Market Research Introduction
Businesses carry out market research to gather data about the market and the needs of the customer. This data is used to help improve the quality of the decisions it takes.
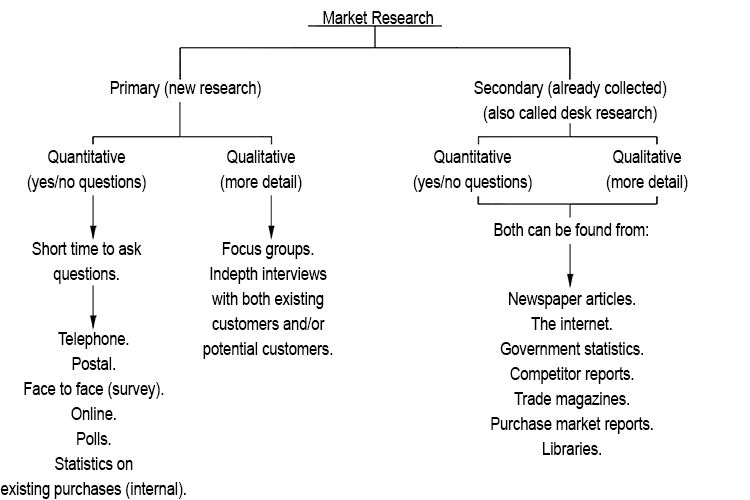
Market research usually consists of a combination of primary market research or secondary market research. Primary market research involves gathering data that has not been collected before. Secondary market research is data that has already been collected, you just have to find it from newspaper articles, the internet, government statistics or competitors reports. Market research can also be used to collect either quantitative or qualitative data. Quantitative research gathers large quantities of data so that calculations can take place, such as what percentage of chocolate lovers also like peanuts. This means that lots of people will be asked to fill in a questionnaire in which the questions have yes/no answers. Qualitative research is more in-depth, involving smaller groups of consumers, perhaps as part of a group discussion. The aim of qualitative research is to find out about customers’ opinions and reasons why they behave the way they do.
This is an example of how market research could work for a small company:
A plumbing merchant (selling plumbing materials and bathrooms to plumbers) wants to open a new branch. Where is the most appropriate place to open. They decide to carry out market research. They choose two areas to compare which is the best.
The plumbing merchant’s staff go on the internet and look at how many plumbers offer services in each of the areas. (Quantitative secondary market research). The more the better, but they find that each area has an equal number of plumbers. The staff then looked at property statistics to find out how affluent the households are (and how many houses there are) in each area. They need an area where there are not only many plumbers but where the customers have high incomes to afford top of the range bathrooms. Here they identify one area with much higher incomes (quantitative secondary market research). Further research using focus groups already carried out in trade magazines state that larger income households change their bathrooms more frequently (qualitative secondary market research). Further research finds that there is only one small competitor in the area. Having chosen the area that the plumbing merchant should open, the company needs to find which plumbing materials need to be stocked. If the plumbers in that area only use a certain brand of boiler there is no point in stocking an alternative because they will not buy from you.
So, the plumbing merchant decides to carry out some primary research. They phone boiler manufacturers and find how many boilers they sell in that area. They find out that one boiler company sells many boilers of one particular kind in that area. The boiler manufacturer is particularly suited to the soft water area and have a very robust product that plumbers know is reliable (primary qualitative research). The plumbing merchant also phone and physically interview potential plumbers in that area and find detailed products that they need , gathering a complete product range needed for them (primary qualitative research).
Here you can see just how important market research is, even for a small company.




