Food Miles – The distance covered supplying food to consumers
To remember the meaning of the term Food Miles, use the following mnemonic:
The food travelled for miles (food miles).

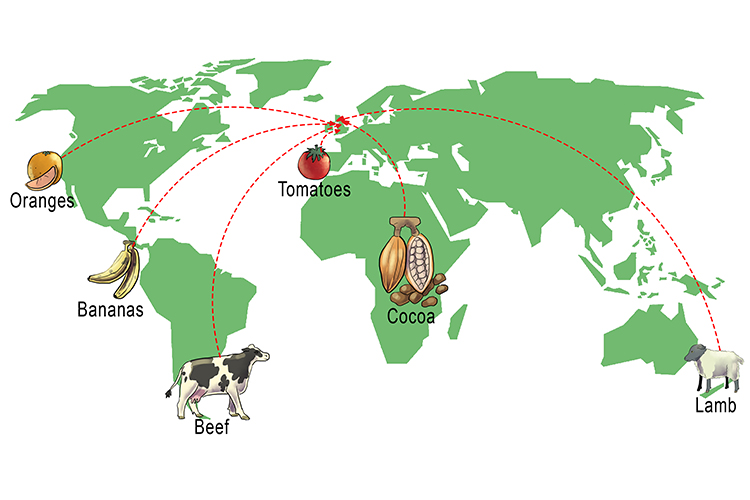
To the United Kingdom
| California | Oranges | 5000 miles |
| West Indies | Bananas | 4000 miles |
| Argentina | Beef | 7000 miles |
| Spain | Tomatoes | 1000 miles |
| Central Africa | Cocoa Beans | 3500 miles |
| New Zealand | Lamb | 11000 miles |
All food must travel some distance to get to your plate, whether it's a few yards from your back garden or 12,000 miles from the other side of the word.
The distance food travels is known as food miles.
Generally, the shorter the distance food travels the better, from the environmental point of view. Transporting food means using energy, and energy based on fossil fuels adds to costs and pollutes the atmosphere, adding to the global warming problem.
People can help to reduce food miles by:
- Buying local produce
- Buying food that is "in season" for your location (e.g., buying British strawberries in summer, but not buying foreign-grown strawberries in winter)
- Growing some of your own food (e.g., potatoes, cabbage, lettuce, tomatoes)
- Shopping at local farmers' markets
- Not driving to the shops if possible




