Barriers to disease
The body has a number of barriers to prevent pathogens getting inside it. They can be described as “pathogen stoppers”.
The path of gin (pathogen) stopped at the Great Barrier Reef (barrier).
Mechanical barriers
These are physical barriers to pathogens, e.g. nostril hairs, skin, and scabs that form on wounds.

The mechanic (mechanical barriers) fended off pathogens with his skin, nasal hair and scabs.
Chemical barriers
These include acid in the stomach, sticky mucus in the lungs and chemicals in tears, which kill or block the progress of pathogens.
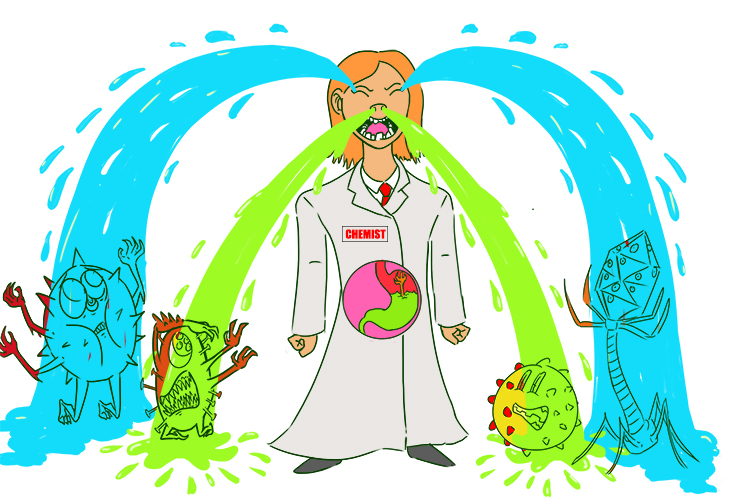
The chemist (chemical barriers) killed off pathogens, brought into her shop by customers, with mucus, tears and stomach acid.
Mucus
Slimy substance secreted by animals for lubrication and protection against invading pollutants and organisms.

A moo cusses (mucus) because it’s stepped into a pool of slime which stops everything getting through the gateway.




