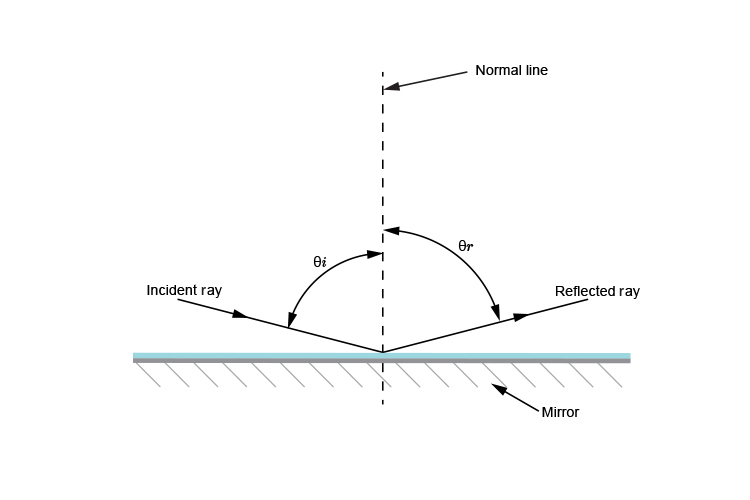
The three laws of reflection
Any mirror obeys the three laws of reflection, flat, curved, convex or concave.
The three laws of reflection are
1. The angle between the incident ray and the normal is equal to the angle between the reflected ray and the normal
2. The incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray are all in the same plane
3. Incident ray and refracted ray are on different sides of the normal
Law 1 explained
The angle between the incident ray and the normal is equal to the angle between the reflected ray and the normal.
This means that `thetai` equals `thetar`
where
`thetai=` angle of incidence
`thetar=` angle of reflection
As the angle of incidence (`thetai`) increases, the angle of reflection (`thetar`) also increases and they are always equal to each other.
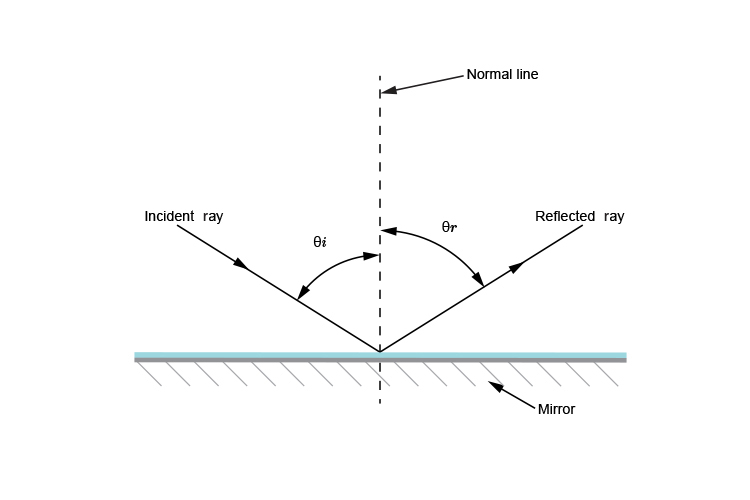
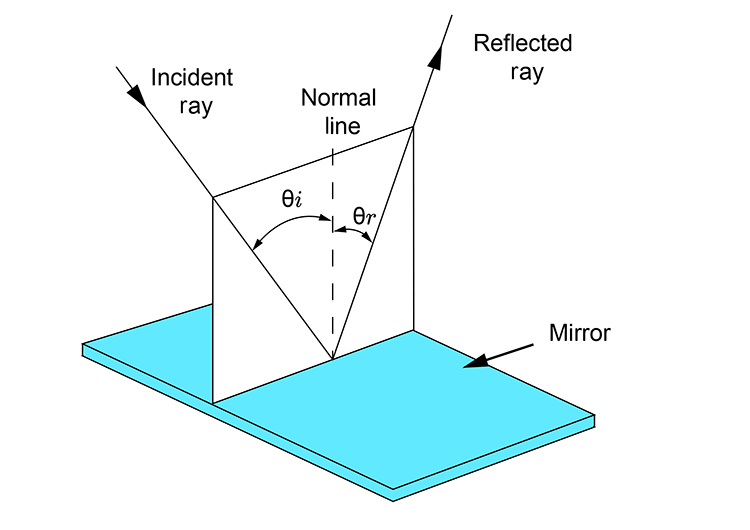
Law 2 explained
The incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray are all in the same plane.
`thetai=thetar`
Changing the direction of the incident ray changes the angle of the plane.
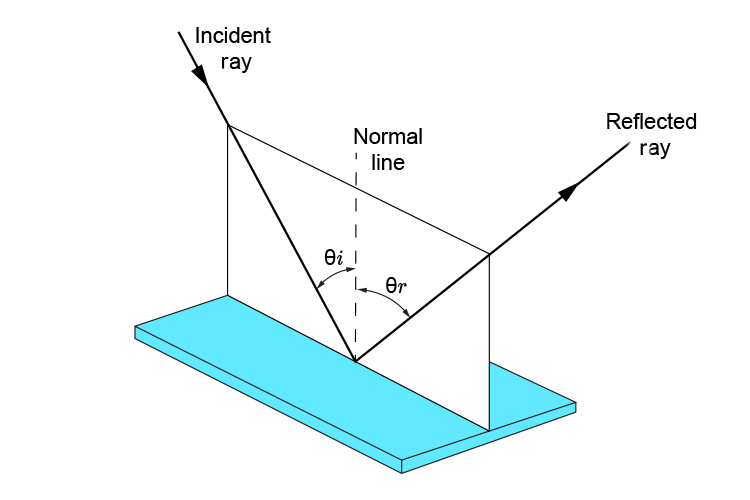
`thetai=thetar`
Again the incident ray, the normal line and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane.
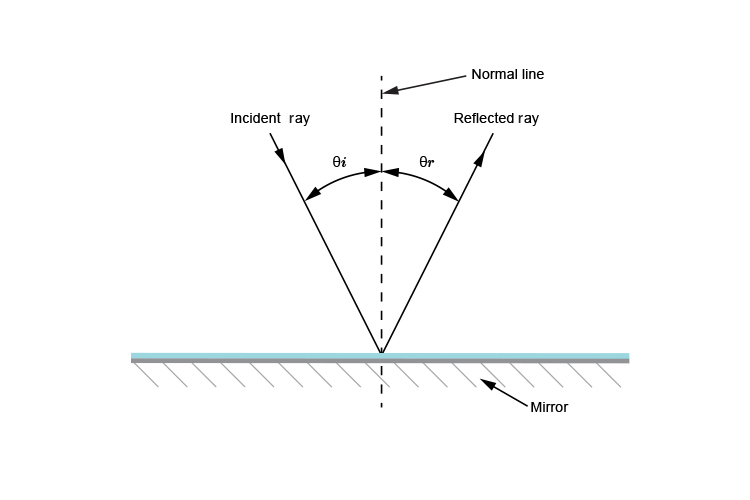
Law 3 explained
The incident ray and the reflected ray are on different sides of the normal.
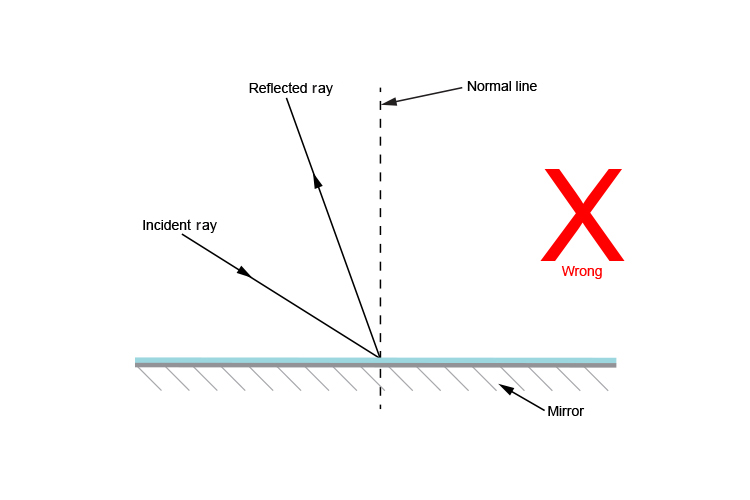
The above diagram is wrong. The incident ray and the reflected ray can not be on the same side of the normal.
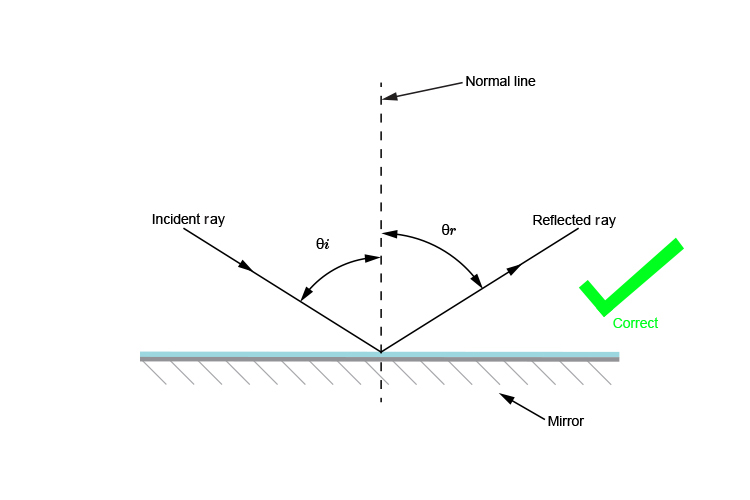
The incident ray and reflected ray must be on different sides of the normal.