The difference between an electromagnet and a solenoid
An electromagnet is an electrically induced magnet.
As the name implies, it is a core of magnetic material (such as iron) surrounded by a coil of wire through which an electric current is passed to magnetise the core.
An electromagnet looks like the following:
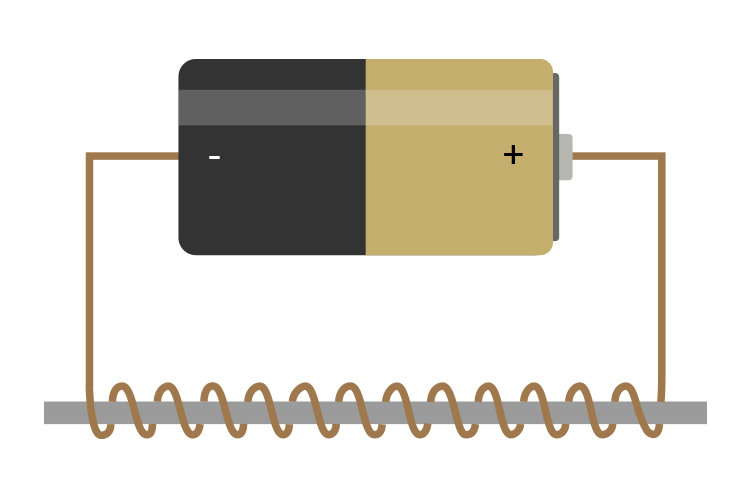
A solenoid is a cylindrical coil of wire acting as a magnet when carrying an electric current. A solenoid is the same as an electromagnet but without a core of material that can be magnetised i.e. iron (which is magnetically soft).
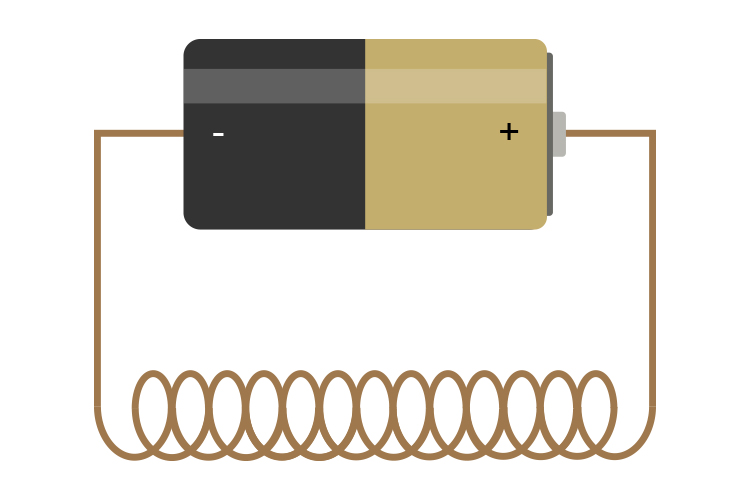
NOTE: A solenoid still produces a magnetic field but not as strong as an electromagnet of the same size. In fact, the magnetic field with the iron core is more than 1,000 times stronger (yes – one thousand times).
To recall what a solenoid is, remember this:
Solenoid = Stolen and Void
Just imagine that the core of an electromagnet has its core stolen and there is now a void.
Summary
An electromagnet is a coil of wire around an iron core.
A solenoid is just a cylindrical coil of wire.
Conclusion
Wrapping the coil around an iron core produces a stronger magnetic field.




