The reaction between potassium and water
| Potassium | + | Water | → | Potassium hydroxide | + | Hydrogen |
| 2K | + | 2H2O | → | 2KOH | + | H2 |
When the potassium is placed in water, it floats because it is less dense than the water. The hydrogen gas given off in the reaction pushes the potassium around on the surface of the water.
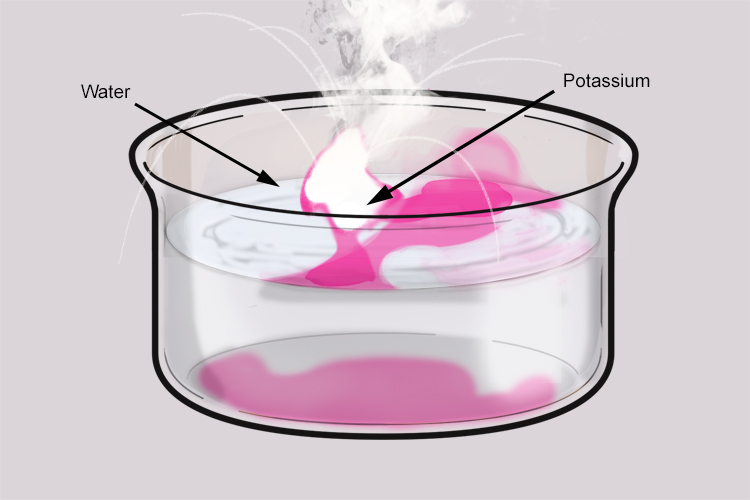
Potassium reacts violently with water. Enough heat is produced in the reaction to ignite the hydrogen gas given off. The hydrogen gas is contaminated with potassium which results in the lilac (bluish pink) flame.
The reaction between potassium and water in more detail
Note: You will not need to know this information but it may help to provide you with a better understanding of what takes place during this reaction.
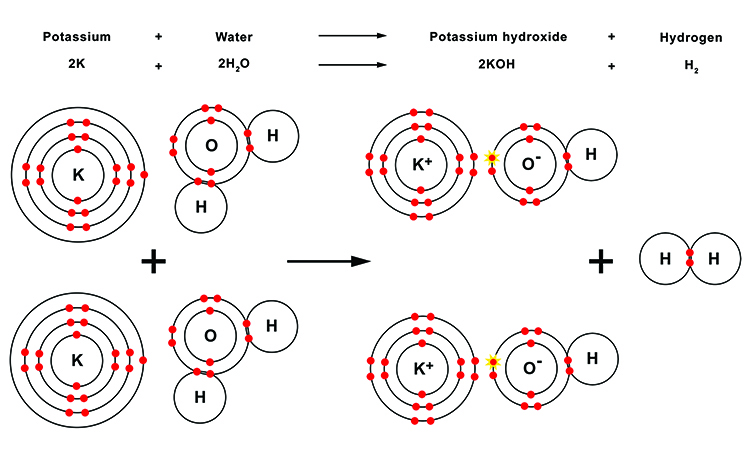
During this reaction, each of the water molecules loses a hydrogen atom (H). These two hydrogen atoms then combine to form a diatomic molecule of hydrogen gas (H2). The oxygen (O) then takes the atom from the outer shell of the potassium (K) to create a positively charged potassium cation (K+). The positively charged potassium (K+) is attracted to the oxygen anion (O-) which is now negatively charged having acquired the extra electron, and forms an ionic bond.
This means the oxygen has both a covalent bond with the one remaining hydrogen atom and an ionic bond with the potassium ion to form the potassium hydroxide molecule (KOH).




