2=473\ \cm^3`
3. A sample of hydrogen has an initial temperature of `50^circC`. When the temperature is lowered to `-5.0^circC`, the volume of hydrogen becomes `212\ \cm^3`. What was the initial volume of the hydrogen?
`V_1/T_1=V_2/T_2`
`V_1=?`
`V_2=212\ \cm^3`
`T_1=50^circC+273=323K`
`T_2=-5^circC+273=268K`
Therefore `V_1=(V_2xxT_1)/T_2`
`V_1=(212xx323)/268`
`V_1=256\ \cm^3`




