What does standard deviation really mean?
If a set of data is said to have a normal distribution then the standard deviation can be used to determine the proportion of values that lie within a particular range of the mean.
The standard deviation is usually presented in conjunction with the mean
For a normal distribution:
- 68% of the data is less than 1 standard deviation away from the mean (1SD).
- 95% of the data is less than two standard deviations away from the mean.
- 99.7% of the data is less than three.
68% = 1 SD
95% = 2 SD
99.7% = 3SD
What does 1 SD (one standard deviation) mean
On a bell curve or normal distribution of data
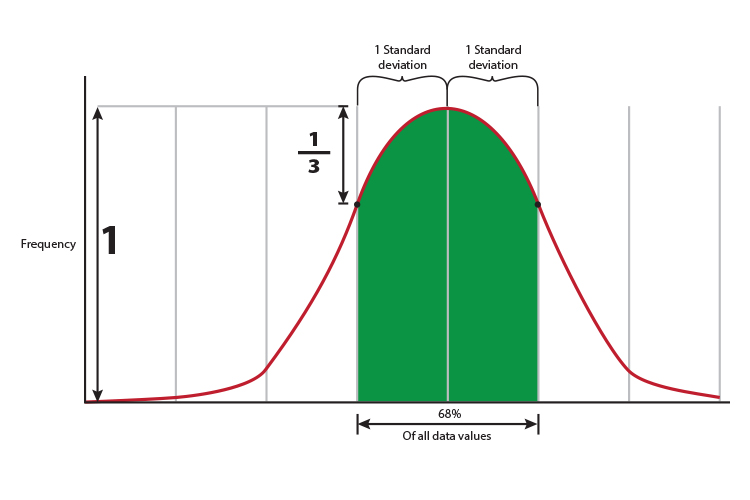
 1 SD = 1 Standard deviation = 68% of the scores or data values is roughly filling the area of a bell curve from a `1/3` of the way down the `y` axis.
1 SD = 1 Standard deviation = 68% of the scores or data values is roughly filling the area of a bell curve from a `1/3` of the way down the `y` axis.
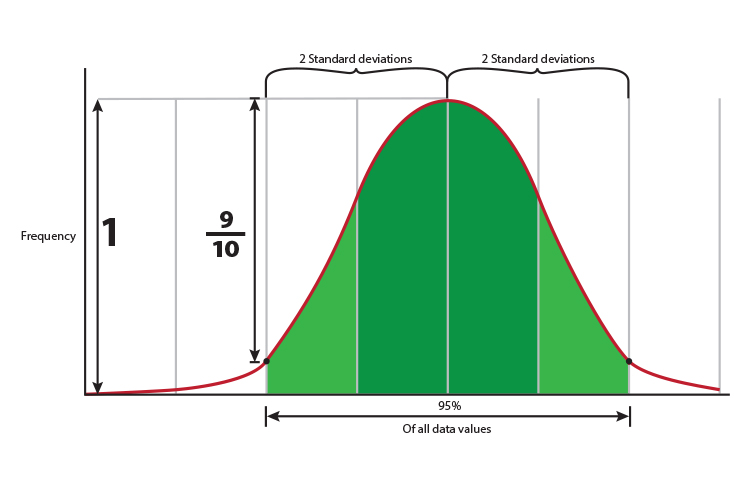
What does 2 SD (two standard deviations) mean
On a bell curve or normal distribution of data
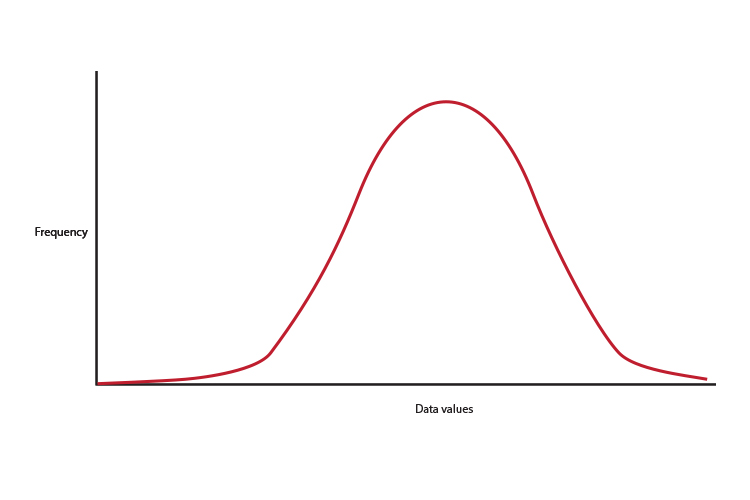
2 SD = 2 Standard deviation = 95% of the scores or data values is roughly filling the area of a bell curve from nine tenths of the way down the `y` axis.
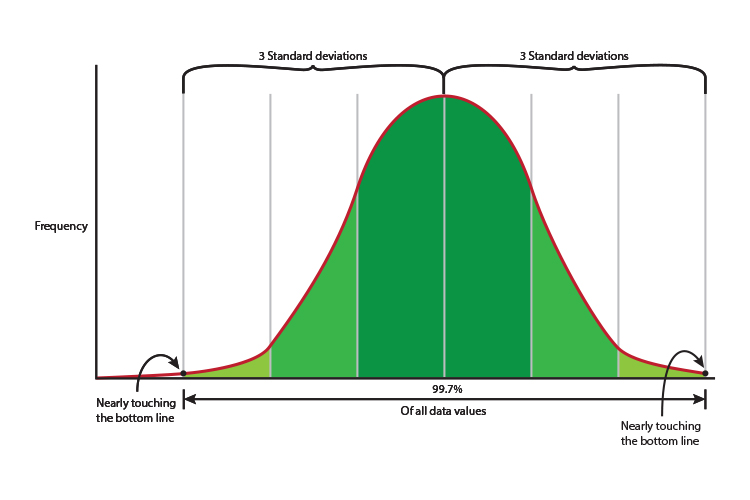
What does 3 SD (three standard deviations) mean
On a bell curve or normal distribution of data
 3 SD = 3 Standard deviation = 99.7% of the scores or data values is roughly filling the area of a bell curve from just before it touches the `x` axis.
3 SD = 3 Standard deviation = 99.7% of the scores or data values is roughly filling the area of a bell curve from just before it touches the `x` axis.