Effectors – muscles and glands
Effectors are parts of the body that produce a response to signals carried by nerve cells, such as a muscle contracting to move an arm or a gland contracting to release a hormone into the blood.
Her muscles gave off sound effects (effectors).
Example
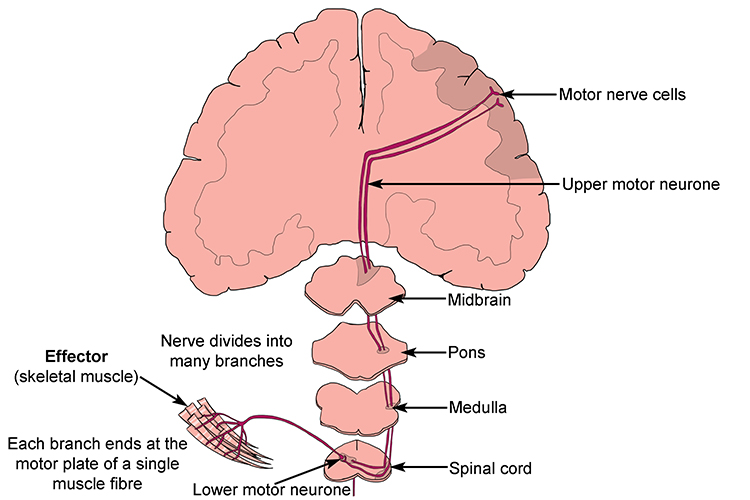
This simple example shows the route of a signal from its origin in the brain, via various other parts of the brain, then down the spine, to an effector - a skeletal muscle – that responds to the message by contacting to move a limb. This example is a non-reflex action – one that is thought about before the action takes place. Note that there are upper motor neurones (from the brain and down the spine) and lower motor neurones (from the spine to the muscle).




