Difference between DNA nucleotides and messenger RNA (mRNA) nucleotides.
There is an important difference between the bases used in DNA nucleotides and messenger RNA (mRNA) nucleotides. While DNA bases pair as follows:
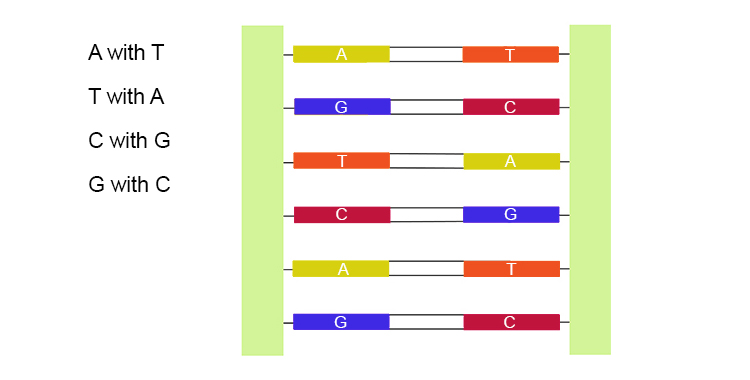
The bases in mRNA pair like this:
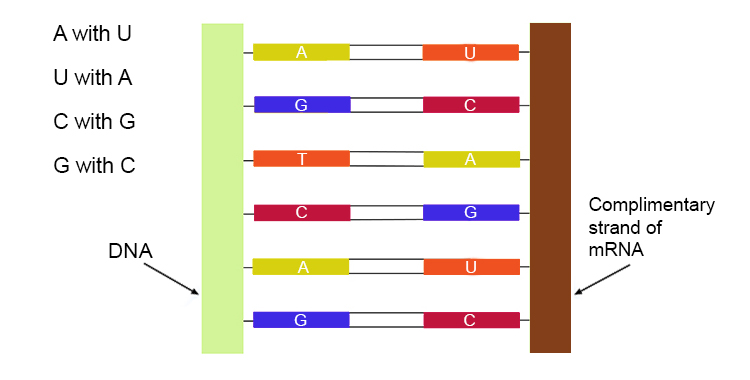
That is U (Uracil) replaces the T (thymine)
This is so that the cell can tell that the messenger RNA (mRNA) is to be treated differently to DNA.
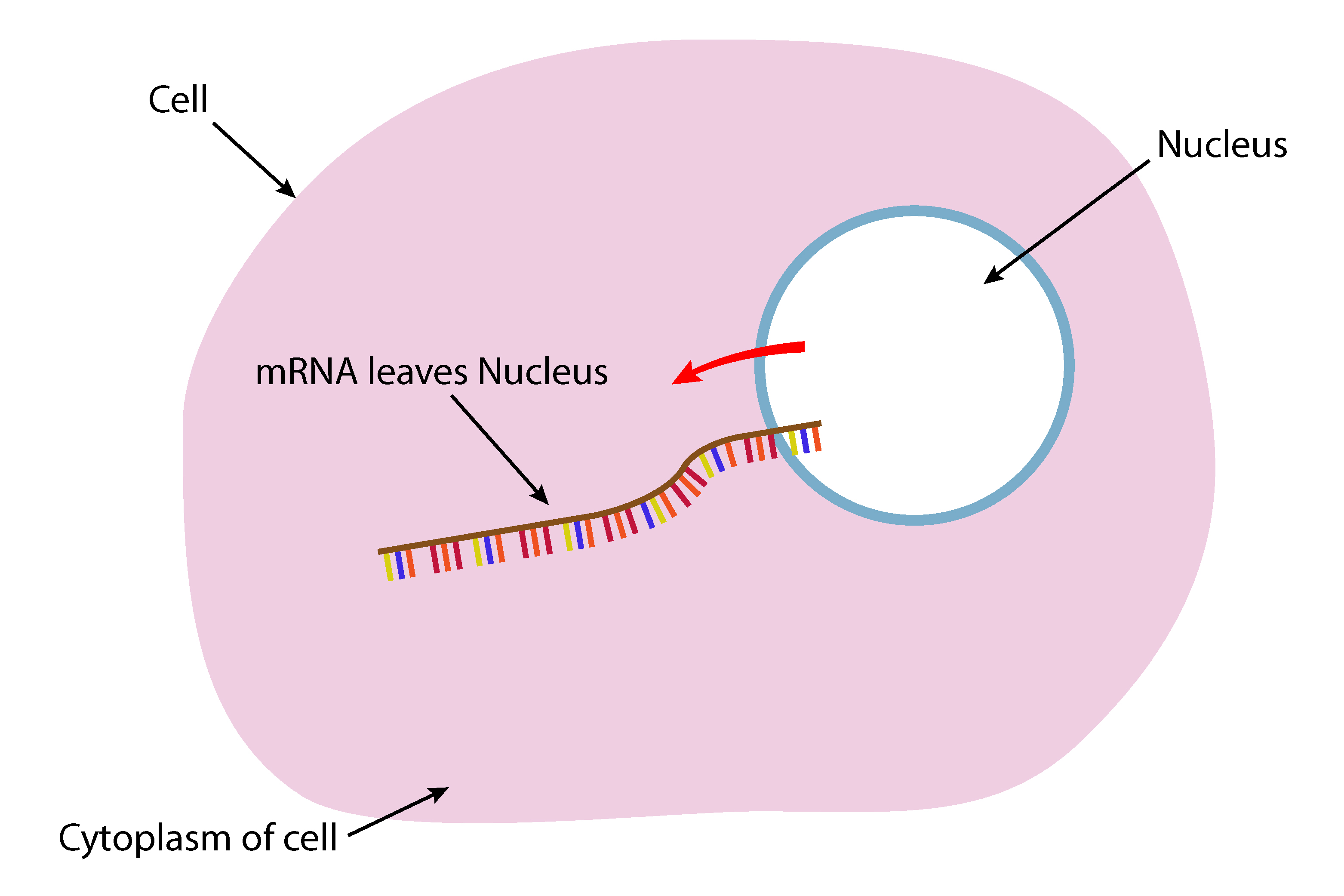
The messenger RNA (mRNA) now floats away from the DNA and is small enough to pass out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm of the cell.
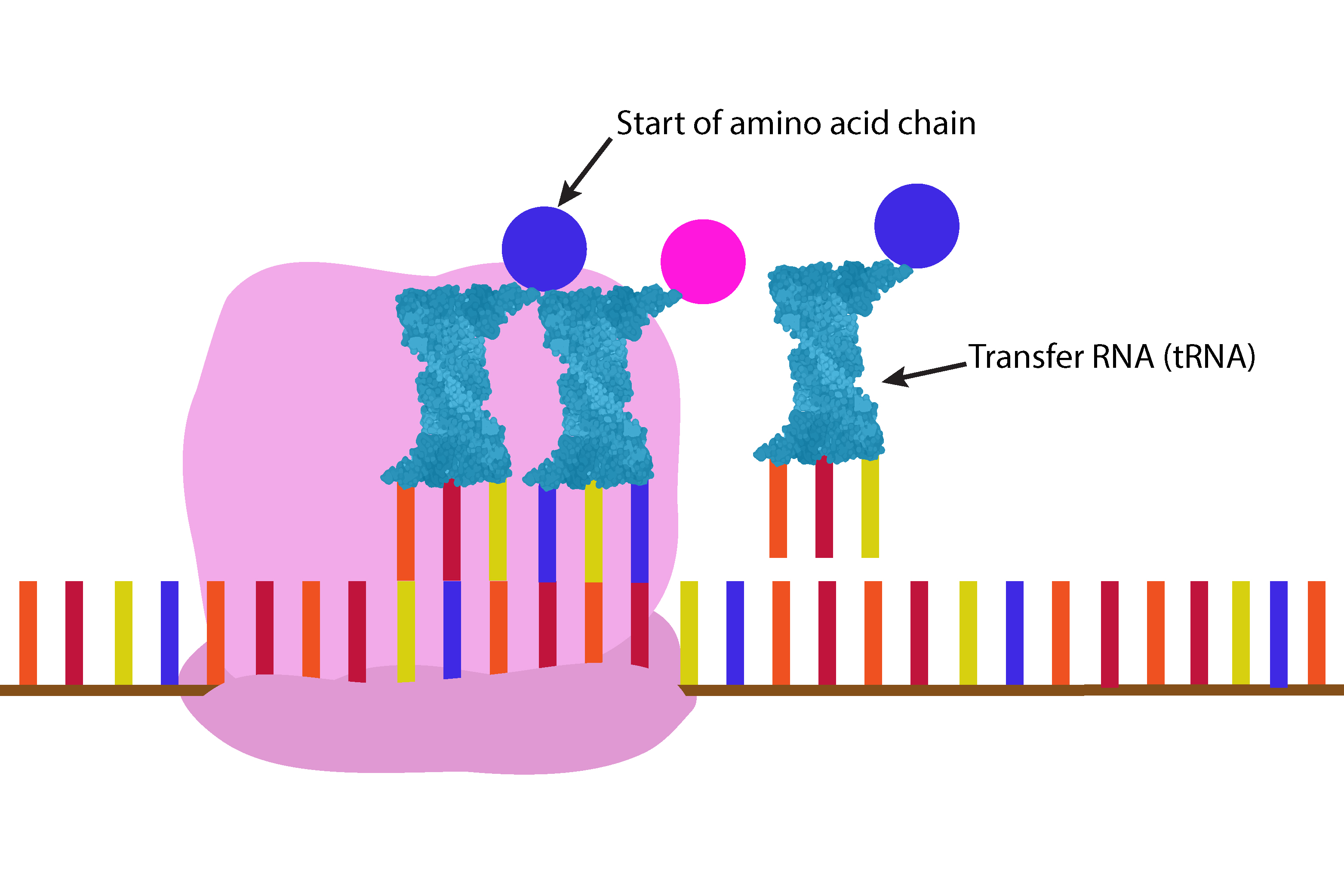
In the cytoplasm there are transfer RNA (tRNA) which have three permanent bases attached. These bases are in combinations of A, U, C, G.
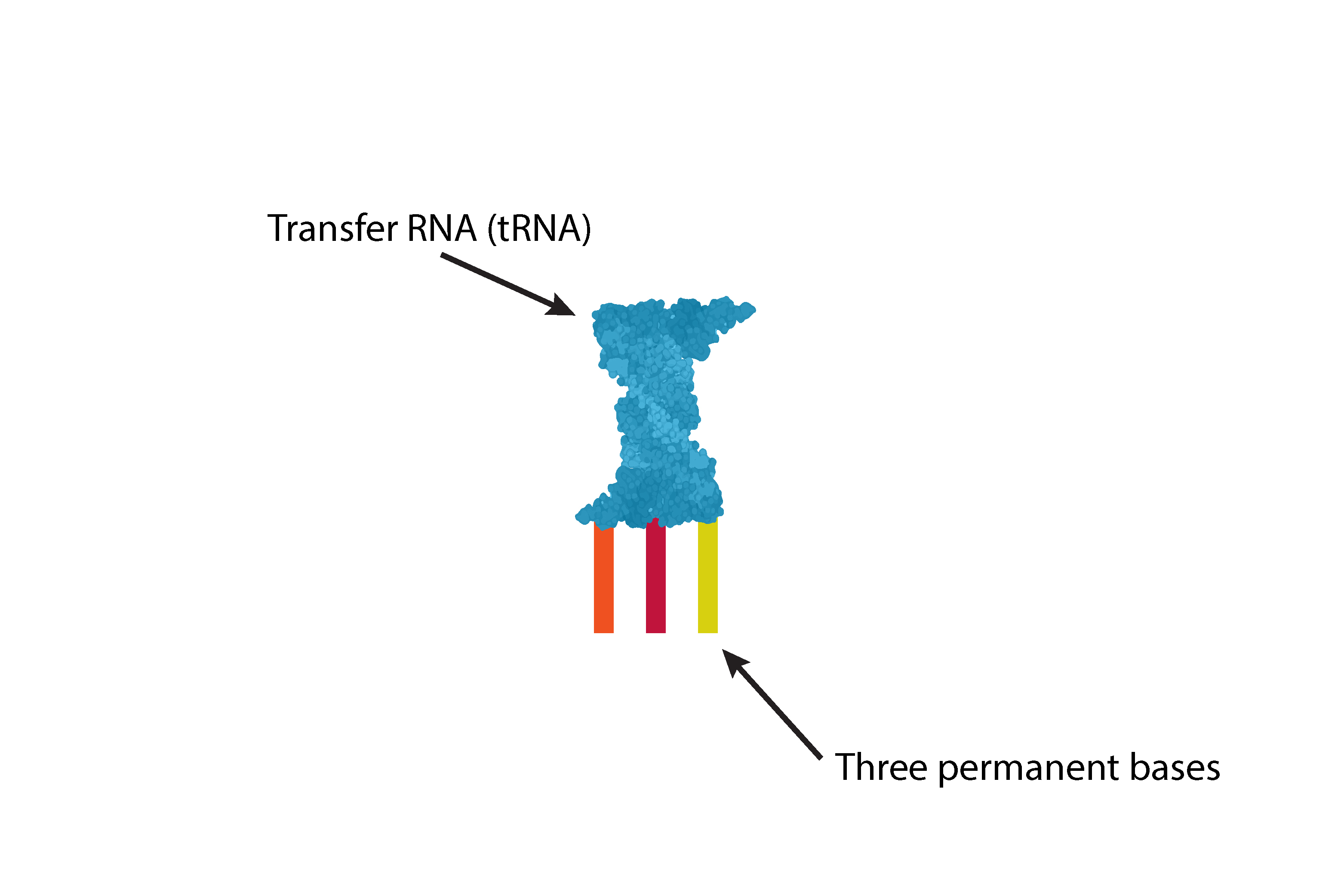
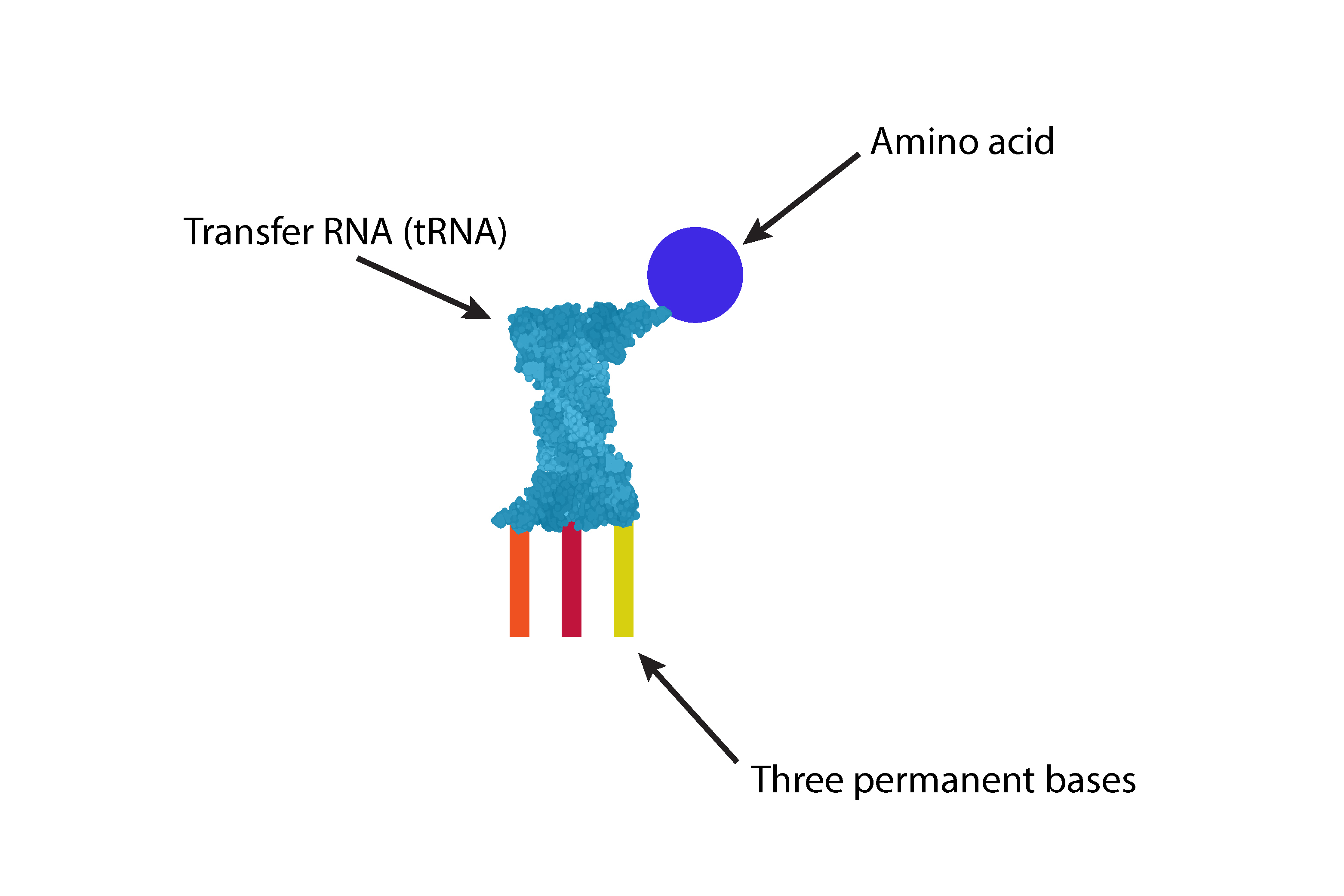
These transfer RNA (tRNA) pick up one of 20 amino acids which correspond to the permanent base combinations and therefore look like:
The ribosome attaches itself to the messenger RNA (mRNA).
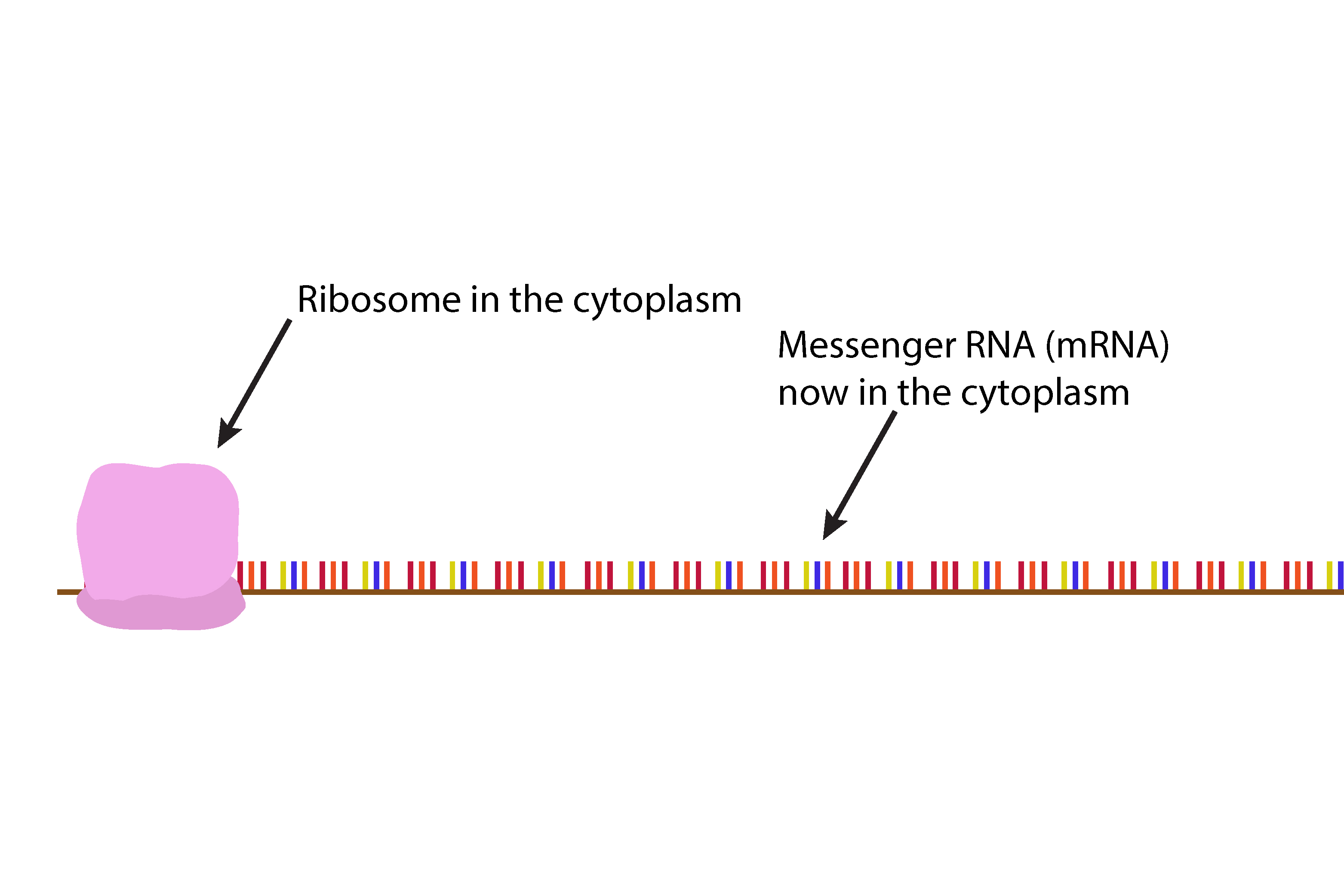
The messenger RNA (mRNA) is then read by the ribosome three bases at a time.
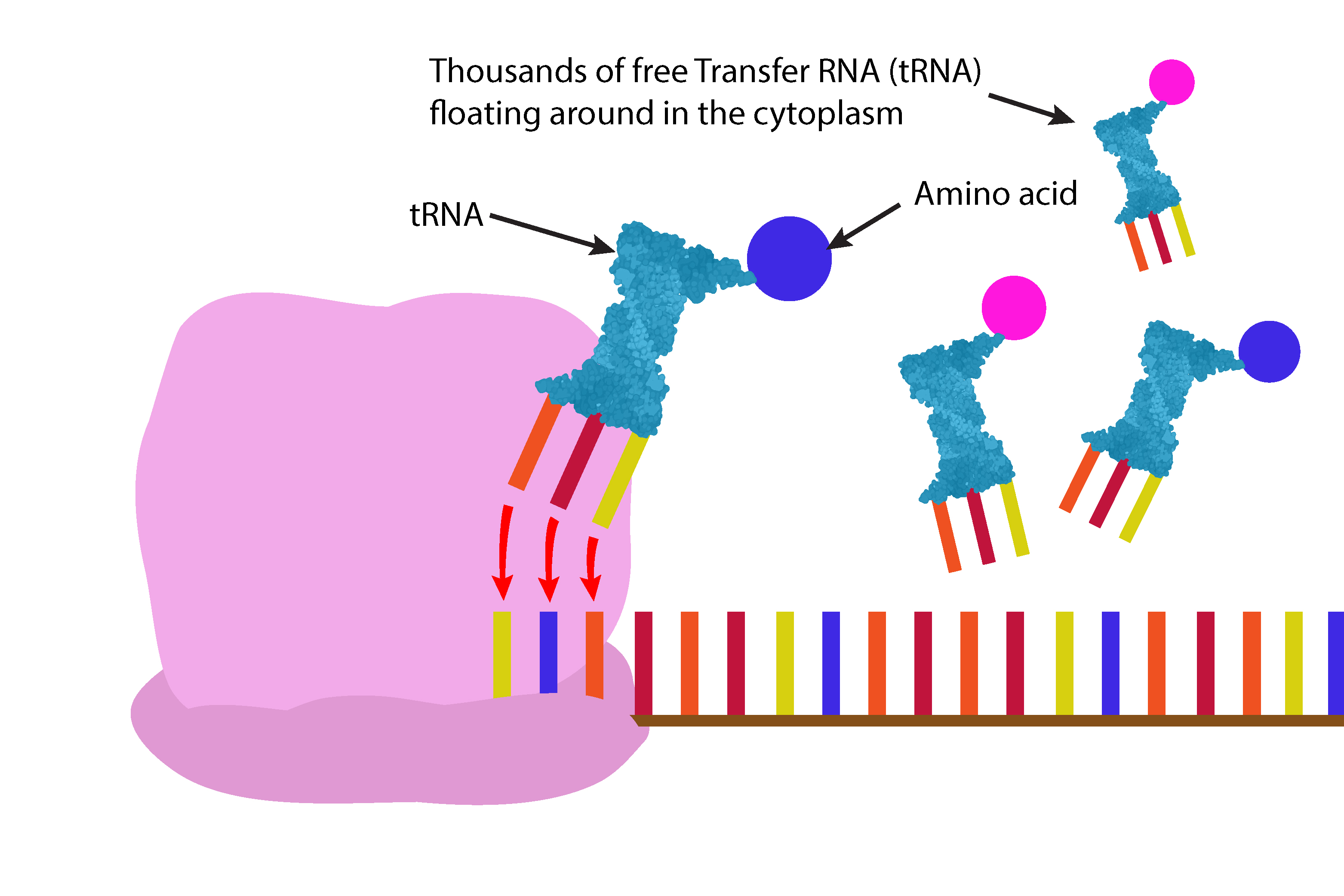
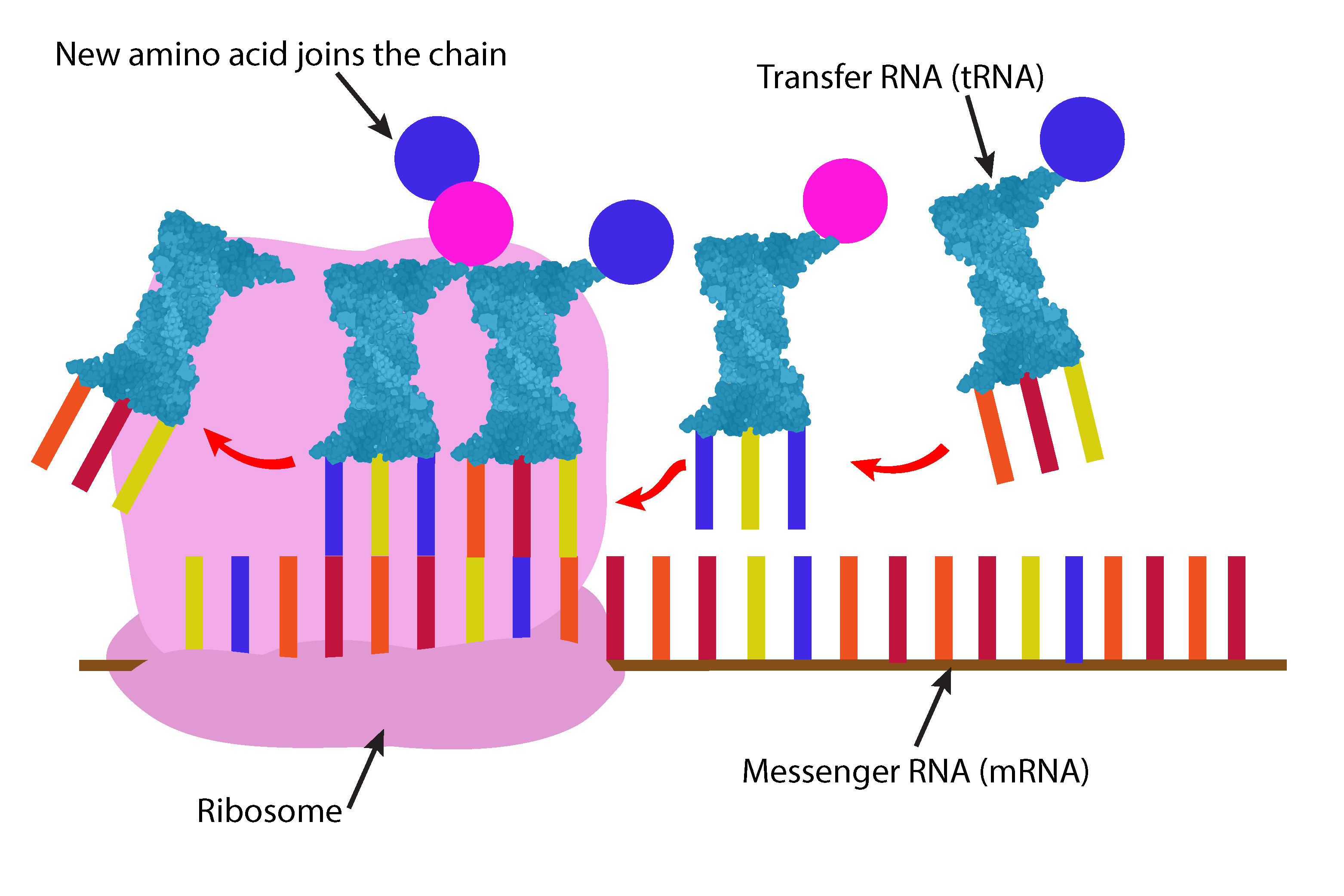
The next transfer RNA (tRNA) moves along onto the messenger RNA (mRNA) in the ribosome producing a chain of amino acids.
The transfer RNA (tRNA) break away leaving the amino acid in the chain.
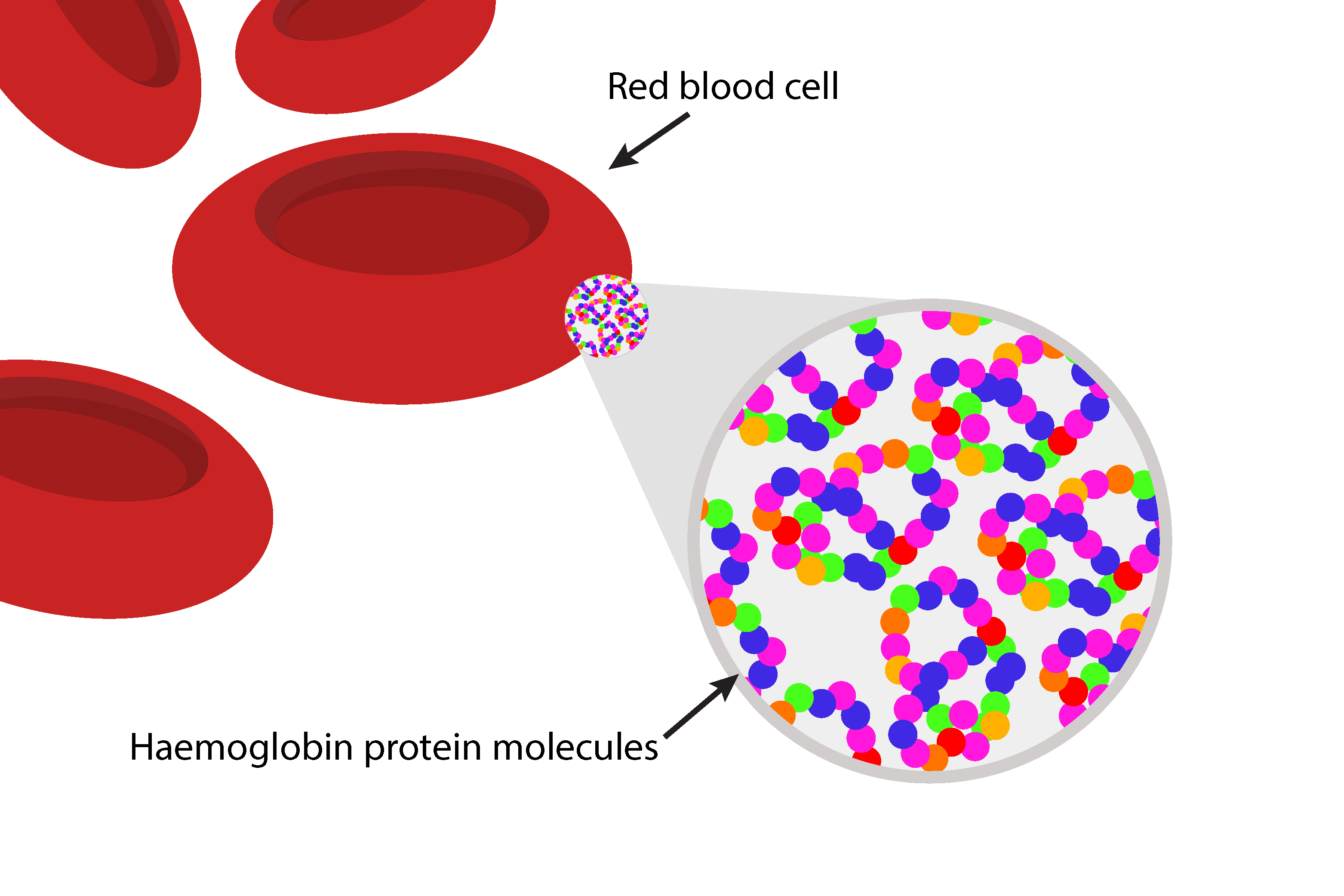
The amino acids form a chain which is known as a protein, in this case a haemoglobin protein.
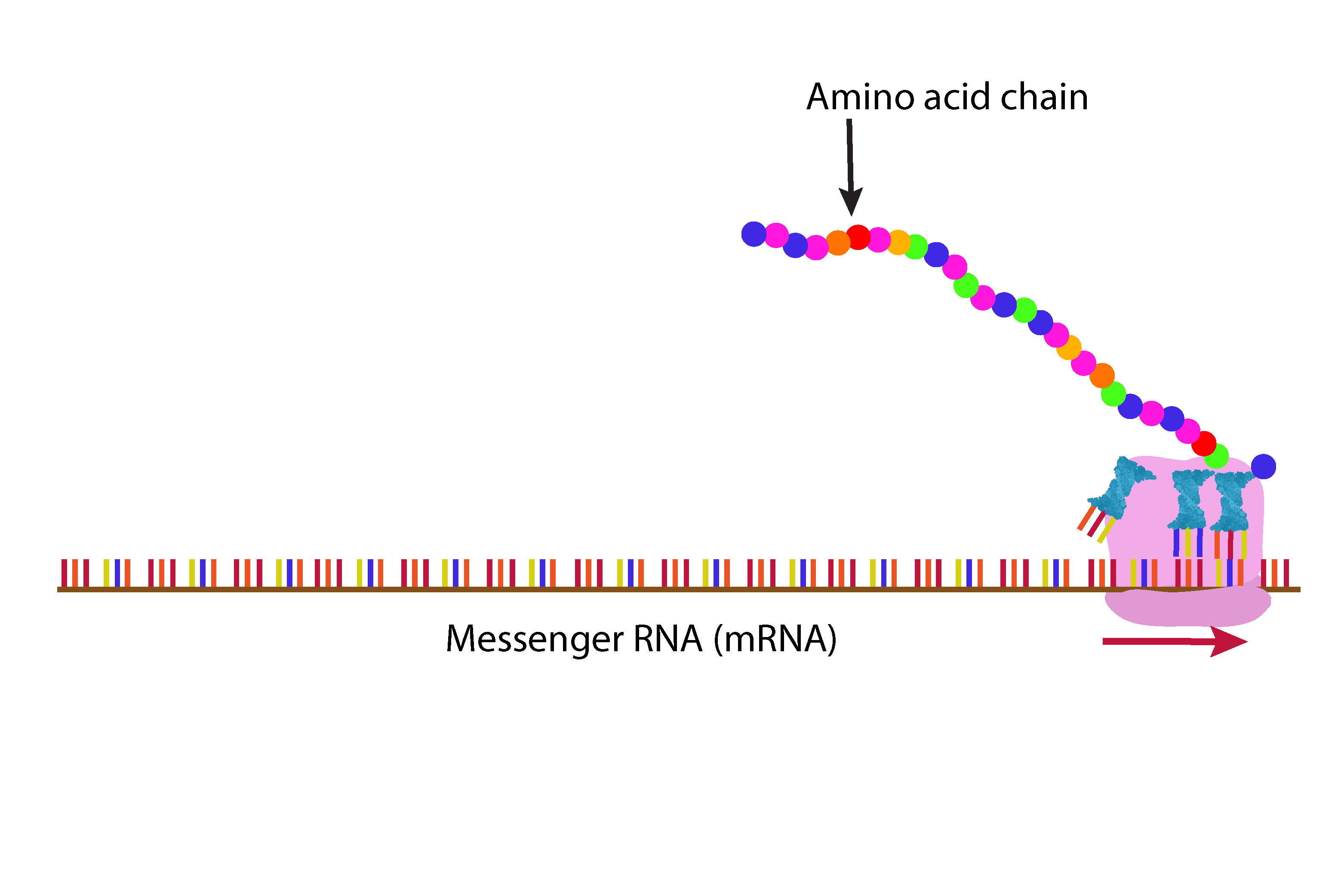
The amino acid chain, when complete, breaks away from the ribosome.
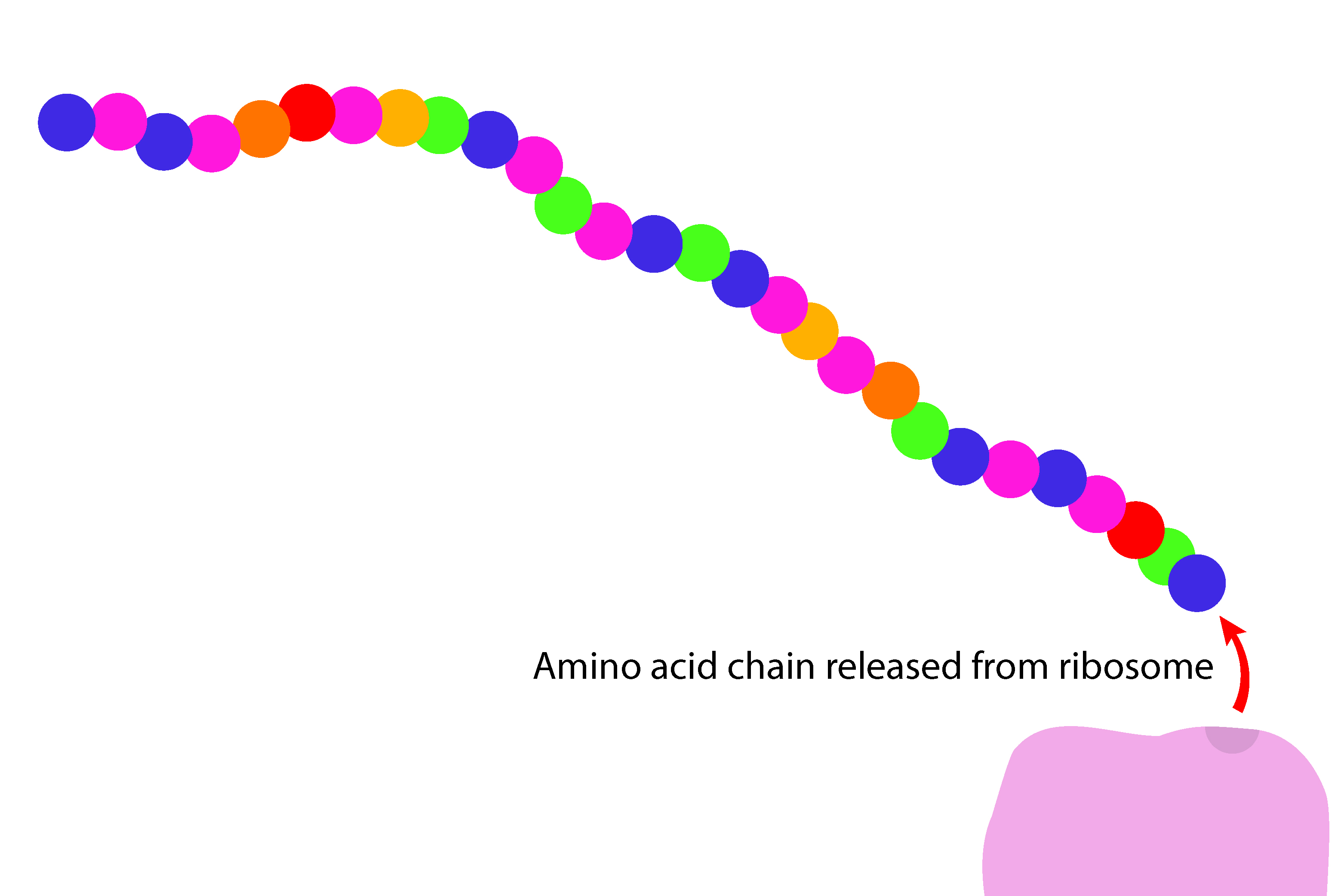

Once released the amino acid chain folds into a complex 3D shape depending on the protein that has been built.
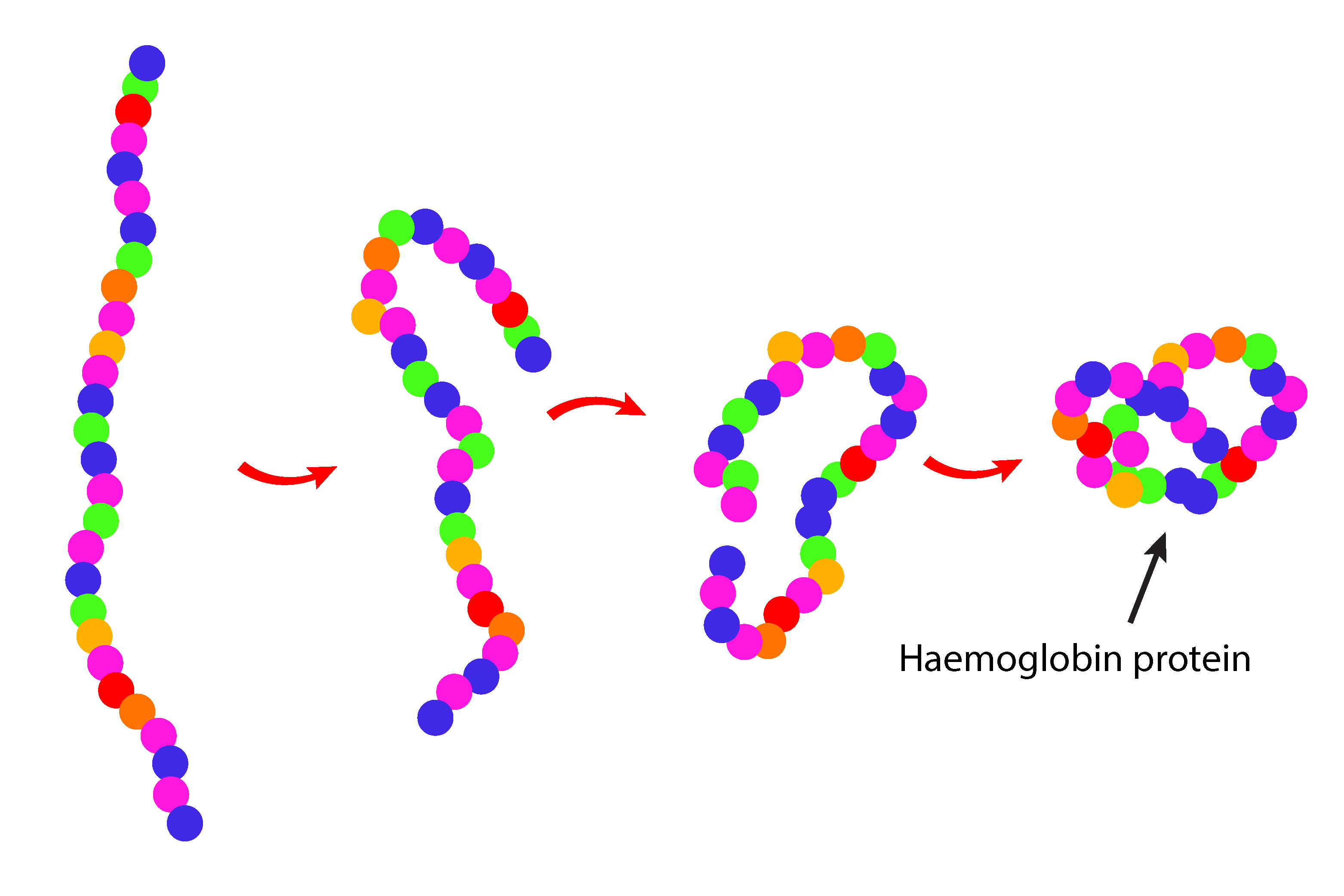
Here the amino acid chain folds into a Haemoglobin protein. Haemoglobin proteins carry the oxygen in our red blood cells.