Completing the square - example 4
Complete the square `x^2+7x+10=0`
Remember
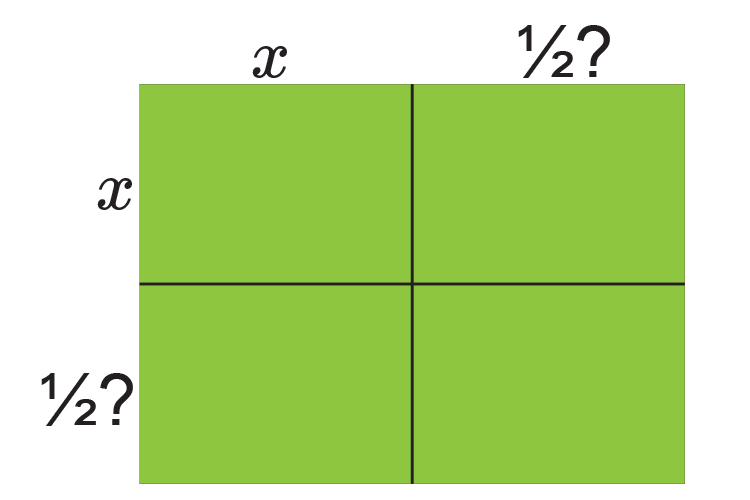
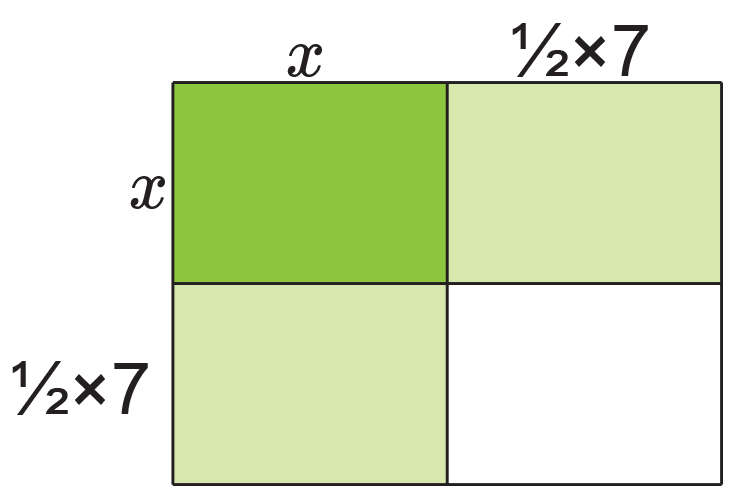
Fill in
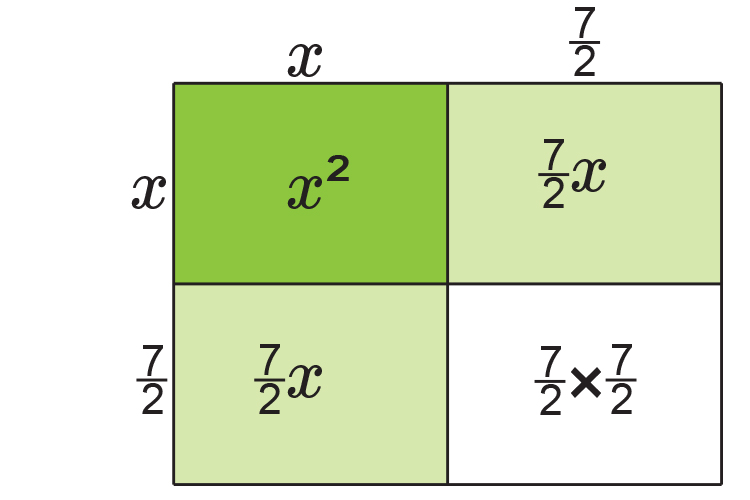
NOTE:
This is the same as `(x+7/2)^2`
If you add up each area you get:
`x^2+7/2x+7/2x+7/2times7/2`
`x^2+7x+49/4`
`x^2+7x+12\1/4`
Always plot this on a number line
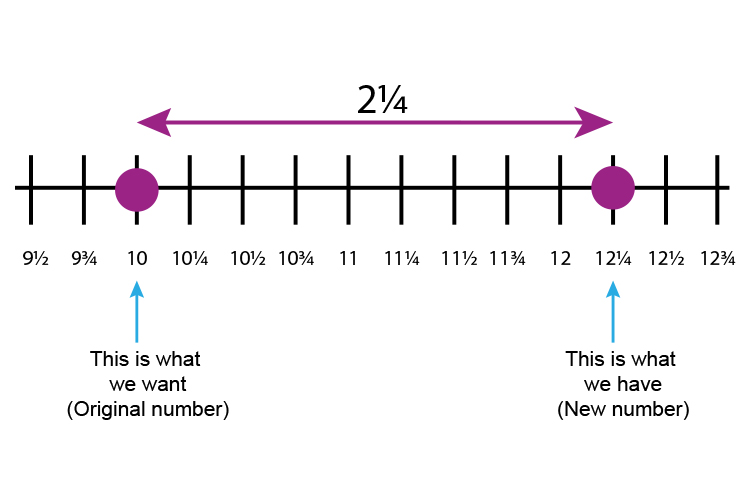
The number line will help you remember
Original number `-` New number
`10-12\1/4=-2\1/4`
So `x^2+7x+10=0`
Is the same as
`(x+7/2)^2-2\1/4=0`
`(x+7/2)^2=2\1/4`
`x+7/2=+-sqrt(2\1/4)`
`x=-7/2+-sqrt(2\1/4)`
Using a calculator
`x=-3.5+-1.5`
`x=-3.5+1.5` and `-3.5-1.5`
`x=-2` and `-5`
Now check
`x^2+7x+10=0`
If `x=-2` `(-2)^2+7times(-2)+10=0`
`+4-14+10=0` Which is correct
If `x=-5` `(-5)^2+7times(-5)+10=0`
`25-35+10=0` Which is correct
Answer:
The roots of `x^2+7x+10=0` are `x=-2` and `x=-5`
NOTE:
This example has also been used in factorising quadratics (easy) and quadratic formula examples to show that the roots`-2` and `-5` can be found using any of these methods.




