Formula for a straight line
The formula for a straight line is:
`y=mx+c`
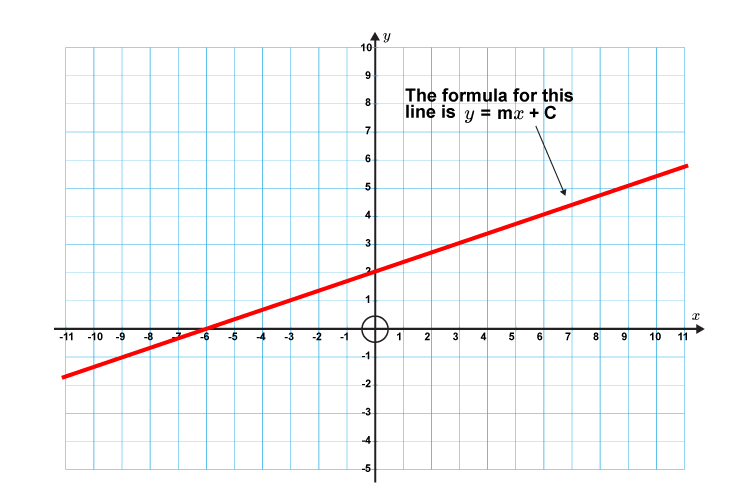
Where `m=` Gradient
`c=` The point where the line crosses the `y` axis (`y` intercept)
Further explanation
Equations of a straight line are in the form of:
`y=mx+c`
If you are given a formula of a straight line and asked to draw it on a graph you do so as follows:
Examples
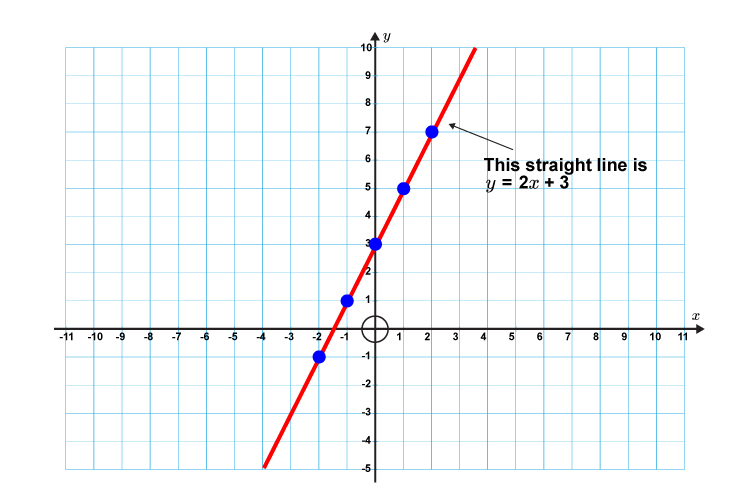
1. Draw the following straight line on a graph
`y=2x+3`
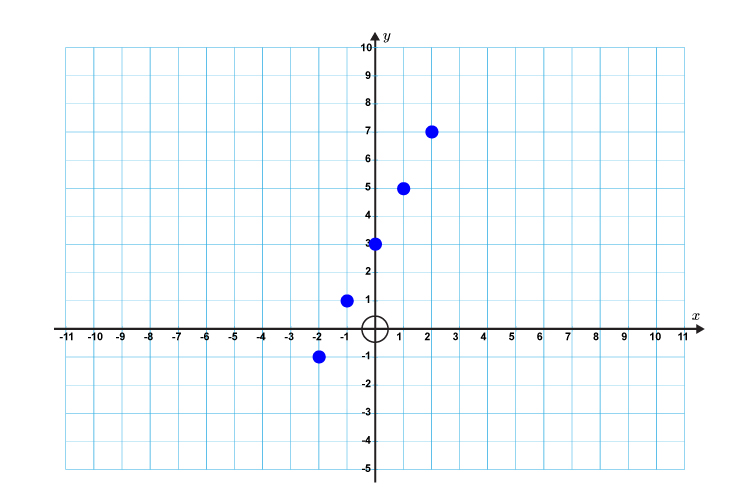
First lets calculate some points on the graph.
If `x=-2` then `y=2times(-2)+3=-1`
`x=-1` then `y=2times(-1)+3=1`
`x=0` then `y=2times0+3\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ =3`
`x=1` then `y=2times1+3\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ =5`
`x=2` then `y=2times2+3\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ =7`
Now draw a graph and plot the above points.
Now draw a straight line through these points
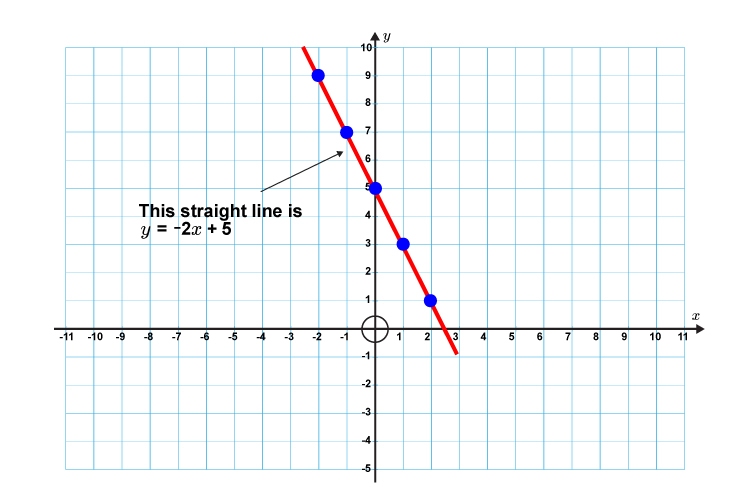
2. Draw the following straight line on a graph
`y=-2x+5`
First lets calculate some points on the graph.
If `x=-2` then `y=-2times(-2)+5=9`
`x=-1` then `y=-2times(-1)+5=7`
`x=0` then `y=-2times0+5\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ =5`
`x=1` then `y=-2times1+5\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ =3`
`x=2` then `y=-2times2+5\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ =1`
Now draw a graph and mark out the above points.
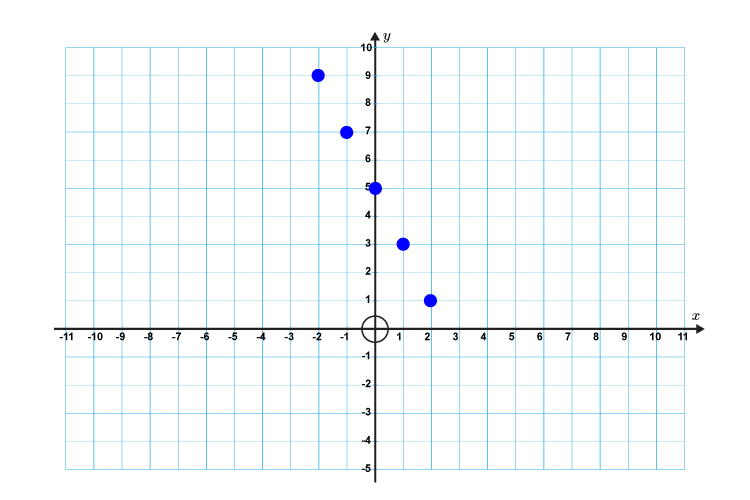
Now draw a straight line through these points