Geography Flash Cards
Here's a really quick way of testing if you've learned the meanings of the key words in this section.
Look at the key word on the card and see if you can remember its definition.
If you get stuck, you can be shown the mnemonic to reveal an image that should help you remember.
To check if you're right, or remind you if you've forgotten, press the card to flip it.
Go through the whole list to see how many definitions you can recall.
Revisit any that you had difficulty remembering until you're confident you can
recall all of them.
Development that meets the needs of the present without limiting the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
Sustainable Development
Sustainable Development – Development that meets the needs of the present without limiting the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
To understand the words "sustainable development" you need to remember the meaning of sustainable and then development.
Sustainable – able to be maintained or continued
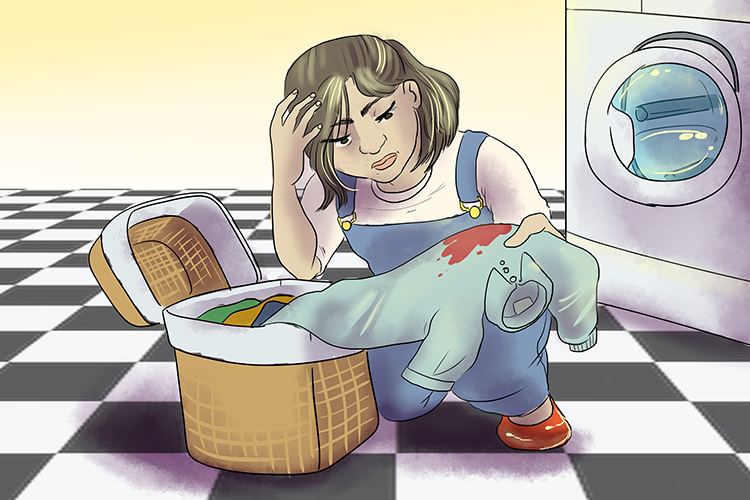
Suds couldn't remove the stain, I wasn't able (sustainable) to get the stain out - it continued to annoy me.
Development – The process in which someone or something changes and becomes more advanced

When we develop it should be on the basis that it is meant (development) to be an improvement on what we did before.
So, sustainable development is advancing as a society in a way that can be continued or maintained.
It's about building both domestic and commercial properties without destroying any ecosystems; using recycled materials and making careful use of energy, water and materials.
It's about how we have learned to rotate crops, which has led to sustainable agriculture.
It's also about developing energy resources that are renewable, such as:
- Solar energy
- Wind energy
- Hydroelectric energy
- Geothermal energy
- Biomass
Energy that can potentially be used well in to the future (continue forever) without harming future generations
Sustainable Energy Supply
Sustainable Energy Supply – Energy that can potentially be used well in to the future (continue forever) without harming future generations
NOTE: Sustainable energy is the combination of energy savings, energy efficiency measures and technologies, as well as the renewable energy sources.
To understand the words "sustainable energy source" you need to remember the meaning of sustainable and then energy supply.
Sustainable – able to be maintained or continued

Suds couldn't remove the stain; I wasn't able (sustainable) to get the stain out. It continued to annoy me.
Energy supply – in this context includes solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal and biomass
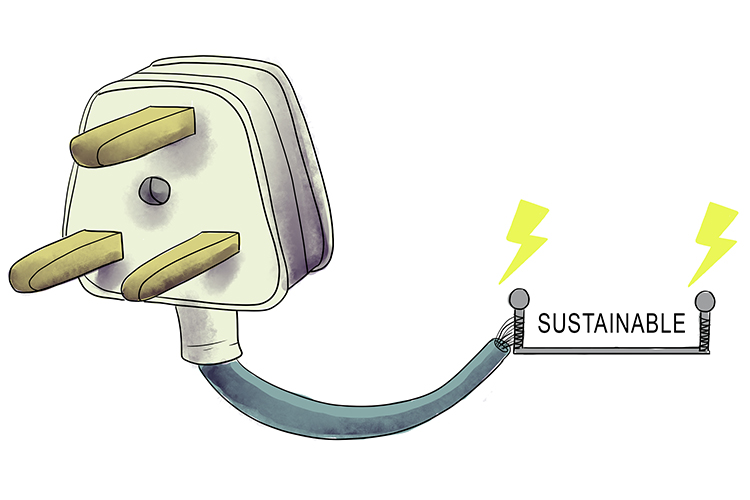
So, a sustainable energy source is energy that can be maintained or continued.
The difference between renewable and sustainable is as follows:
If I have a single tree in my backyard and I cut it down: this is a renewable source because the tree will grow back from the stump, but very slowly. If I try to heat my house with the tree this is not sustainable because the renewable rate is too slow.
A sustainable energy supply is therefore one that can continue forever without harming future generations.
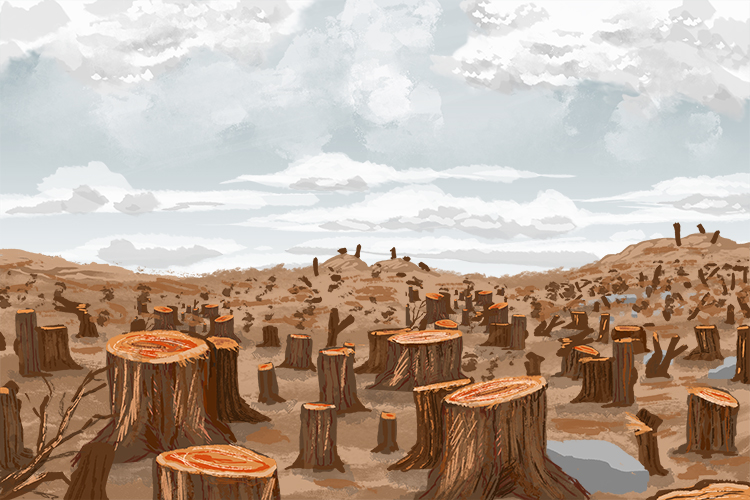

This deforestation of tropical rain forests is NOT sustainable.
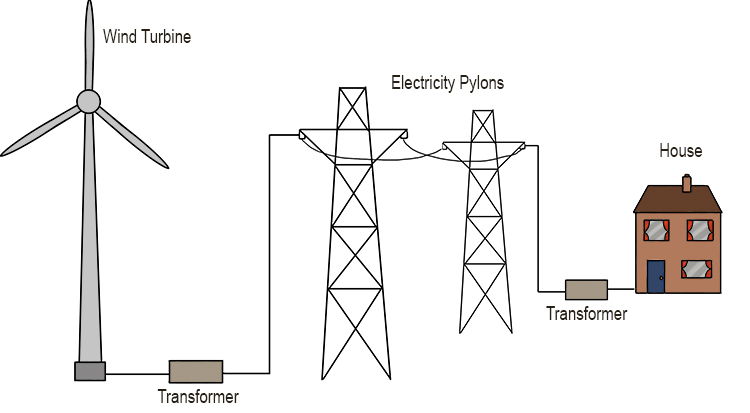
Electrical energy obtained from harnessing the wind with windmills or wind turbines
Wind Energy
Wind Energy – Electrical energy obtained from harnessing the wind with windmills or wind turbines
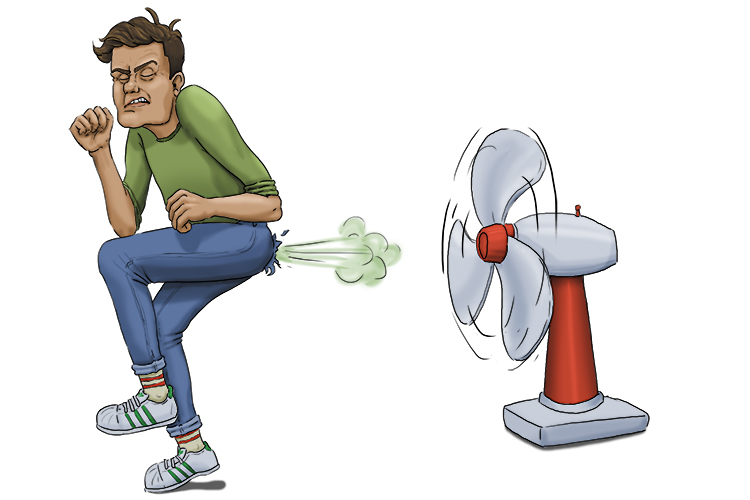
Wind can be strong enough to move a fan or propeller blades and convert the movement to electrical energy (wind energy).
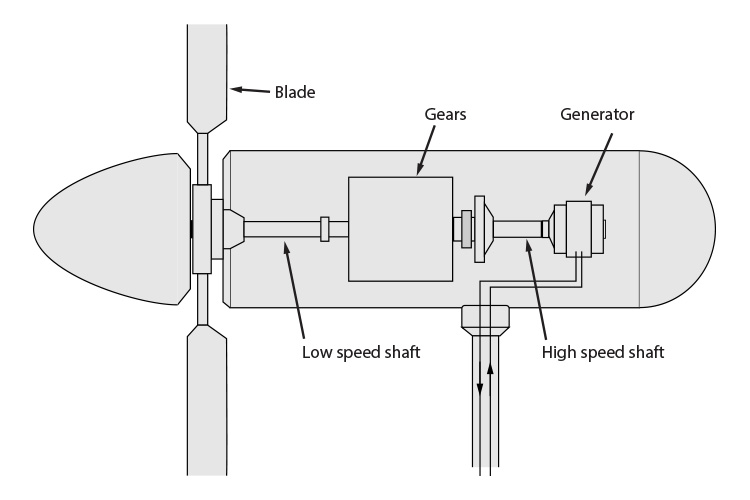
The sun heats the earth. As hot air rises, cooler air moves in to fill the void. The resultant wind spins the blades which turn a shaft connected to a generator that produces electricity.
Wind power is among the fastest-growing forms of renewable energy – its use is increasing worldwide.
One of the main reasons for this is that the cost of making the turbines and other equipment needed has fallen dramatically due to improved manufacturing methods as the industry has matured.
Globally, the installed wind-generation capacity, both onshore and offshore, increased by a factor of almost 87 in the 22 years from 1997, jumping from 7.5 gigawatts (GW) to around 651 GW by 2019.
When wind hits a turbine’s blades, it causes them to rotate and turn the turbine connected to them. The turbine is connected to a generator, which produces electrical energy through electromagnetism.
Advantages of wind power include:
- Renewable and clean source of energy
- Low operating costs
- Relatively efficient use of space
Disadvantages include:
- Power generation is intermittent (only when the wind blows)
- Visual intrusion
- Threat to some wildlife – some birds are killed by turbines, and some animals are possibly displaced by construction











