Tenses Example 2
 |
MORE ON PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS
MORE ON PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS
MORE ON FUTURE PERFECT CONTINUOUS Future perfect continuous
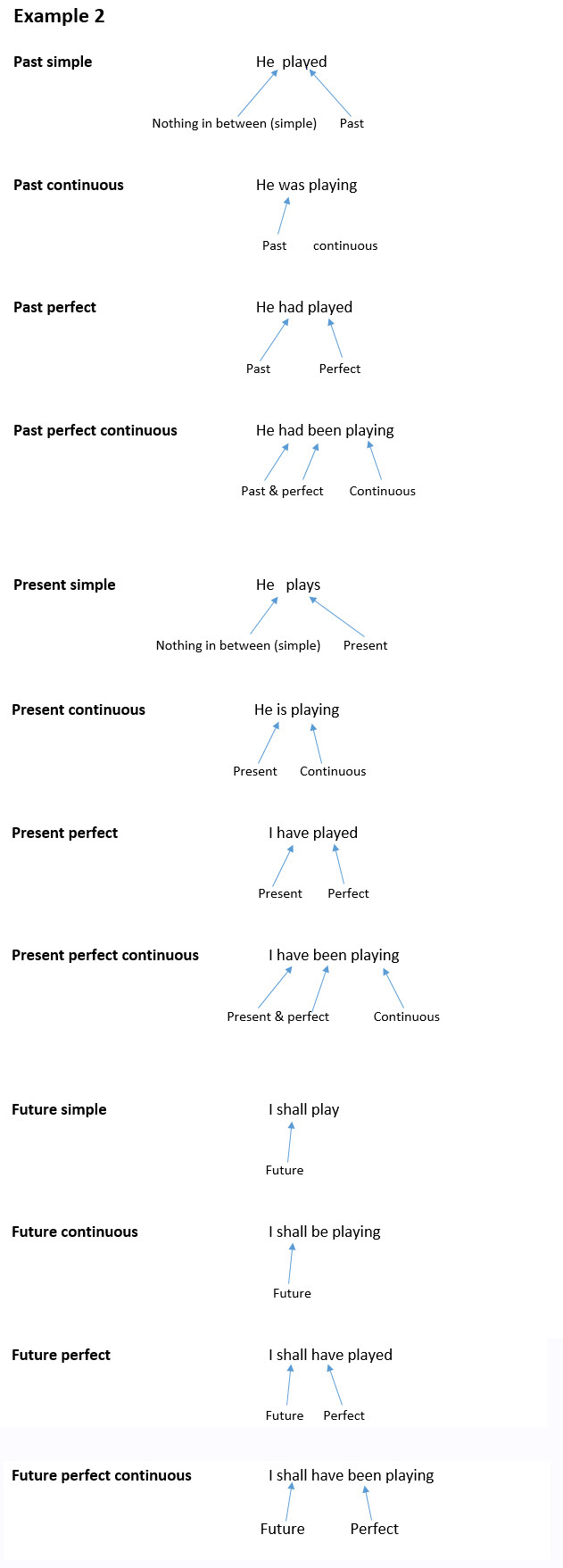
Example: I shall have been playing
Usage: This tense is used to describe an action or state that will continue up to a point in the future. It is formed by “will have been” followed by the verb with “‑ing” on the end. Future perfect
Example: I shall have played
Usage: Future perfect tense is used when speaking or writing about an action or state that will happen in the future and be completed before some other point in the future. It is formed by “will have” plus the past participle of the verb (in this case “eaten”.) Future continuous
Example: I shall be playing
Usage: This tense indicates that something will occur in the future and continue for an expected length of time. It is formed by “will” plus “be” plus the verb with “‑ing” on the end. Future simple
Example: I shall play
Usage: This tense is used to write or talk about things that have not yet happened – events or states that will begin and end in the future. It is formed by using “will”, “shall”, “may” or “might” followed by the verb. Present perfect continuous
Example: I have been playing
Usage: used to talk about how long something has continued up until now (e.g. I have been eating for the past ten minutes). This tense is formed by using has/have been plus the verb with “‑ing” on the end. Present perfect
Example: I have played
Usage: Used when referring to an action or state that either occurred sometime in the past or began in the past and continued into the present time. This tense is formed by have/has plus the past participle of the verb (in this case “eaten”.) Present continuous
Example: He is playing
Usage: Used to indicate that an action or situation is happening now and may continue into the future. This tense is formed by am/is/are plus the verb with “‑ing” on the end. Present simple
Example: He plays
Usage: This is used when an action is happening right now. There are no keywords (such as has, have, is or was) between the subject (“I”) and the verb “eat” – which is what makes it “simple”: just the subject and the verb. Past perfect continuous
Example: He had been playing
Usage: This tense is used to show that an action that started in the past continued up until another time in the past – in other words, the event or state began in the past, continued in the past and ended in the past. It is formed by using “had been” or “have been” plus the verb with “‑ing” on the end. Past perfect
Example: He had played Usage: This tense shows that an action or condition occurred prior, or previous to, some point in the past – in other words, something that happened before Past continuous
Example: He was playing
Usage: Past continuous tense refers to a continuing action or state that was happening at some point in the past. It is formed by combining “was” (single thing or person) or “were” (plural things or people) and the verb with “‑ing” on the end. Past simple
Example: He played
Usage: This tense is used to write or talk about things that happened or existed in the past. It makes it clear that the action is now finished. There are no keywords such as “has”, “have”, “is” or “was” between the subject (in this case “I”) and the verb (ate), which makes it “simple”. |




