Muscle Contraction Glossary
To learn about muscle contractions in sports science, you must first learn the following part definitions.
1. Contraction = Tension
Note: You must think of muscle contraction in sport science as a "tension", not shortening because contracting a muscle can be shortening, lengthening or remaining the same length. When contraction is used as a normal vocabulary word it does mean shortening but not in sport science or physical education.
2. Iso = Constant
3. Tonic = Movement
4. Metric = Measure of the distance moved
5. Concentric = Shorten
6. Eccentric = Lengthen
If you learn these part definitions you will then be able to understand all the following sports science terms:
1. Isotonic contraction =
- Constant movement
- Muscle in tension
In other words = Muscle tension that results in limb movement.
This can be one of two ways:
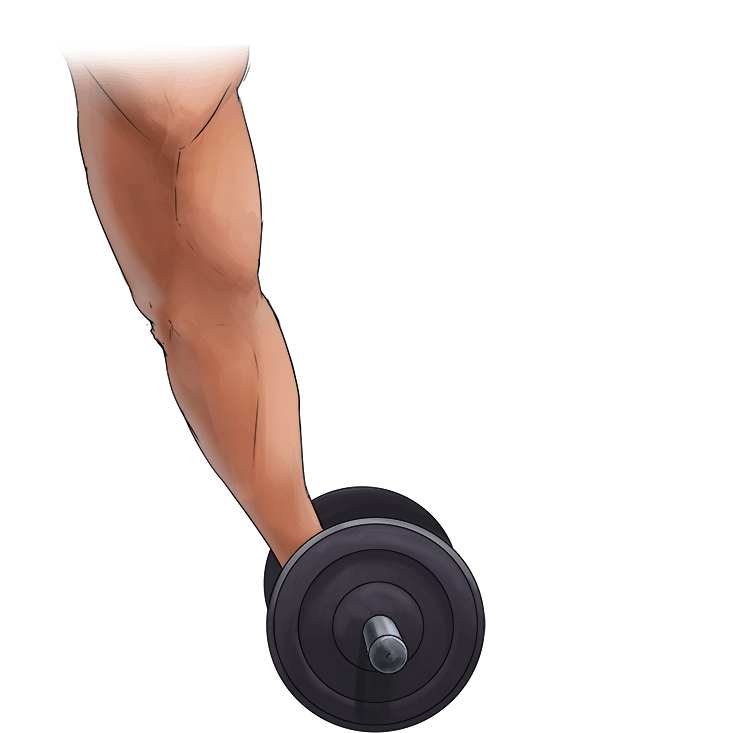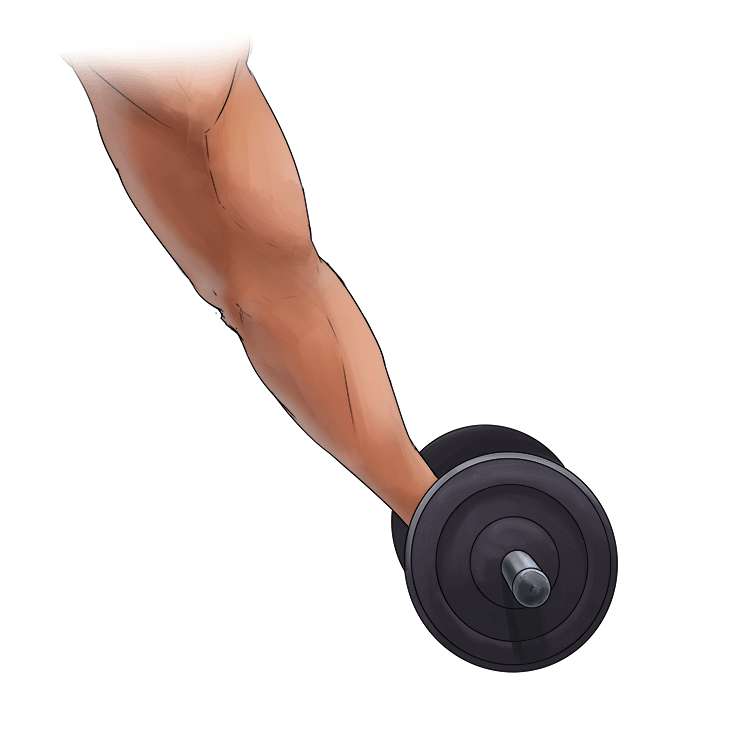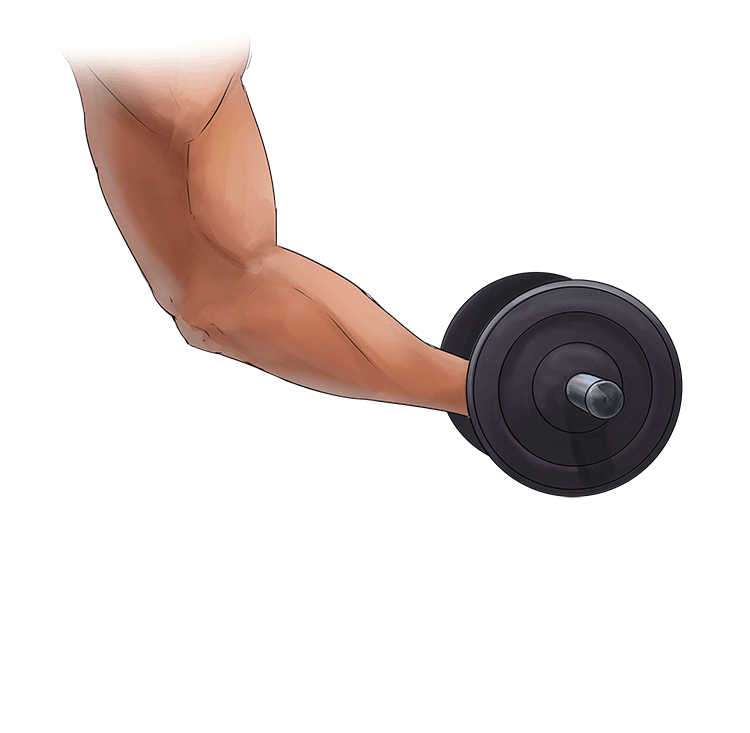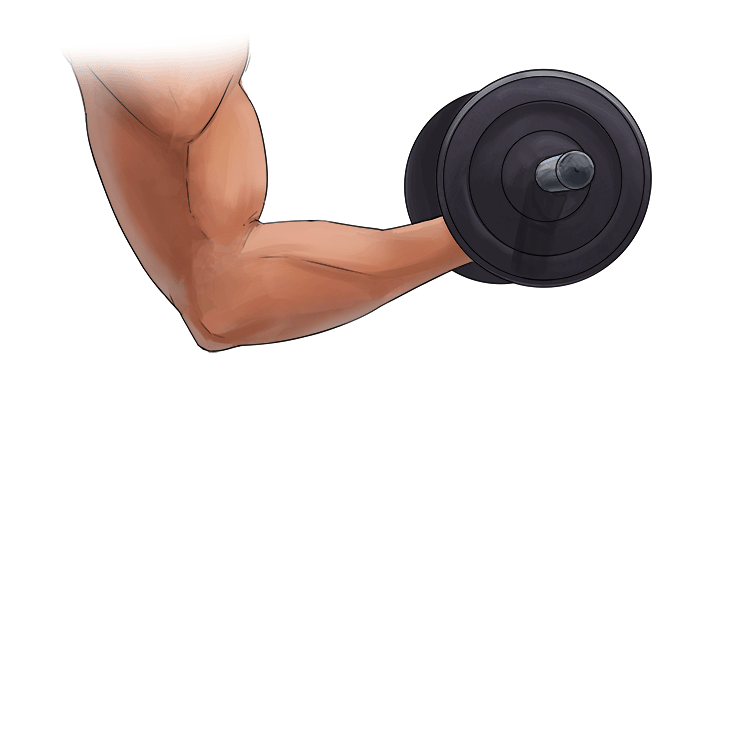
A. Concentric Contraction =
- Shortening of the muscle
- The muscle is in tension.
In other words = Shortening of the muscles.
Example: Lifting a dumbbell in a bicep curl.
B. Eccentric Contraction =
- Lengthening of the muscle
- Muscle is in tension
In other words = Lengthening of the muscle.
Example: Slowly putting down a dumbbell.
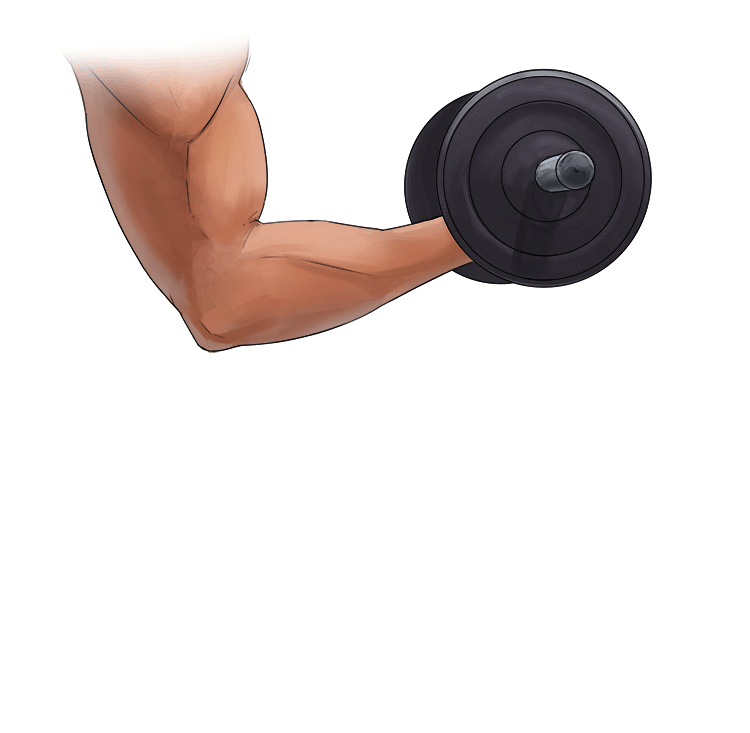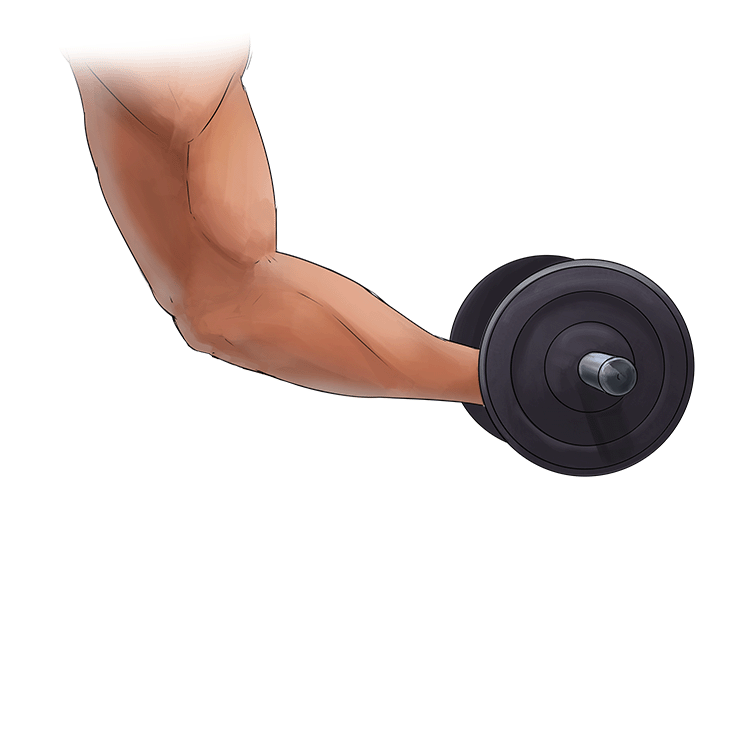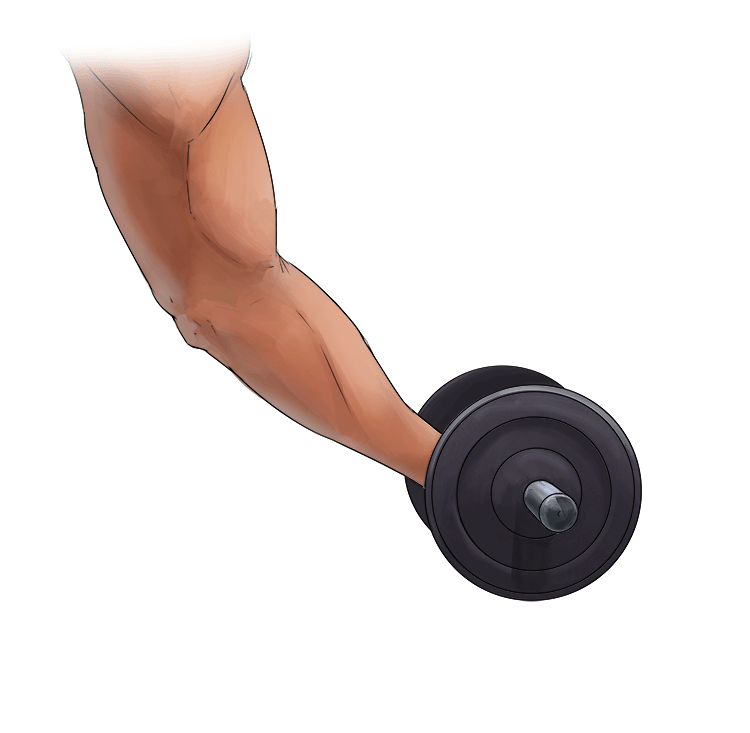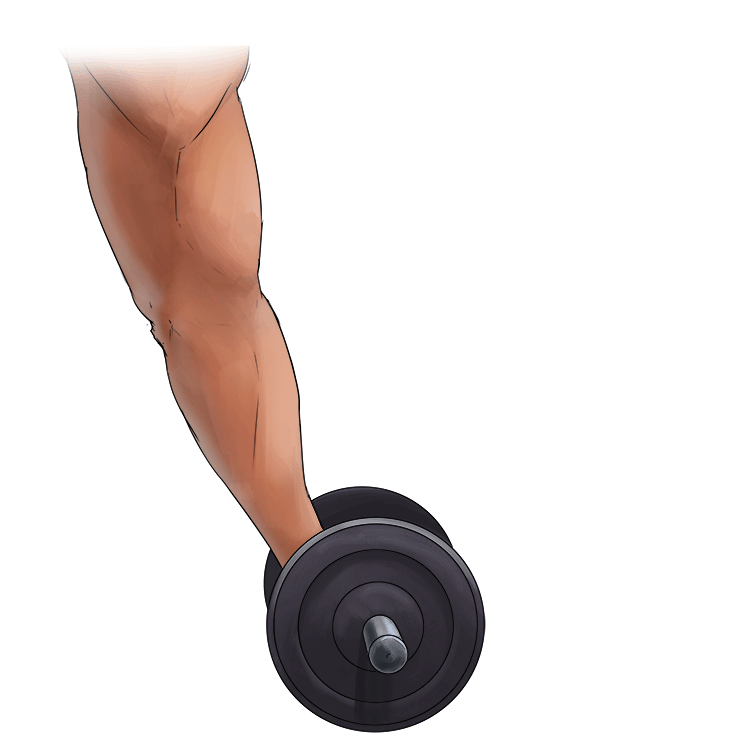
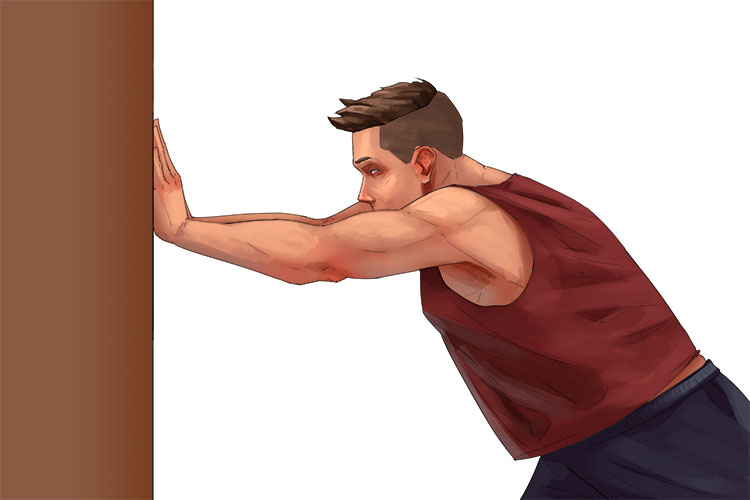
2. Isometric Contraction =
- Constant length
- Muscle is in tension
In other words = Muscle length does not alter under tension
Example: Pushing against a load but not moving, or pulling a door that won't open.





