Electrical charge
Electrical current within a circuit is the flow of electrical charge over time. The formula for calculating electrical charge is:
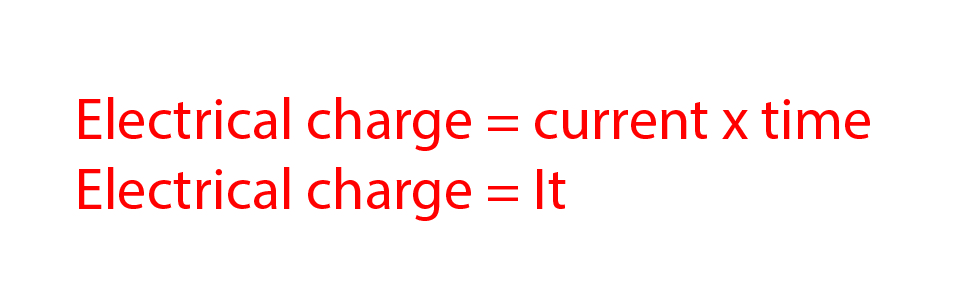

A bull charges into the IT department.
NOTE:
You may see this formula written as `Q = It`
Electrical charge is measured in coulombs (`C`)
Current is measured in amps (`A`)
And time is measured in seconds (`s`)
The internationally agreed symbols for this formula are:
`Q =` Charge
`I =` Current
`t =` time
To remember that charge is measured in coulombs think of this image:

The bull charges into columns (Coulombs) of computers.
Example 1
A current of 12A flows for 20 minutes into an electric cooker. How much charge has the cooker used?
Answer:
`E\l\e\c\t\rical\ ch\a\r\g\e = Currentxxtime`
But don’t forget that the time has to be converted to the standard unit.
So `20\ m\i\n\u\tes = 20xx60 = 1200\ s\e\c\o\nds` Therefore:
`E\l\e\c\t\rical\ ch\a\r\g\e = 12xx1200=14400\ co\u\l\ombs`
Example 2
If `18400 C` of charge flows through an air conditioning unit every hour, what current does it draw?
Answer:
`E\l\e\c\t\rical\ ch\a\r\g\e = Currentxxtime`
Divide both sides by time to make current the subject,
`(E\l\e\c\t\rical\ ch\a\r\g\e)/(time) = (Currentxxcancel(time))/cancel(time)`
`Current=(E\l\e\c\t\rical\ ch\a\r\g\e)/(time)`
The time must be converted from hours to the standard unit of seconds, so:
`1\ hour = 60\ m\i\n\u\tes = 60xx60 = 3600\ s\e\c\o\nds`
therefore:
`Current=18400/3600=5.1\ amps`




