Immune system
The immune system comprises the body’s tools for fighting pathogens (as detailed below).

An emu used its system of tools (immune system) to smash up the path of gin (pathogen).
White blood cells
White blood cells defend against pathogens.

The white cell (white blood cell) contained the path of gin (pathogen) so it couldn’t do any harm.
Phagocytes and lymphocytes
There are two main types of white blood cell: phagocytes and lymphocytes.
Phagocyte: White blood cell that ingests and absorbs (called consuming) foreign matter and dead cells.
Lymphocyte: White blood cell that produces antibodies and antitoxins.
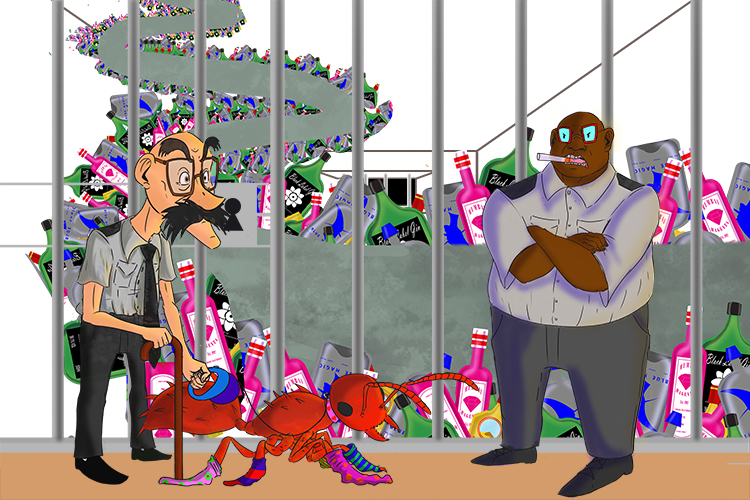

Two jailers guard the white cell. One jailer has a limp and bad eyesight (lymphocyte), and a pet with an ant’s body (antibody) that wears ant socks (antitoxin). The other jailer is smoking a fag and has bad eyesight. (phagocyte).
Phagocytosis
The action of a phagocyte white blood cell ingesting and absorbing (consuming) foreign and dead matter is called phagocytosis.
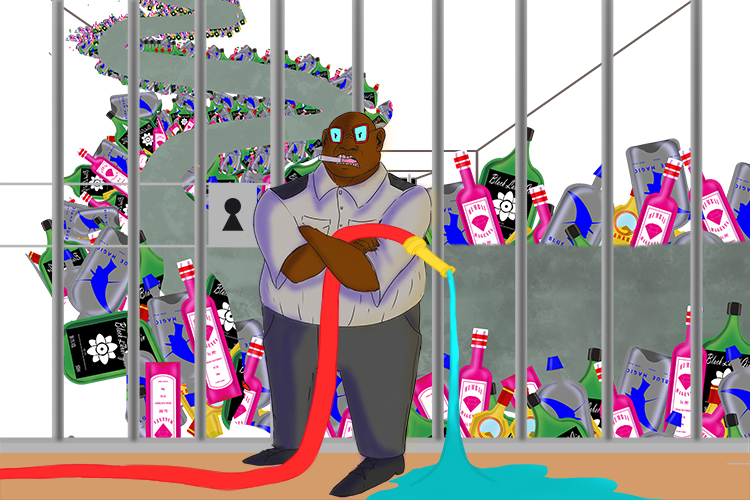

The jailer who likes a fag on site (phagocyte) sometimes plays with the fire hoses (phagocytoses). Although it looks like he is smoking, it is actually a sweet cigarette and he has already consumed half of it.
NOTE:
Never refer to consuming as “eating” in biology.
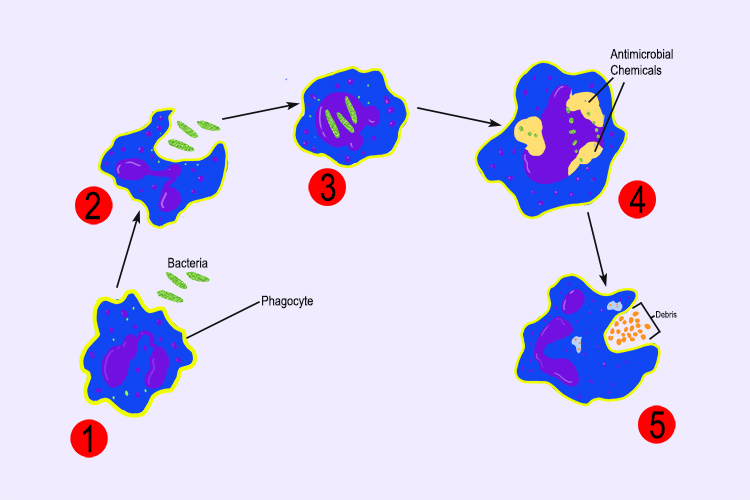
Example of phagocytosis
Phagocyte ingests and destroys bacteria:
Lymphocytes: antibody and antitoxin
An antibody is a protein that latches on to pathogens to make them ineffective.
An antitoxin is a protein that makes a toxin ineffective.

A protesting teen (protein) riding on an ant’s body (antibody) with its ant socks on (antitoxin) fastened the latch on (latches on) the door and stopped the pathogen and its toxic mate in their tracks.
Example of lymphocyte
Lymphocyte releases antibodies that latch on to antigens:
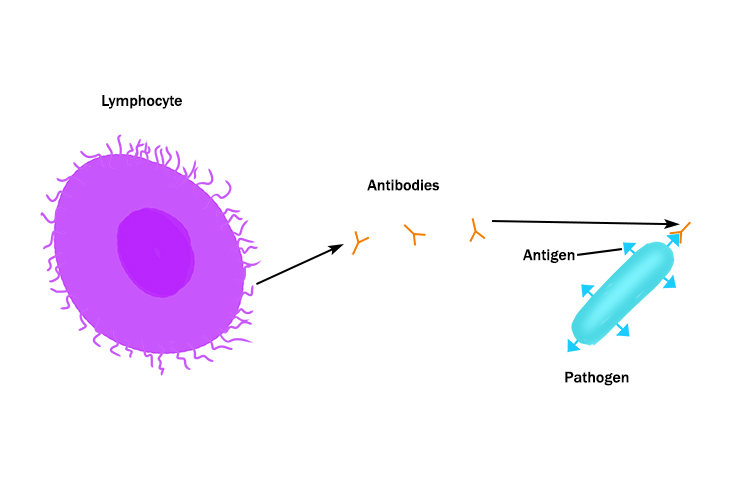
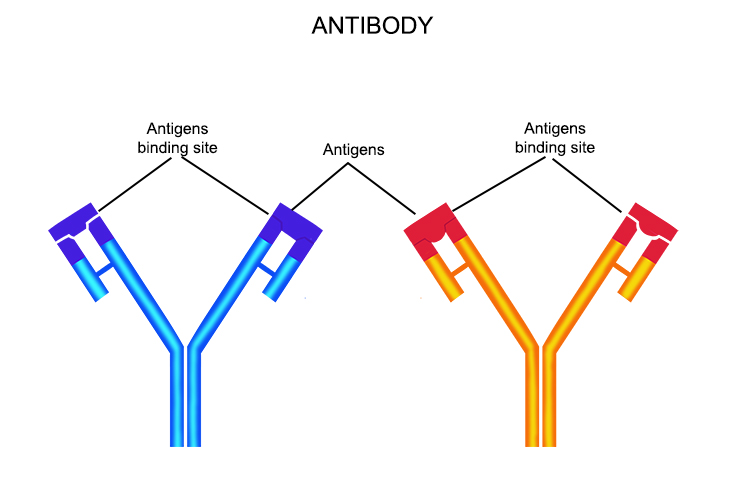
Antibodies are Y-shaped and are produced by lymphocytes to perfectly fit specific antigen shapes. (See Antigen on next page).




