Soft Engineering – Use of the natural environment surrounding a river for schemes that work with the river's natural processes
To remember the meaning of the term Soft Engineering, use the following mnemonic:
The soft engineer (soft engineering) wasn't really that soft - he used stones, sand and other materials as well as plants.

Examples of soft engineering around rivers:
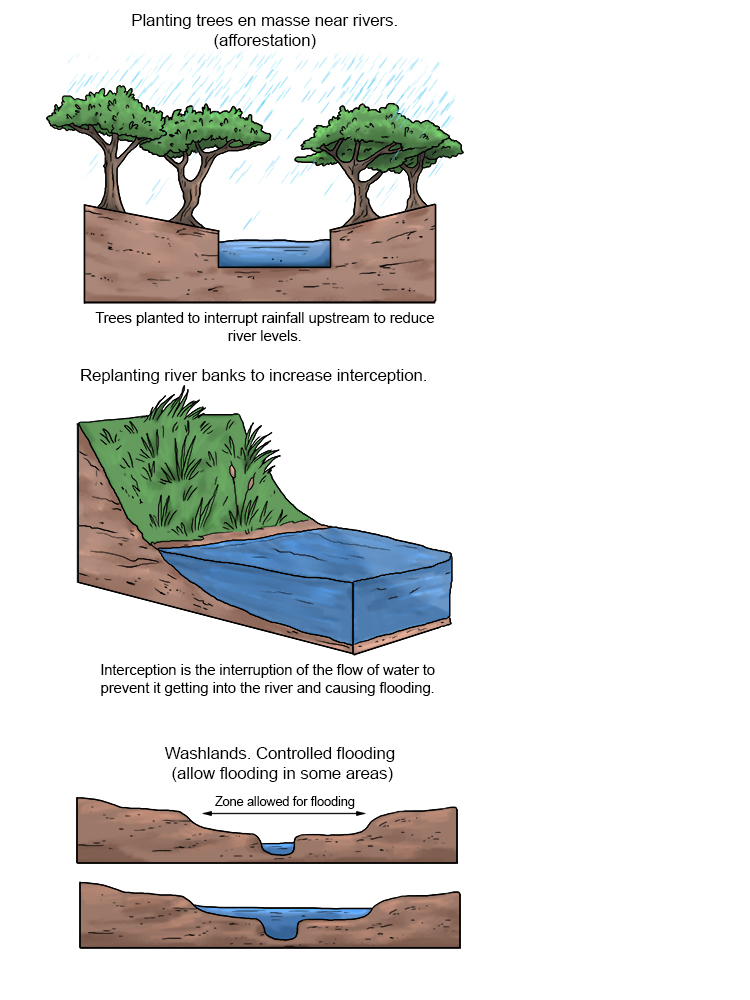
Soft engineering avoids the use of artificial materials, taking a more sustainable and natural approach to managing river landscapes.
Compared to hard engineering, soft engineering is generally less expensive, more long-term, attractive, and sustainable.
Soft engineering in river landscapes is usually aimed at flood prevention.
Examples include planting vegetation to help reduce run-off of rainwater into the river, and dredging – excavating sediment from the riverbed to improve its flow. The excavated sediment may be placed along banks to further help prevent flooding.




