Manipulating parabolas further examples
Example 1
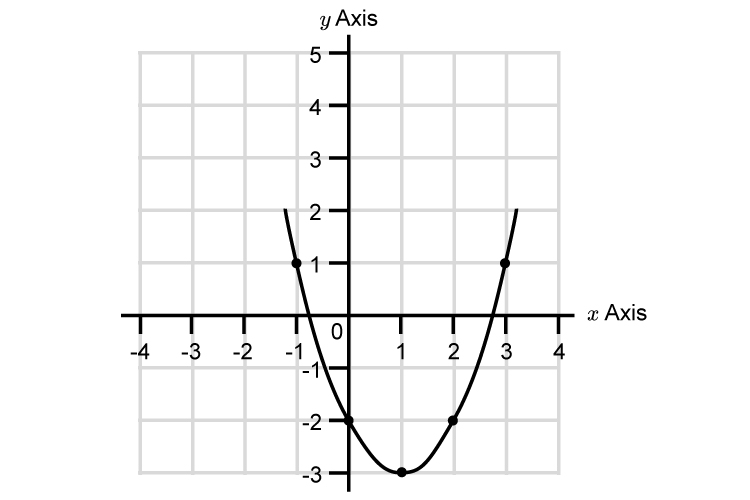
An equation of a parabola is `y=x^2-2x-2`
Translate this equation upwards by `3`.
To answer this, first plot `y=x^2-2x-2`
| `x=3` | `y=3^2-2times3-2` | `=9-6-2` | `=1` | |
| `x=2` | `y=2^2-2times2-2` | `=4-4-2` | `=-2` | |
| `x=1` | `y=1^2-2times1-2` | `=1-2-2` | `=-3` | |
| `x=0` | `y=0^2-2times0-2` | `=0-0-2` | `=-2` | |
| `x=-1` | `y=(-1)^2-2times-1-2` | `=1+2-2` | `=1` |
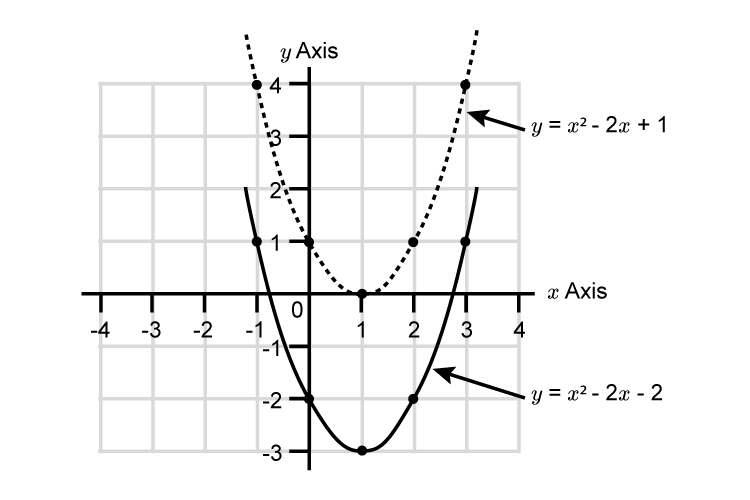
To translate `y=x^2-2x-2` upwards by `3`
First remember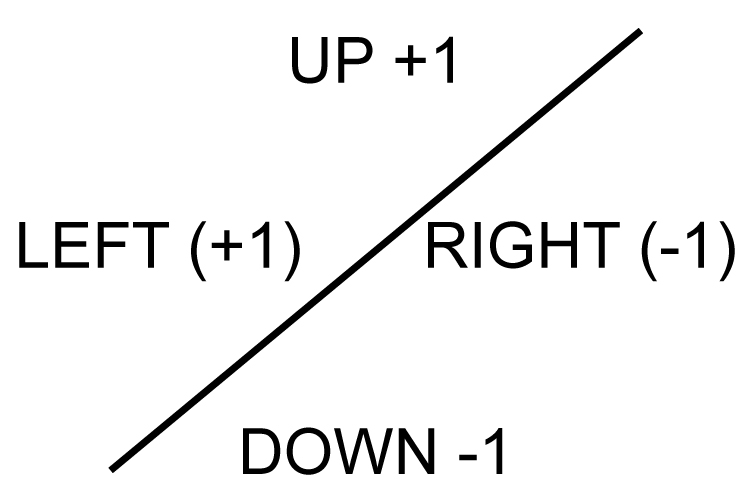
Upwards is therefore add `+3` to the whole equation.
`y=x^2-2x-2+3`
`y=x^2-2x+1`
Now plot this new parabola.
| `x=3` | `y=3^2-2times3+1` | `=9-6+1` | `=4` | |
| `x=2` | `y=2^2-2times2+1` | `=4-4+1` | `=1` | |
| `x=1` | `y=1^2-2times1+1` | `=1-2+1` | `=0` | |
| `x=0` | `y=0^2-2times0+1` | `=0-0+1` | `=1` | |
| `x=-1` | `y=(-1)^2-2times(-1)+1` | `=1+2+1` | `=4` |
Example 2
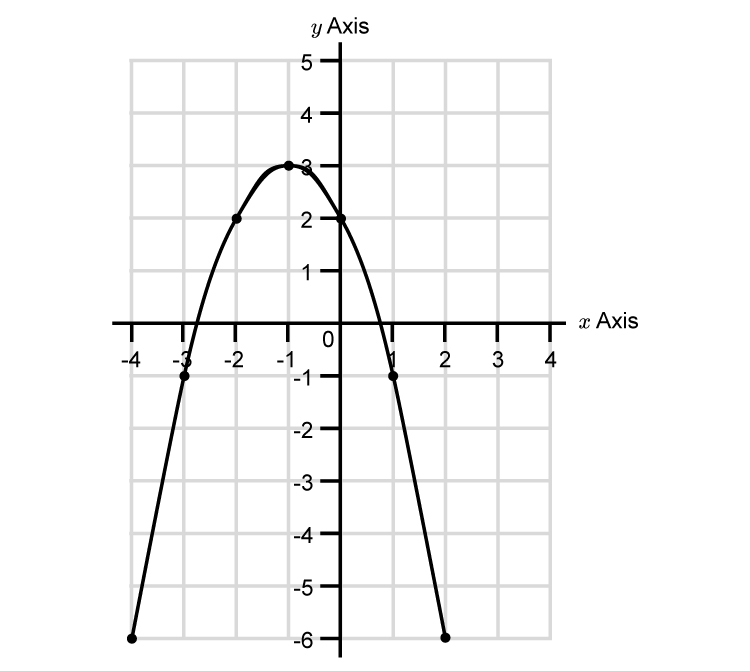
An equation of a parabola is `y=-1(x^2)-2x+2`
Translate this equation downwards by `3`.
To answer this, first plot `y=-1(x^2)-2x+2`
| `x=3` | `y=-(3)^2-2times3+2` | `=-9-6+2` | `=-13` | |
| `x=2` | `y=-(2)^2-2times2+2` | `=-4-4+2` | `=-6` | |
| `x=1` | `y=-(1)^2-2times1+2` | `=-1-2+2` | `=-1` | |
| `x=0` | `y=0^2-2times0+2` | `=0-0+2` | `=2` | |
| `x=-1` | `y=-(-1)^2-2times(-1)+2` | `=-1+2+2` | `=3` | |
| `x=-2` | `y=-(-2)^2-2times(-2)+2` | `=-4+4+2` | `=2` | |
| `x=-3` | `y=-(-3)^2-2times(-3)+2` | `=-9+6+2` | `=-1` | |
| `x=-4` | `y=-(-4)^2-2times(-4)+2` | `=-16+8+2` | `=-6` |
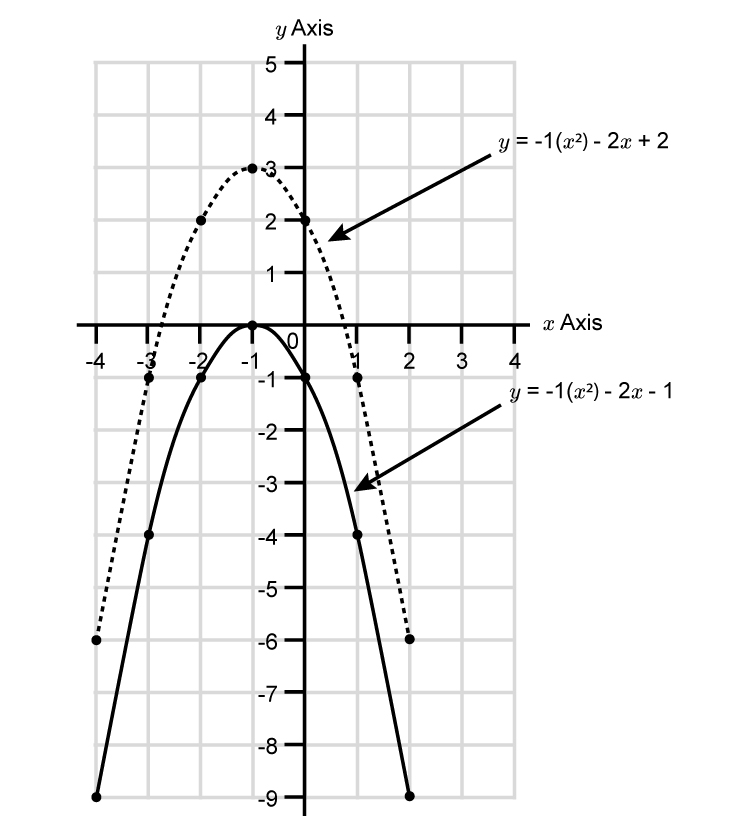
To translate `y=-x^2-2x+2` downwards by `3`
First remember
Upwards is therefore subtract `3` from the whole equation.
`y=-x^2-2x+2-3`
`y=x^2-2x-1`
Now plot the new parabola
| `x=3` | `y=-(3)^2-2times3-1` | `=-9-6-1` | `=-16` | |
| `x=2` | `y=-(2)^2-2times2-1` | `=-4-4-1` | `=-9` | |
| `x=1` | `y=-(1)^2-2times1-1` | `=-1-2-1` | `=-4` | |
| `x=0` | `y=0^2-2times0-1` | `=0-0-1` | `=-1` | |
| `x=-1` | `y=-(-1)^2-2times(-1)-1` | `=-1+2-1` | `=0` | |
| `x=-2` | `y=-(-2)^2-2times(-2)-1` | `=-4+4-1` | `=-1` | |
| `x=-3` | `y=-(-3)^2-2times(-3)-1` | `=-9+6-1` | `=-4` | |
| `x=-4` | `y=-(-4)^2-2times(-4)-1` | `=-16+8-1` | `=-9` |
Example 3
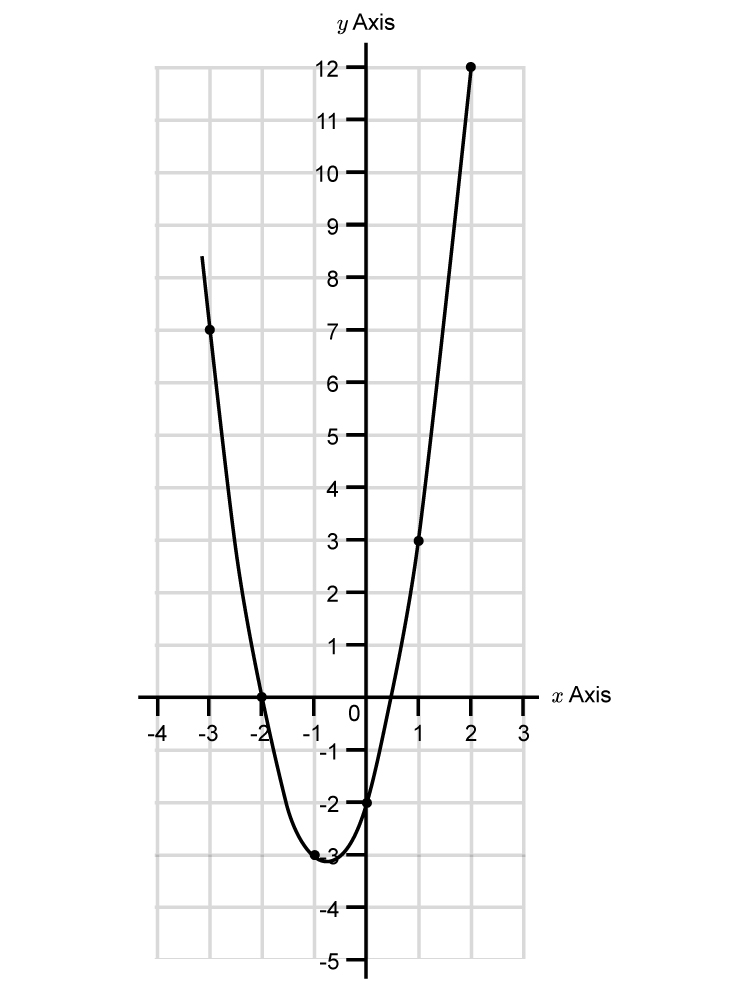
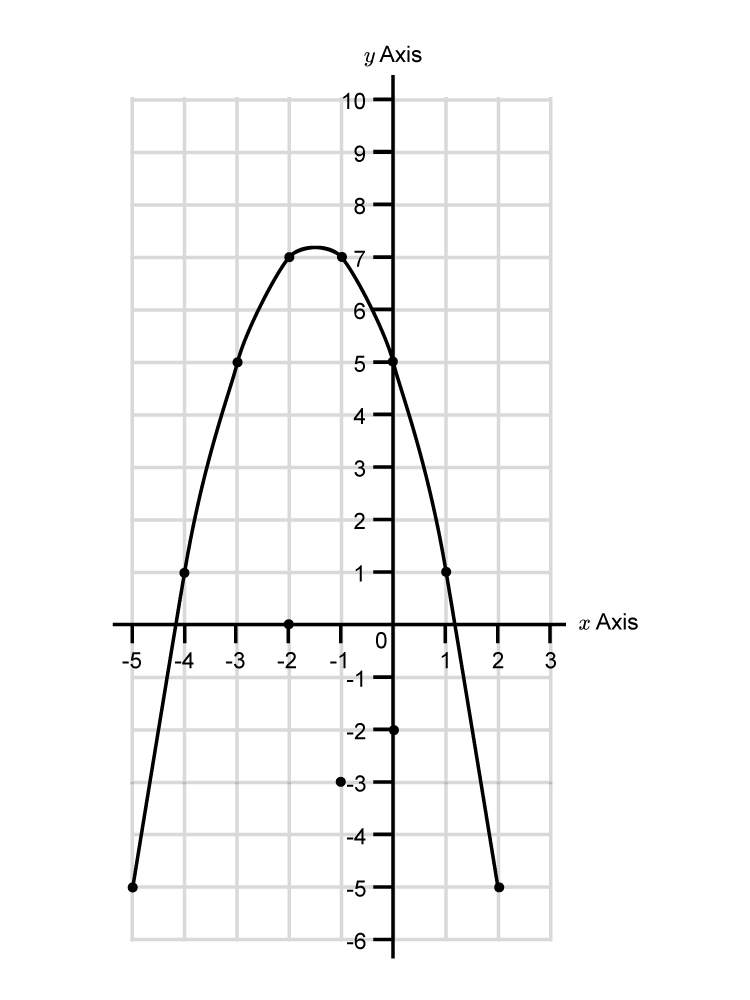
An equation of a parabola is `y=2x^2+3x-2`
Translate this equation to the right by `4`.
To answer this, first plot `y=2x^2+3x-2`
| `x=2` | `y=2times2^2+3times2-2` | `=8+6-2` | `=12` | |
| `x=1` | `y=2times1^2+3times1-2` | `=2+3-2` | `=3` | |
| `x=0` | `y=2times0^2+3times0-2` | `=0+0-2` | `=-2` | |
| `x=-1` | `y=2times(-1)^2+3times(-1)-2` | `=2-3-2` | `=-3` | |
| `x=-2` | `y=2times(-2)^2+3times(-2)-2` | `=8-6-2` | `=0` | |
| `x=-3` | `y=2times(-3)^2+3times(-3)-2` | `=18-9-2` | `=7` |
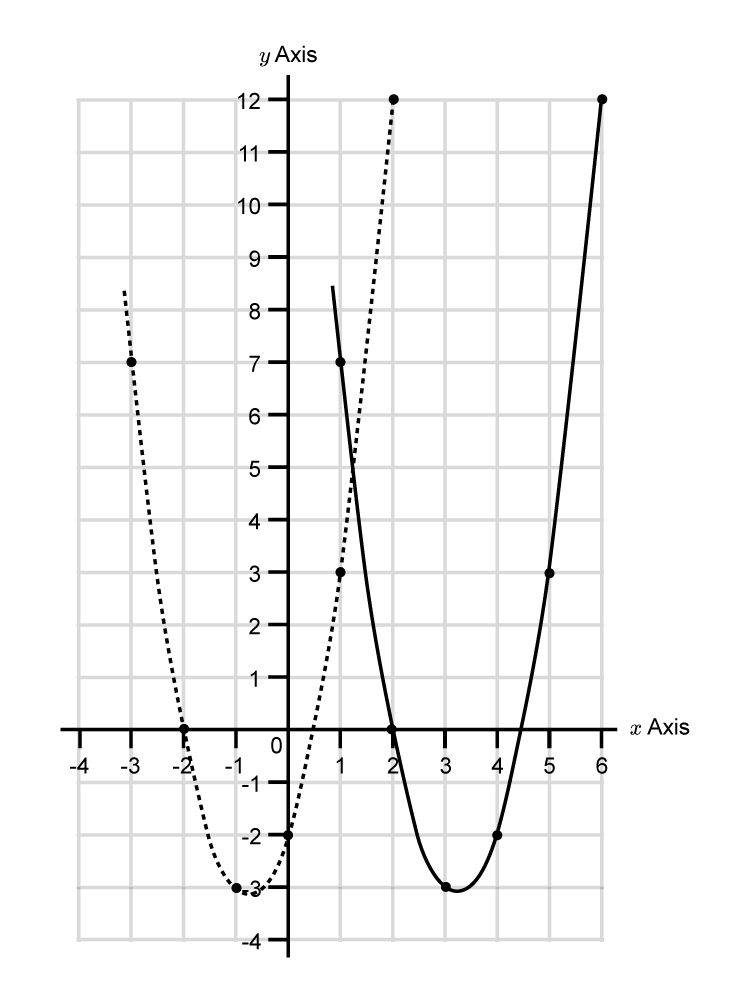
To translate `y=2x^2+3x-2` to the right by `4`
First remember
To the right is therefore `(-4)` from each `x`
`y=2(x-4)^2+3(x-4)-2`
Plot this on the original curve.
| `x=6` | `y=2(6-4)^2+3(6-4)-2` | `=8+6-2` | `=12` | |
| `x=5` | `y=2(5-4)^2+3(5-4)-2` | `=2+3-2` | `=3` | |
| `x=4` | `y=2(4-4)^2+3(4-4)-2` | `=0+0-2` | `=-2` | |
| `x=3` | `y=2(3-4)^2+3(3-4)-2` | `=2-3-2` | `=-3` | |
| `x=2` | `y=2(2-4)^2+3(2-4)-2` | `=8-6-2` | `=0` | |
| `x=1` | `y=2(1-4)^2+3(1-4)-2` | `=18-9-2` | `=7` |
Example 4
An equation of a parabola is `y=x^2-3x+4`
Translate this equation to the left by `3`.
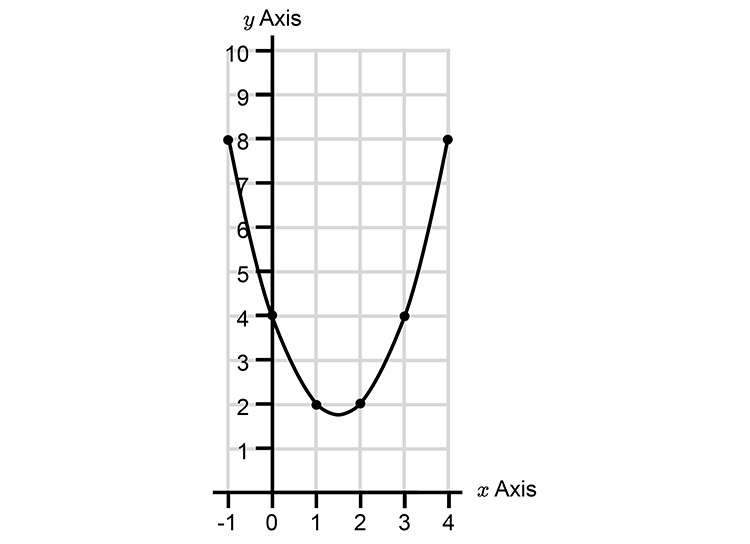
To answer this, first plot `y=x^2-3x+4`
| `x=4` | `y=4^2-3xx4+4` | `=16-12+4` | `=8` | |
| `x=3` | `y=3^2-3xx3+4` | `=9-9+4` | `=4` | |
| `x=2` | `y=2^2-3xx2+4` | `=4-6+4` | `=2` | |
| `x=1` | `y=1^2-3xx1+4` | `=1-3+4` | `=2` | |
| `x=0` | `y=0^2-3xx0+4` | `=0-0+4` | `=4` | |
| `x=-1` | `y=(-1)^2-3times(-1)+4` | `=1+3+4` | `=8` |
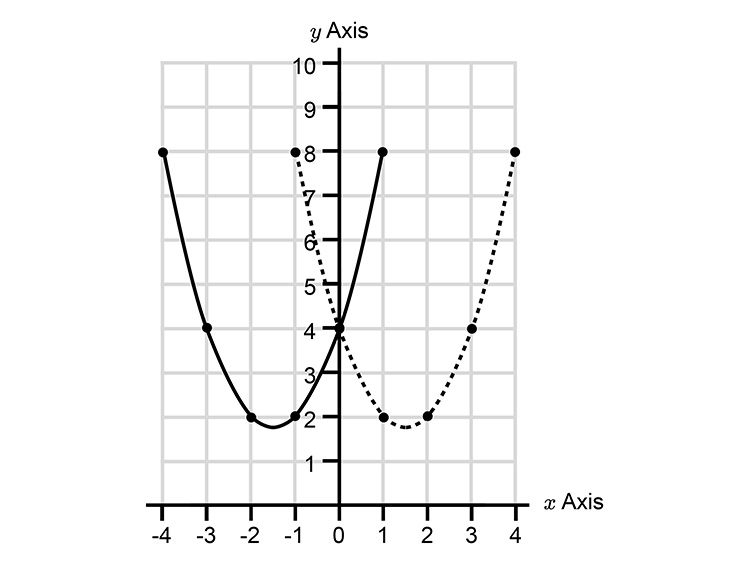
To translate `y=x^2-3x+4` to the left by `3`
First remember
To the left is therefore`(+3)` for each `x`
`y=(x+3)^2-3(x+3)+4`
| `x=1` | `y=(1+3)^2-3(1+3)+4` | `=16-12+4` | `=8` | |
| `x=0` | `y=(0+3)^2-3(0+3)+4` | `=9-9+4` | `=4` | |
| `x=-1` | `y=(-1+3)^2-3(-1+3)+4` | `=4-6+4` | `=2` | |
| `x=-2` | `y=(-2+3)^2-3(-2+3)+4` | `=1-3+4` | `=2` | |
| `x=-3` | `y=(-3+3)^2-3(-3+3)+4` | `=0-0+4` | `=4` | |
| `x=-4` | `y=(-4+3)^2-3(-4+3)+4` | `=1+3+4` | `=8` |
Example 5
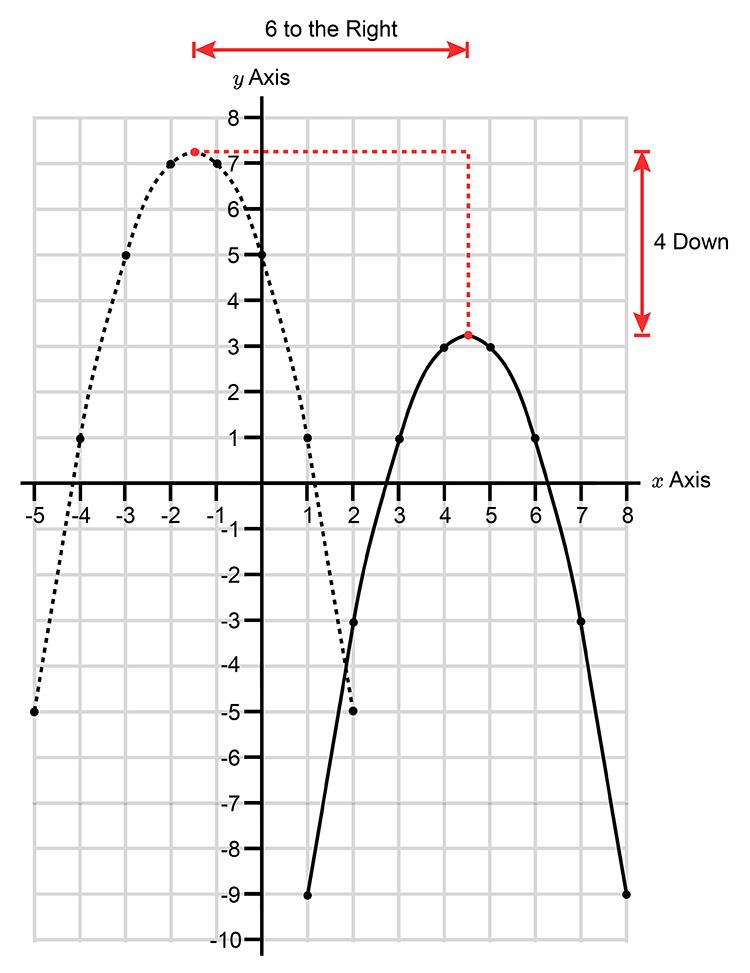
An equation of a parabola is `y=-1(x^2) -3x+5`. Translate this equation 6 to the right and 4 down.
To answer this first plot `y=-1(x^2)-3x+5`
| `x=2` | `y=-(2)^2-3times2+5` | `=-4-6+5` | `=-5` | |
| `x=1` | `y=-(1)^2-3times1+5` | `=-1-3+5` | `=1` | |
| `x=0` | `y=-(0)^2-3times0+5` | `=-0-0+5` | `=5` | |
| `x=-1` | `y=-(-1)^2-3times-1+5` | `=-1+3+5` | `=7` | |
| `x=-2` | `y=-(-2)^2-3times-2+5` | `=-4+6+5` | `=7` | |
| `x=-3` | `y=-(-3)^2-3times-3+5` | `=-9+9+5` | `=5` | |
| `x=-4` | `y=-(-4)^2-3times-4+5` | `=-16+12+5` | `=1` | |
| `x=-5` | `y=-(-5)^2-3times-5+5` | `=-25+15+5` | `=-5` |
To translate 6 to the right and 4 down
Remember 
`6` to the right is therefore `(-6)` from each `x`
`4` down is therefore `-4` from whole equation.
So `y=-1(x^2)-3x+5`
Becomes
`y=-1(x-6)^2-3(x-6)+5-4`
`y=-(x-6)^2-3(x-6)+1`
| `x=8` | `y=-1times(8-6)^2-3(8-6)+1=-4-6+1` | `=-9` | |
| `x=7` | `y=-1times(7-6)^2-3(7-6)+1=-1-3+1` | `=-3` | |
| `x=6` | `y=-1times(6-6)^2-3(6-6)+1=0-0+1` | `=1` | |
| `x=5` | `y=-1times(5-6)^2-3(5-6)+1=-1+3+1` | `=3` | |
| `x=4` | `y=-1times(4-6)^2-3(4-6)+1=-4+6+1` | `=3` | |
| `x=3` | `y=-1times(3-6)^2-3(3-6)+1=-9+9+1` | `=1` | |
| `x=2` | `y=-1times(2-6)^2-3(2-6)+1=-16+12+1` | `=-3` | |
| `x=1` | `y=-1times(1-6)^2-3(1-6)+1=-25+15+1` | `=-9` |