Mutualism – both benefit
Relationship where both species benefit.

The relationship counsellor had to mute (mutualism) both sides so they could benefit from hearing her advice without being interrupted.
Examples
An example of mutualism would be the relationship between humans and their gut bacteria. The bacteria are provided with their ideal temperature and a food source in the form of semi digested food in the intestine. In turn the bacteria break down the remaining food, releasing amino acids and vitamins that can then be absorbed by the gut.
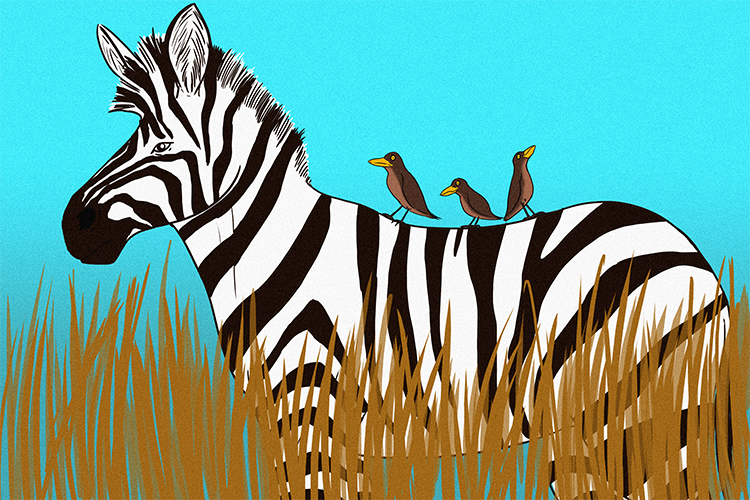

Oxpeckers are birds that exhibit mutualism with several other species such as hippos and zebras. The oxpecker removes and eats parasites such as ticks and mites from the skin of the zebra/hippo etc.




