Chemical bonding: An introduction
Bonding is about atoms achieving full outer shells or orbits.
There are three key types of bonding:
- ionic
- covalent (including simple covalent structures and giant covalent structures)
- metallic
The two main types of bonding are ionic bonding and covalent bonding.
Ionic (attracted atoms)
Ionic bonding is a chemical reaction where oppositely charged atoms (ions) are attracted to each other to form a bond.
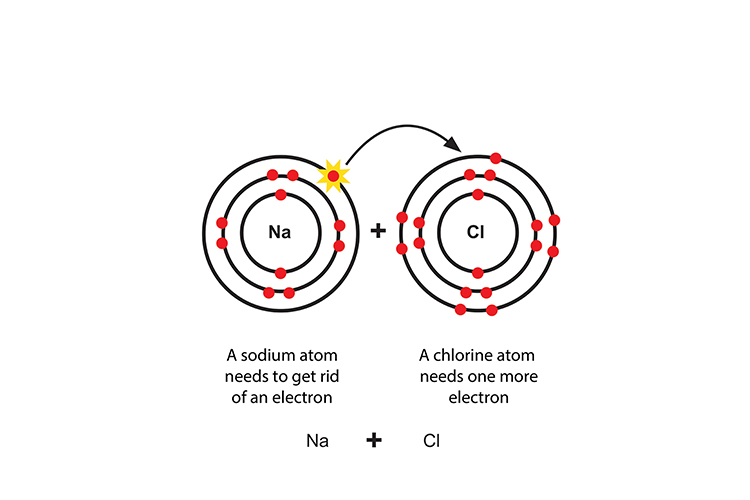
Sodium transfers an electron to chlorine to make a positive sodium ion and a negative chloride ion.
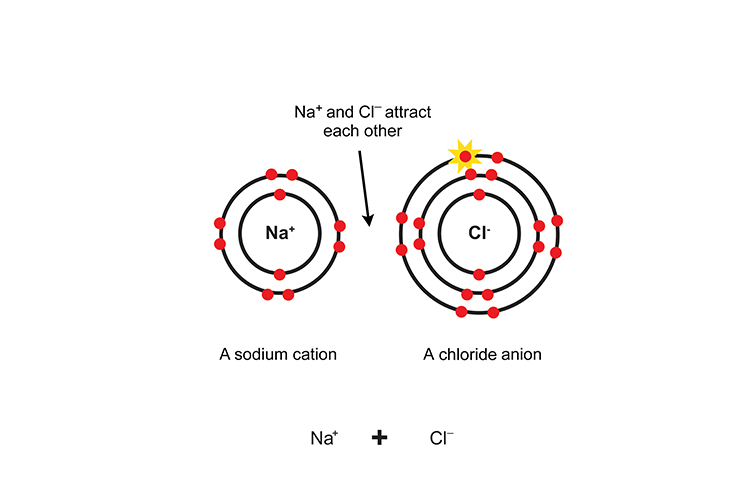
Because they are oppositely charged, the ions are attracted to each other like magnets and an ionic bond is formed.
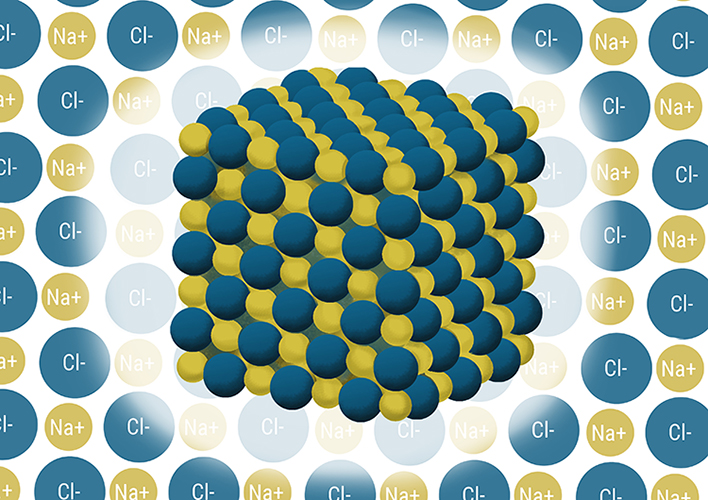
Covalent bonding (sharing)
Covalent bonding is the sharing of electrons.
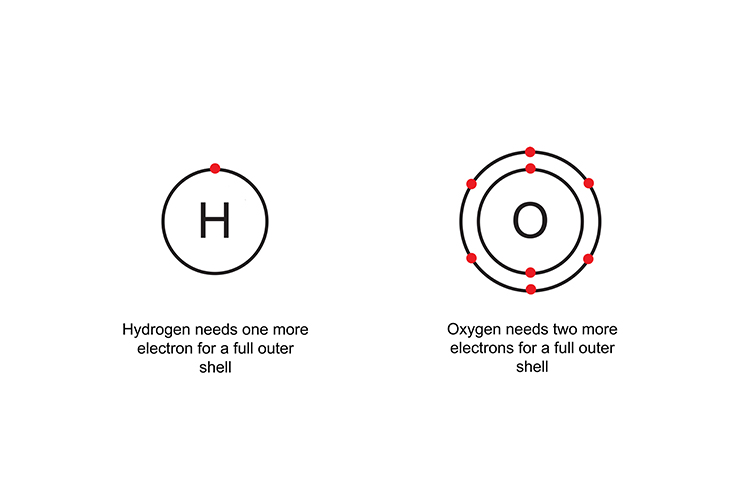
Two hydrogen atoms are needed to complete oxygen’s outer shell and form a covalent compound (H2O).
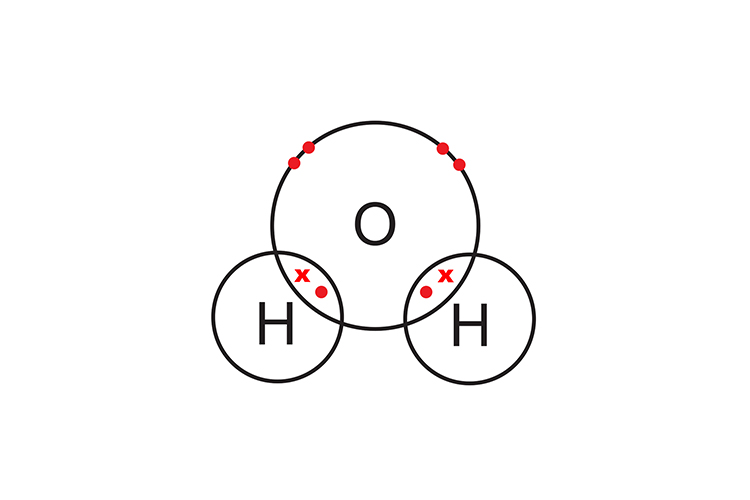
Note for higher tier Chemistry students
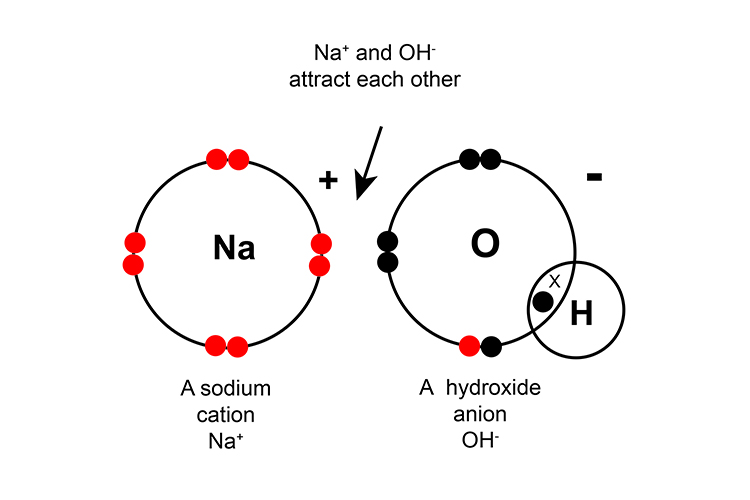
Some compounds contain both ionic and covalent bonds such as sodium nitrate NaNO3, sodium hydroxide NaOH and calcium carbonate CaCO3.
Metallic bonding
Metallic bonding involves a sea of electrons.
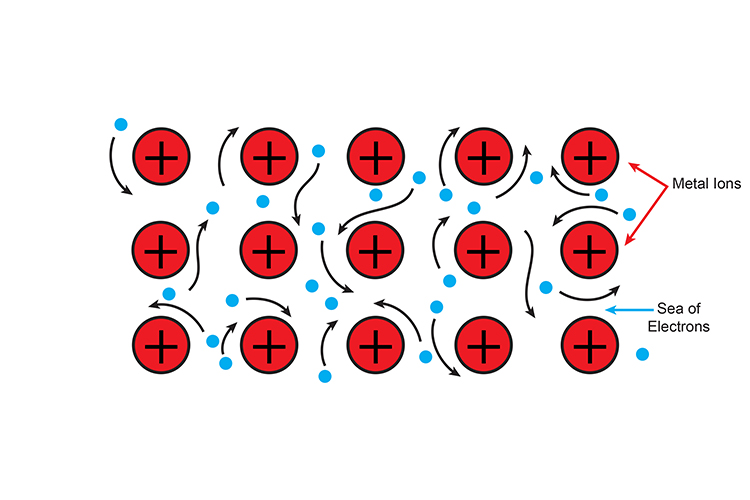
A sea of electrons around positive metal ions.




