Price Elastic or Inelastic Demand – Price Sensitivity
Business people say that the general law of demand is that the cheaper a product/service is, the more a consumer is likely to buy.
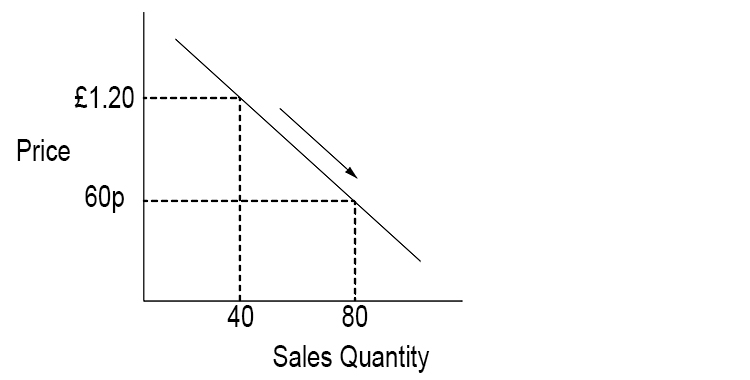
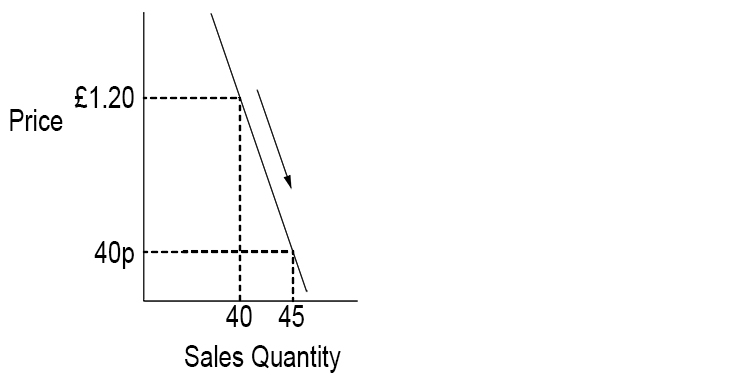
Price elastic demand (PED) – When the quantity sold of a product or service is sensitive to price changes
A fall in price leads to a bigger increase in the quantity demanded. The price is sensitive.
ELASTIC - THINK SENSITIVITY
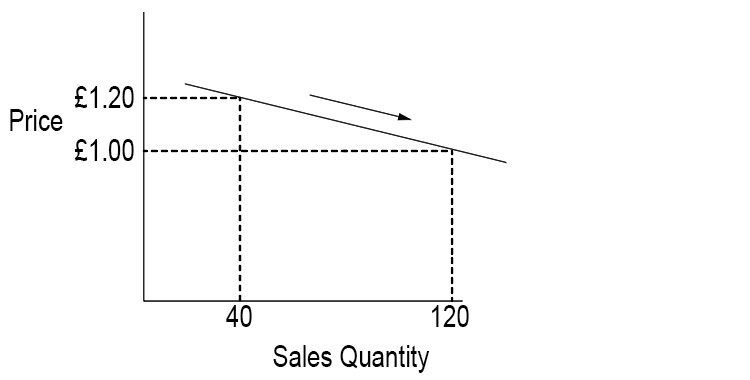
Price inelastic demand (PID) – When the quantity sold of a product or service is unresponsive to changes in price
A fall in price leads to a very small increase in the quantity demanded. The price is insensitive.
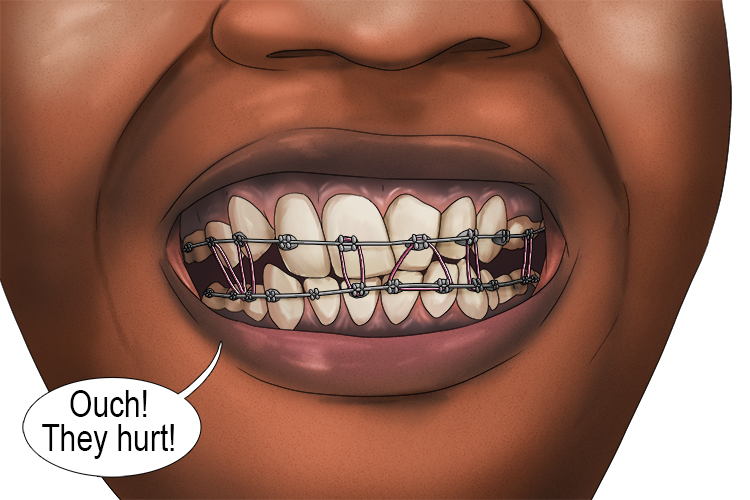
To remember what elastic means, use the following mnemonic:
She had elastic (elastic) bands fitted in her mouth and it made her gums and teeth very sensitive (sensitive).
Examples
An example of a product that has a price inelastic demand is petrol. If you have a petrol car, there are no other alternatives to buying petrol if you want to drive it. An increased price has failed to reduce the demand for petrol significantly.
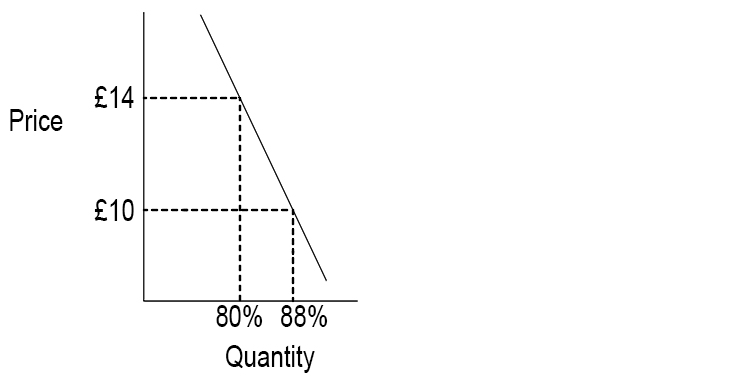
An example of a product that has a price elastic demand is a chocolate bar. If you increase a chocolate bar’s price by a considerable amount, people will switch to an alternative chocolate bar because there is a large choice of substitutes.
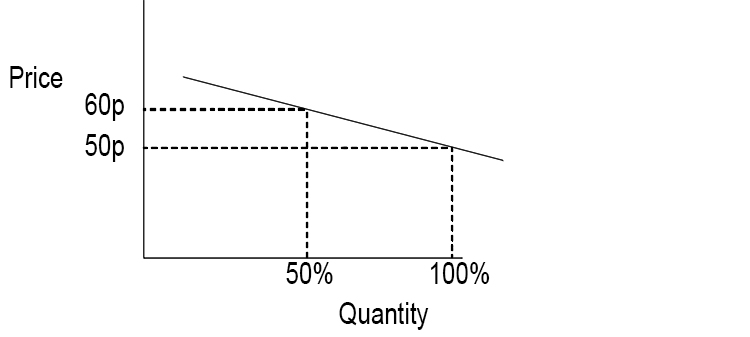
Summary
Price inelastic – A large change in price causes a small change in demand
Price elastic – A large change in price causes a large change in demand
(The “in” you can think of as insensitive)




