Practical examples of trigonometry
Example 1
An air traffic controller is told by a pilot that she wants to land. She is currently at 40,000ft and wants to know what angle of descent to take. The air traffic controller can see on the radar that her plane is 100,000ft away from the runway.
NOTE:
The radar only measures directly to the plane and back, therefore the 100,000ft is the hypotenuse.
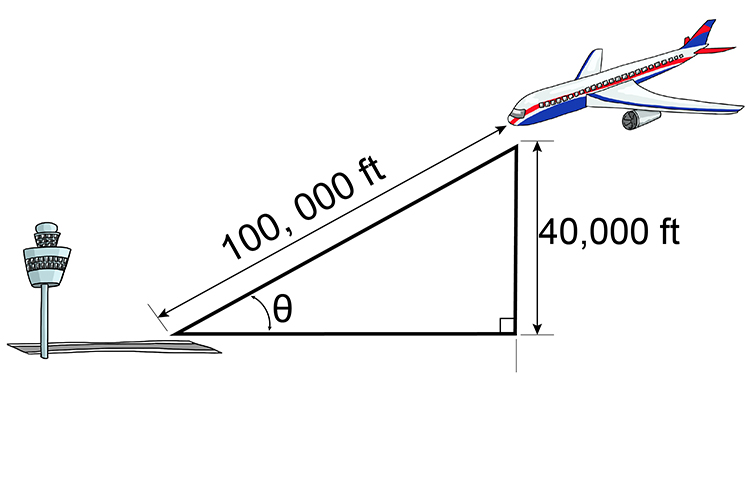
Start by writing down the name of the great trigger-happy Indian war chief.
SOH CAH TOA
Work out which part of the triangle is which:
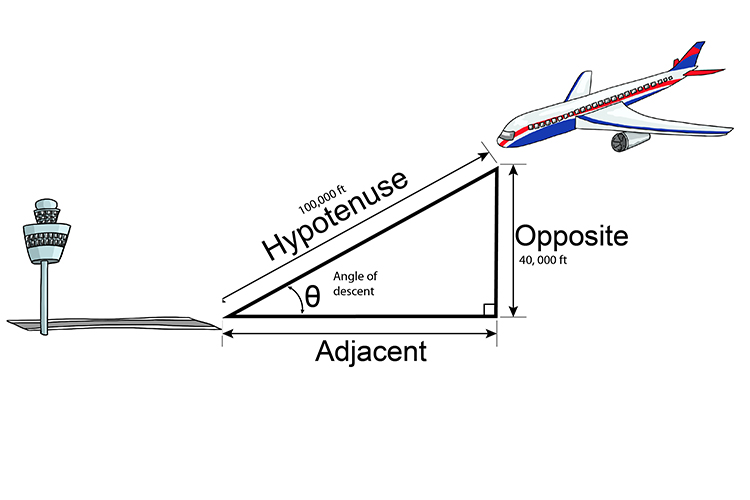
Looking at the diagram, we need `theta` (the angle of descent) and we know the lengths of the hypotenuse and the opposite. The only formula with hypotenuse, `theta` and opposite in it is:
`sin\ theta= (O)/(H)`
Or `sin\ theta= (Opposite)/(Hypoten\use)`
`sin\ theta= (40,000)/(100,000)`
`sin\ theta= 0.4`
Put 0.4 in your calculator and then press inverse sin or (sin-1). This gives = 23.6
Answer:
The pilot must descend at an angle of 23.6°
Example 2
A home owner is worried that a particular tree could fall onto her house. The house is 80 feet away, but she is not sure how tall the tree is. She asks the schoolkid next door to work it out for her.

The kid measured the shadow length from the tree. She also had a large protractor and measured the angle as 50°.
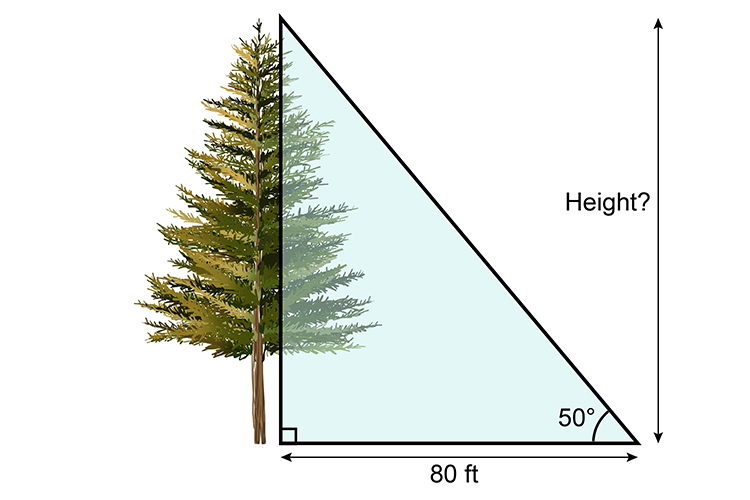
Then she did the following calculation:
She started by writing down the name of the great trigger-happy Indian war chief.
SOH CAH TOA
She worked out which part of the triangle she needed:
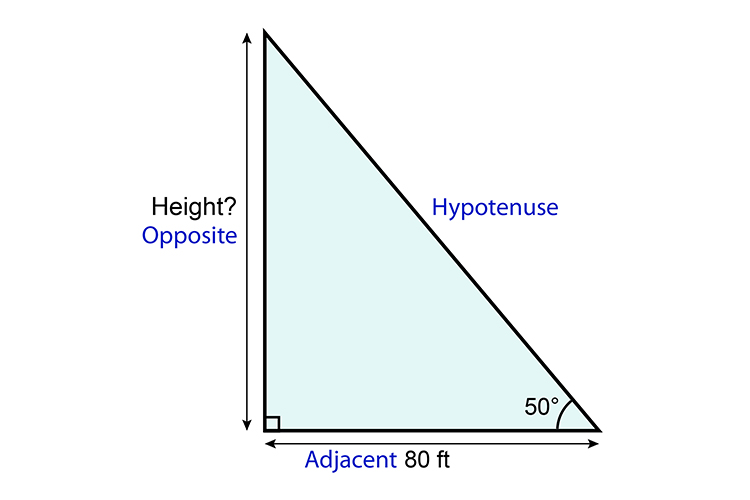
She needed opposite and adjacent.
So she chooses `tan\ theta= (O)/(A)`
Or `tan\ theta= (Opposite)/(Adjacent)`
`tan\ 50= (O)/(A)`
`tan\ 50= (Opposite\ (height))/80`
`Opposite\ (height)=tan\ 50times80`
(To find `tan\ 50` put 50 into your calculator and then press the tan button. You should get 1.1918)
`Opposite\ (height)=1.1918times80`
`Height=95.3\ feet`
Answer:
Yes, the house is in danger of being hit if the tree falls over.
Example 3
You have to build a ramp into a building, but it must be no more than a 5° angle, as required by building regulations. If the height of the door above the ground is 400mm, how long should the ramp be?
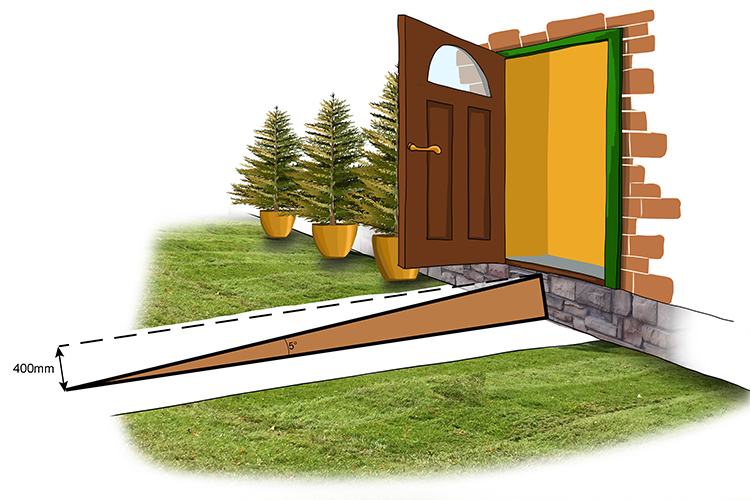
Start by writing down the name of the great trigger-happy Indian war chief.
SOH CAH TOA
Work out which part of the triangle is which:
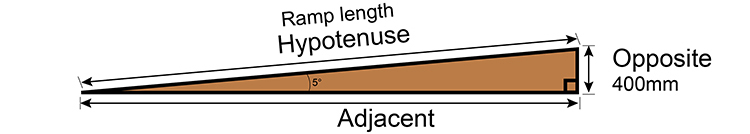
So we choose opposite and hypotenuse.
Choose `sin\ theta= (O)/(H)`
Or `sin\ theta= (Opposite)/(Hypoten\use)`
Or `sin\ 5= (400mm)/(Hypoten\use)`
Rearrange the formula
`Hypoten\use=(400mm)/sin5`
On a calculator press 5 and then sin and you get 0.08716.
`Hypoten\use=(400mm)/0.08716`
`Hypoten\use=4589mm\ \ or\ \ 4.6m` (to the nearest 0.1m)
Answer:
The ramp has to be 4.6m long.




