Neurone overview
Neurones come in a number of different shapes and forms but are best described as “nerve impulse carriers”.
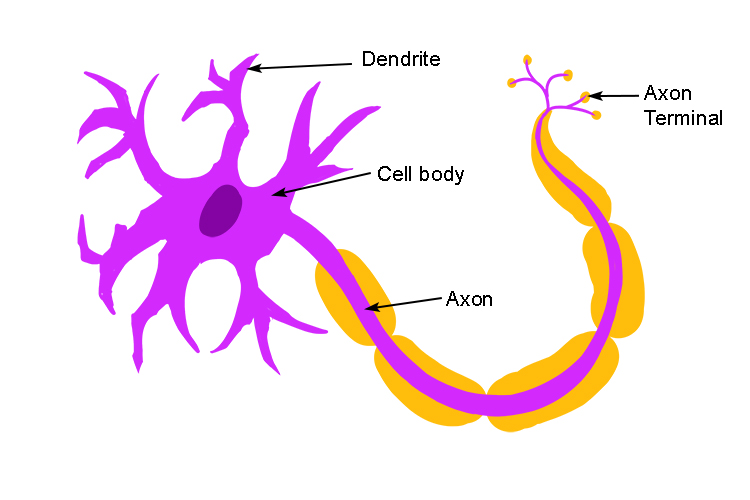
For basic biology, neurones are first described as having dendrites, a cell body, an axon and an axon terminal.
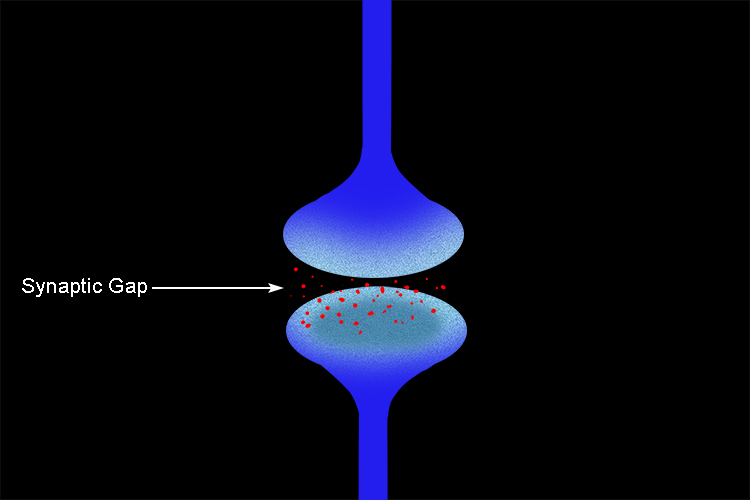
Neurones are further described as having synaptic gaps which allow signals to pass one way only.
Three basic forms of nerve cell are first discussed, which are sensory neurones, relay neurones (also known as interneurons) and motor neurones.
Changes in the environment are picked up by sense organ receptors which turn the stimulation into an electrical impulse.
This signal can be passed directly through to the brain or can pass to a dendrite and through further neurones.
Basic biology goes no further but, for information only, on the following pages there are some more details of neurones and their complexity.




