Geography Test Yourself
Here's a really quick way of testing if you've learned the meanings of the key words in this section.
Look at the key word on the card and see if you can remember its definition.
If you get stuck, you can be shown the mnemonic to reveal an image that should help you remember.
To check if you're right, or remind you if you've forgotten, press the card to flip it.
Go through the whole list to see how many definitions you can recall.
Revisit any that you had difficulty remembering until you're confident you can
recall all of them.
Analyse
Explain each part
Analyse – Explain each part

And here are a set of lies (analyse): Please explain each one.
Assess
Explain advantages and disadvantages
Assess – Explain advantages and disadvantages
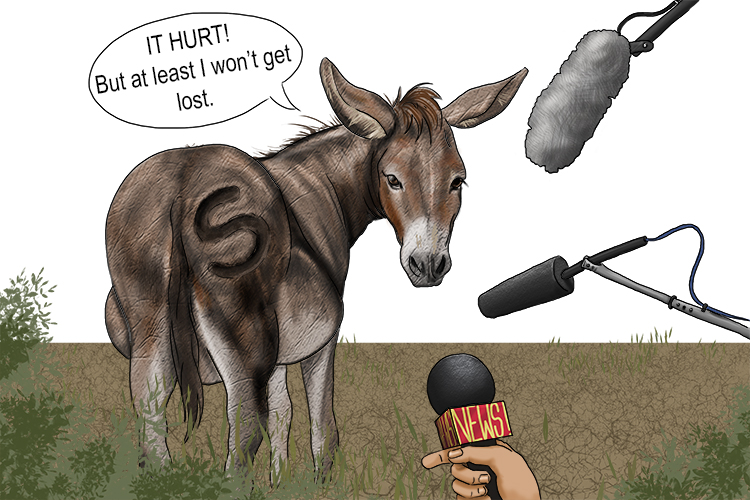

The ass had an 'S' (assess) branded on its backside. "Explain to me, Mrs Ass, what the advantages and disadvantages of that 's' are."
Compare
Identify similarities and differences
Compare – Identify similarities and differences
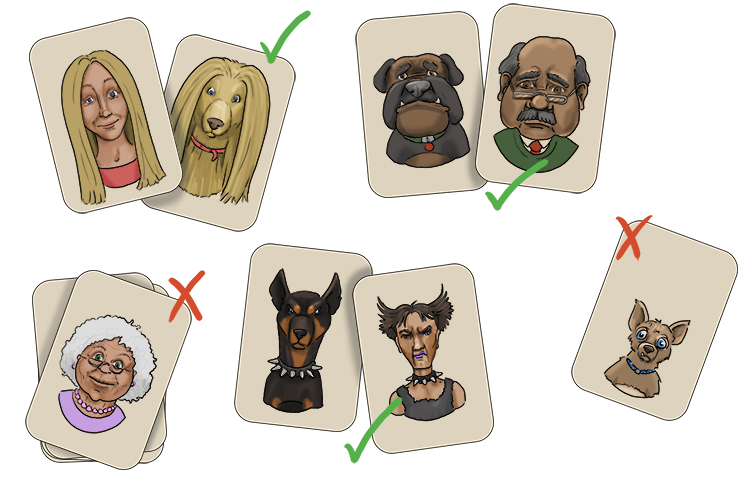
Come pair (compare) two pictures that have similarities and discard all those with too many differences. This will allow you to put the correct owner and dog together.
Contrast
Identify differences
Contrast – Identify differences
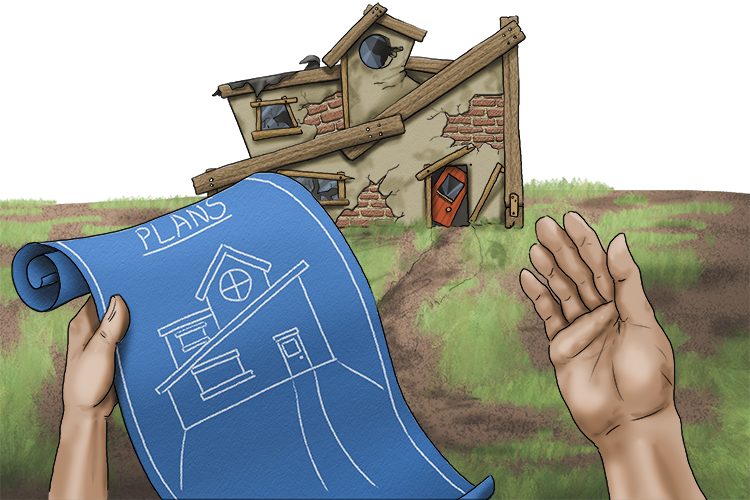

The contract didn't last (contrast). He was asked to build something similar to the plans, but you can easily identify the differences.
Criticise
Explain weaknesses and strengths
Criticise – Explain weaknesses and strengths
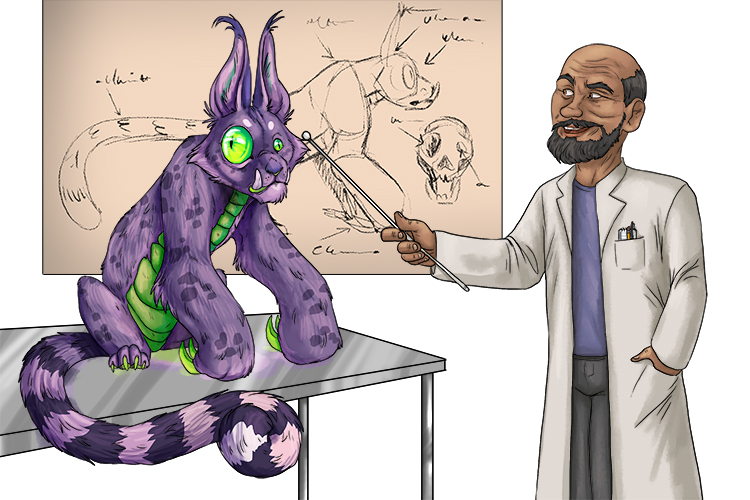
The critter's eyes (criticise) were odd - one was bigger than the other. "Now junior vet, please explain why one eye is weak and the other strong".
Describe
Simply say what you see
Describe – Simply say what you see
Note: If you are not there, simply say what you would see if you were there or how it works.
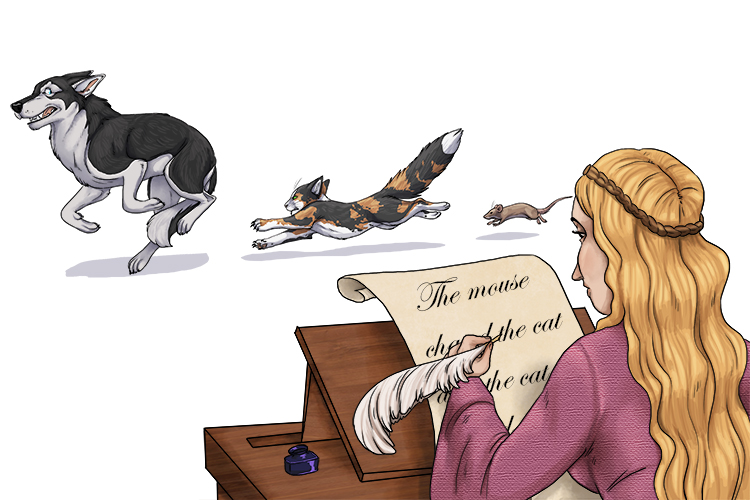

The scribe (describe) wrote down what she could see was happening.
Discuss
Give advantages, disadvantages and form a conclusion
Discuss – Give advantages, disadvantages and form a conclusion

In the discus (discuss), she could choose a disc of any shape or size. She had to work out the advantages and disadvantages of each disc and finally conclude by choosing one.
Distinguish
Describe difference
Distinguish – Describe difference
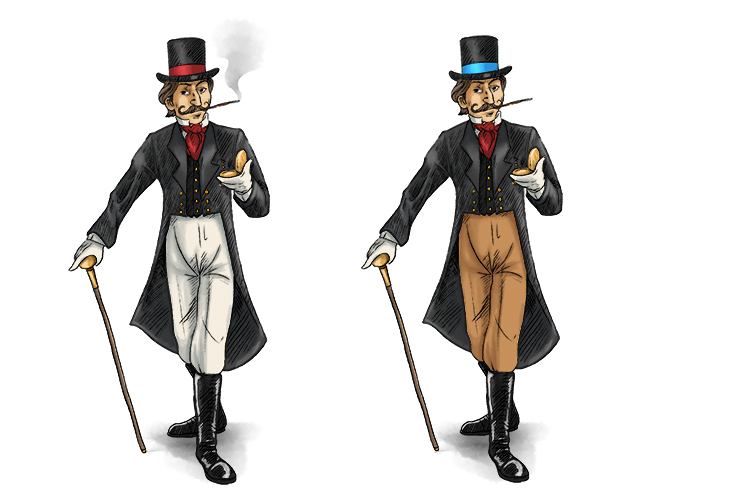

Here are two pictures of a distinguished fellow, but can you spot and describe the differences? See the different coloured trousers, see the smoke not coming out of the cigarette, see the blue band on the hat.
Evaluate
Give the advantages and disadvantages
Evaluate – Give the advantages and disadvantages
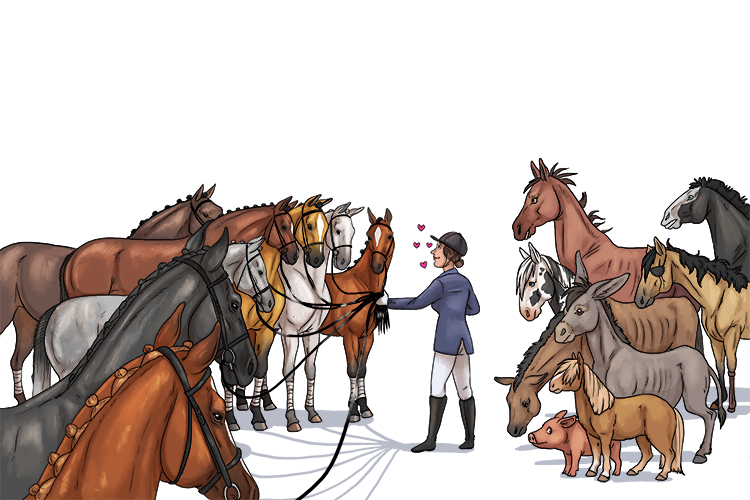

She valued eight (evaluate) of them very highly: they had all the advantages she needed. The other eight she didn't want. They had all the disadvantages.
Explain
Give reasons
Explain – Give reasons
Note: It helps if you can use the word "because" where you can.
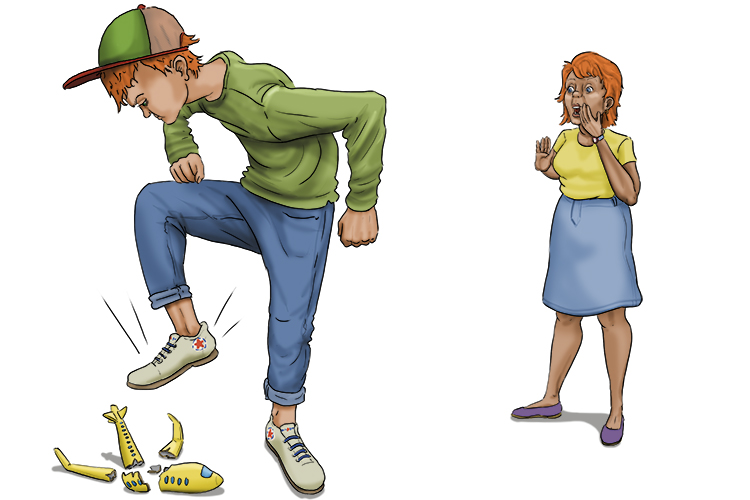

It's now an ex-plane (explain). "Johnny, why did you stamp on that plane? Give me your reasons!"
Illustrate
Give examples
Illustrate – Give examples
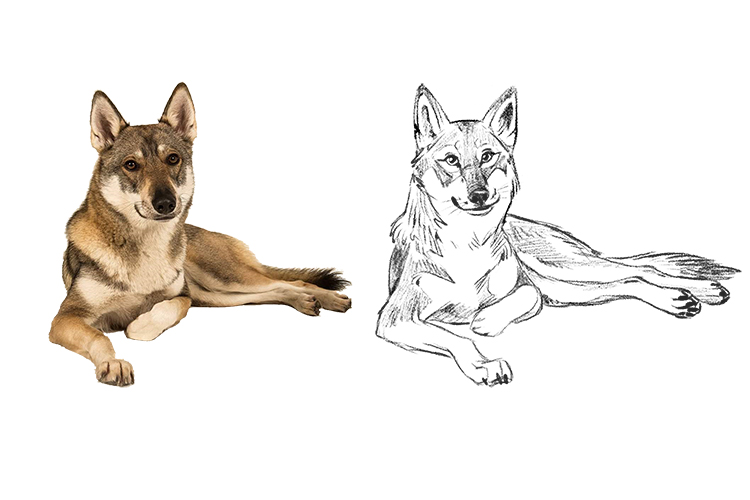

Do you want some illustrations? (Illustrate). Here we give you some examples.
Note: "illustrate" might be used in one of two contexts - i.e. illustrate how something happened or how something works in writing; or draw a diagram or representation to explain something. In some cases maybe both approaches are required. The way the question is phrased by the exam board should make clear what is required.
Justify
Give evidence to support answer
Justify – Give evidence to support answer
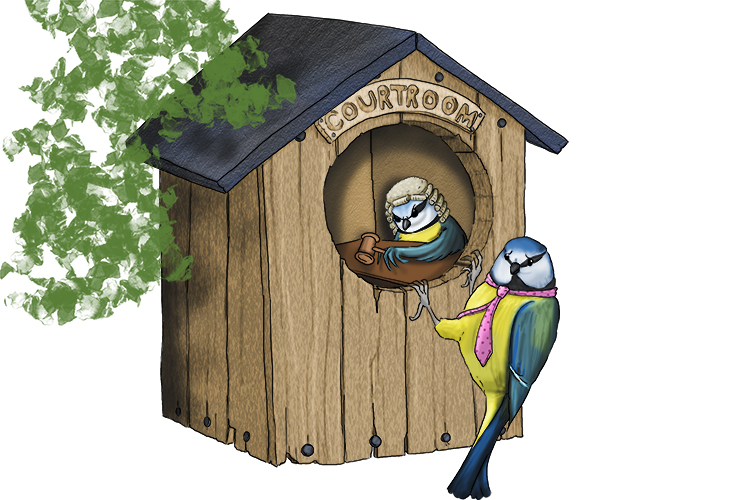

You're just in time to fly (justify) into the courtroom to give evidence and answer questions to support your friend.
Outline
What it is about, briefly
Outline – What it is about, briefly
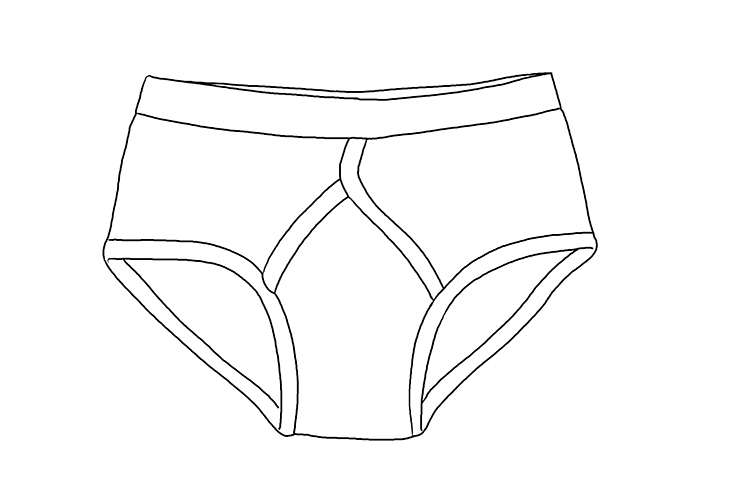

This is an outline (outline) drawing. What is it about? A pair of briefs.
State
Recall a fact or facts
State – Recall a fact or facts
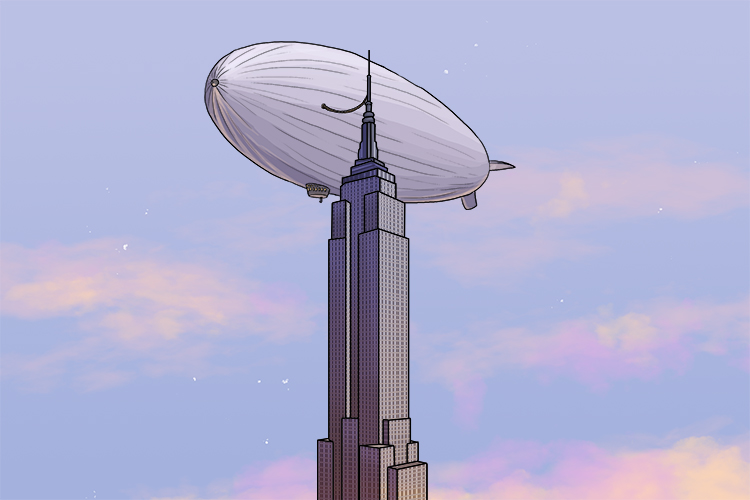

If I said the words "Empire State building", could you recall an interesting fact about it? It's upper tower was originally designed as a mooring mast for airships.
Suggest
Present a possible case
Suggest – Present a possible case
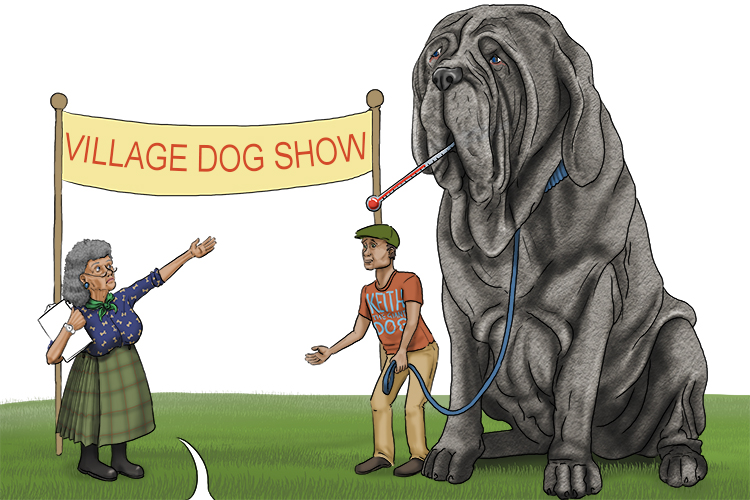

"I suggest you don't present him because he has a possible case of flu."
Summarise
Main Point
Summarise – Main Point
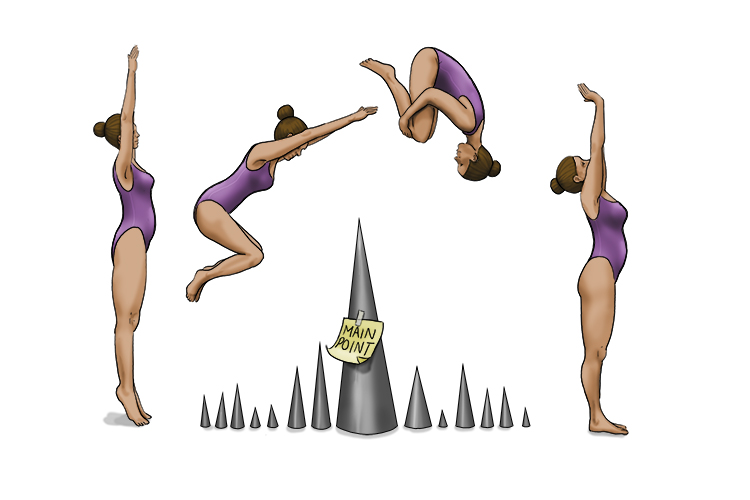
Somersault and rise (summarise) above the main point.
To What Extent
Judge the effect (result) of something
To What Extent – Judge the effect (result) of something
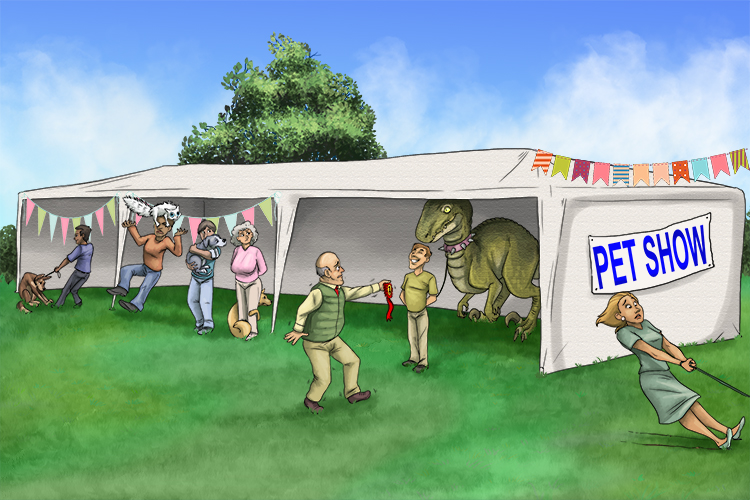

It was in the extension of the tent (extent) that the judges decided the results of the town's pet competition.
HIC
High-Income Country
HIC – High-Income Country
High-income countries are those that have an average income per person above a figure that is worked out each year by the World Bank. For instance, in 2013 the high-income figure was 12,746 US dollars (or equivalent).
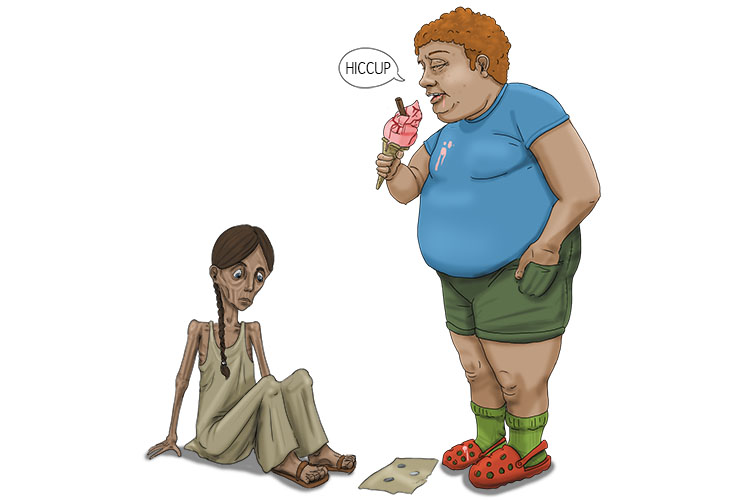

He had hiccups (HIC) after stuffing his face with ice cream. He could afford to, being from such a high-income country.
NOTE:
Refer to Mammoth Memory remembering numbers before trying to understand the following:
How to remember 12,746 dollars is the amount high-income countries were based on in 2013:
Try to imagine that after the high-income person finished his ice cream, he went home in a tank.
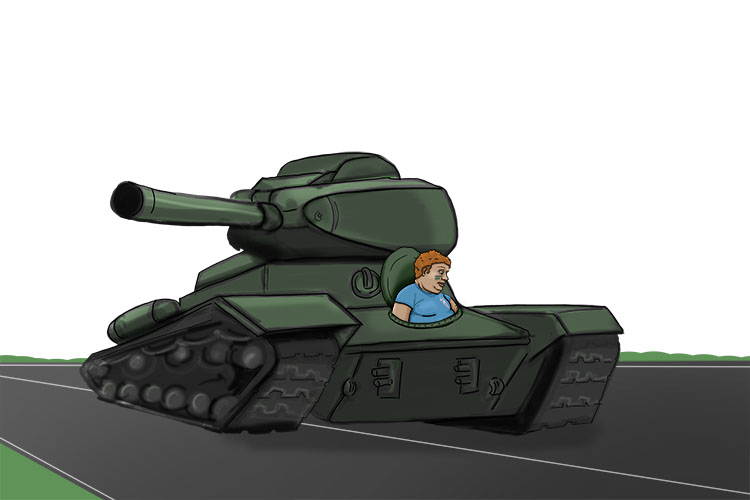

And in Mammoth Memory's numbers system:
TANK = 127
Then imagine it was rush hour and the tank got caught in a traffic jam.

In the Mammoth Memory number system:
RUSH = 46
When used together:
TANK RUSH = 12746
PLEASE NOTE: This figure is updated every year by the World Bank. As you get closer to your exam you might want to update the figures you will use. We chose 2013 as an example, to show you how easy it can be to remember specific numbers.
LIC
Low-Income Country
LIC – Low-Income Country
Low-income countries are those that have an average income per person below a figure that is worked out each year by the World Bank. For instance, in 2013 the low-income figure was 1,045 US dollars (or equivalent).
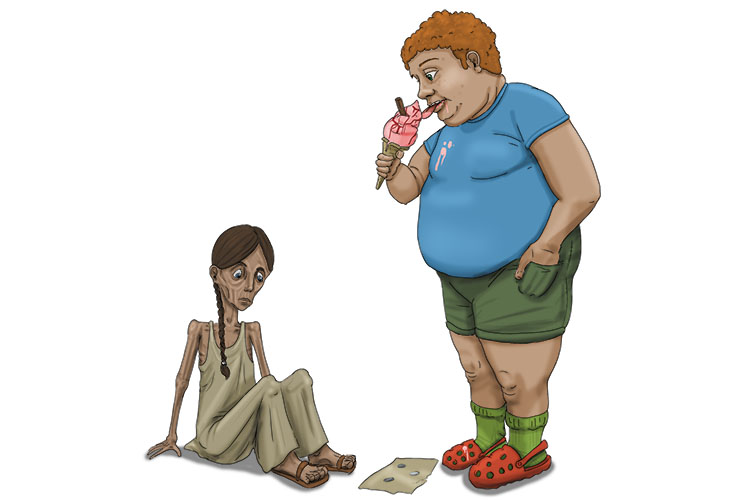

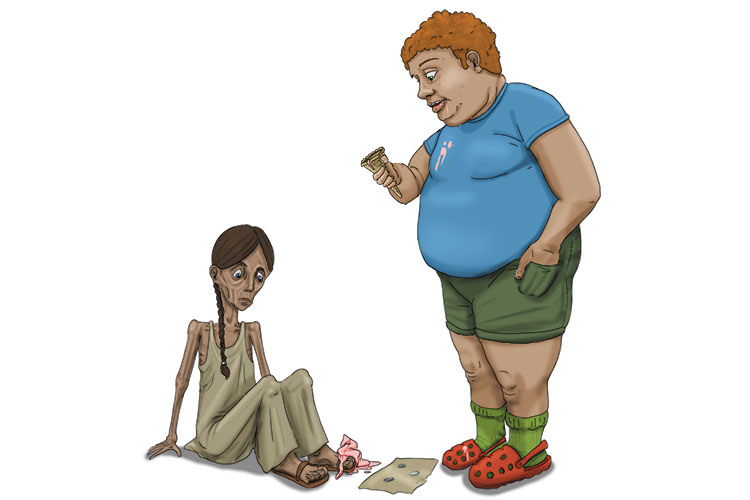
She couldn't afford one lick (LIC) of ice cream because she was from such a low-income country.
NOTE:
Refer to Mammoth Memory remembering numbers before trying to understand the following:
How to remember 1045 dollars is the amount low-income countries are based on in 2013:
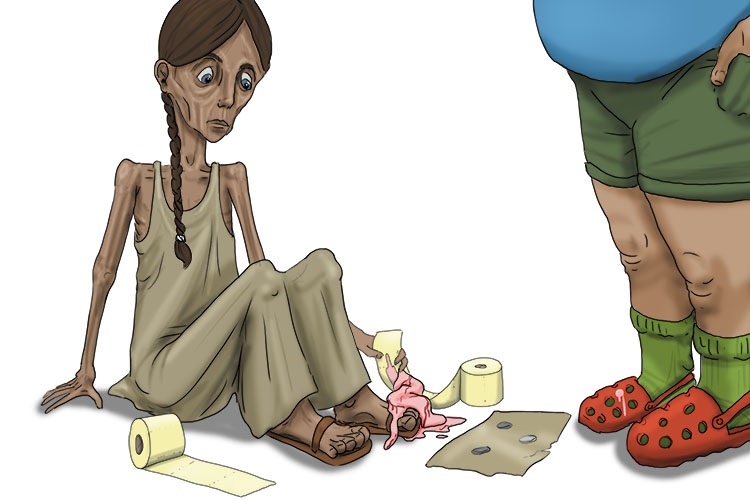
Try to imagine that the ice cream from the previous picture dropped on the low-income person's toes.

And in Mammoth Memory's number system:
TOES = 10
Then imagine toilet roll was used to clean the ice cream off her toes.

In the Mammoth Memory number system:
ROLL = 45
When used together:
TOES ROLL = 1045
PLEASE NOTE: This figure is updated every year by the World Bank. As you get closer to your exam you might want to update the figures you will use. We chose 2013 as an example, to show you how easy it can be to remember specific numbers.
NEE
Newly Emerging Economy
NEE – Newly Emerging Economy
A country that has begun to experience higher rates of economic development, usually with higher levels of industrialisation. An NEE differs from an LIC in that it no longer relies primarily on agriculture, has made gains in infrastructure and industrialised growth, and is experiencing increasing incomes and high levels of investment. Examples include Brazil, Russia, China and South Africa.
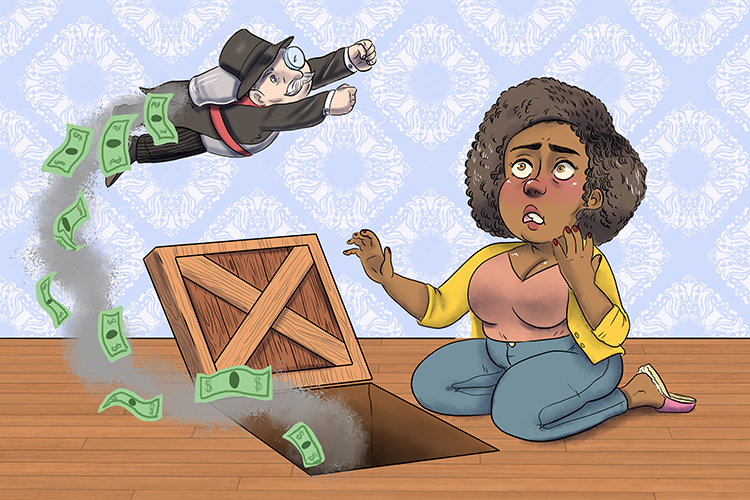

She got down on her knees (NEEs), lifted the hatch and a newly emerging economy shot out.
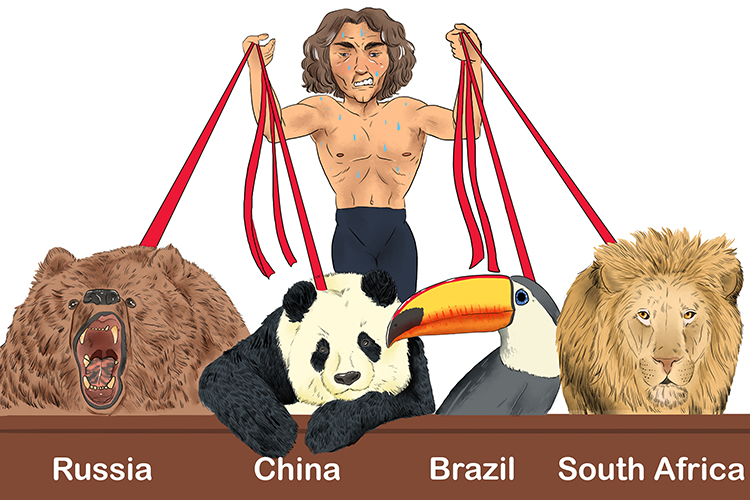

Russia, China, Brazil and South Africa all emerged from below.


























