Nuclear Power – The energy released by a nuclear reaction, especially by fission or fusion
Nuclear energy uses fuel made from mined and processed uranium to make steam and generate electricity.
Now Use Caution, Loose Electrons Are Reacting
The initial letters of "now use caution, loose electrons are reacting" make the word nuclear to remind you that nuclear power is all about the energy from the atom.
An atom with electrons, neutrons and protons:
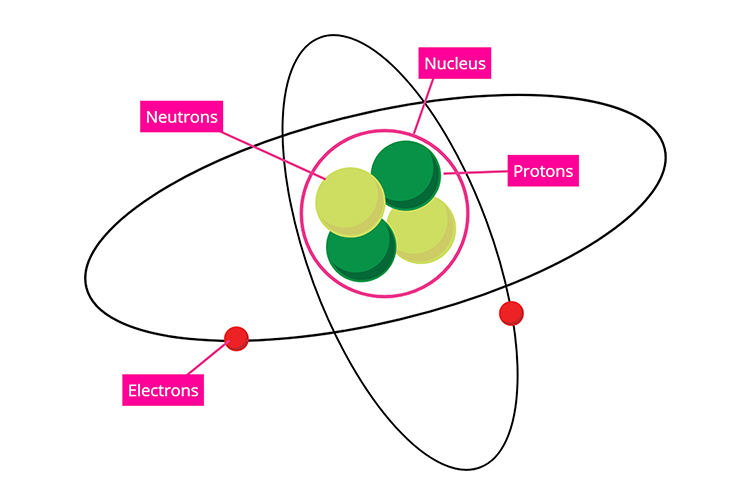
Nuclear energy is the energy in the nucleus, or core, of an atom.
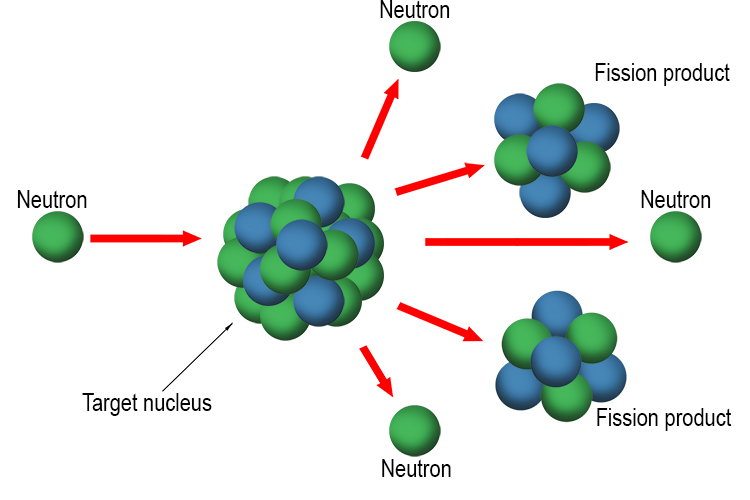
Nuclear power is the practice of splitting atoms to boil water, turn turbines and generate electricity.
Nuclear Power Generator:
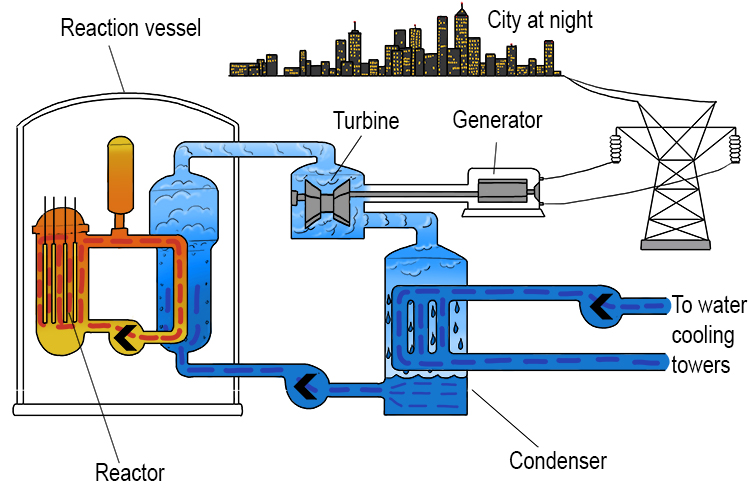
Steam is produced from the nuclear reactor, which turns a turbine, which then generates electricity.
It is predicted that there will be an increasing role for nuclear power as a means of producing reliable electricity on a large scale.
Electricity demand is increasing about twice as fast as overall energy use and is likely to rise by more than half over the next twenty years.
Nuclear power currently provides about 10% of the world's electricity.
While several countries have decided to phase out their nuclear energy programmes because of perceived risks associated with the technology, almost all reports on future energy supplies predict an increase in nuclear power generation.
The risks associated with nuclear power include the possibility of accidental releases of radiation which can threaten lives and wellbeing, and the problem of disposing of waste, which remains radioactive for lengthy periods.
Nuclear disasters at Chernobyl, Ukraine, in 1986 (the result of an accident), and at Fukushima, Japan, in 2011 (the result of an earthquake that caused a tsunami) are evidence of the dangers of nuclear power generation.
Other issues with nuclear power include:
- Decommissioning nuclear power stations (dismantling and making them harmless) at the end of their lives is very expensive.
- The uranium and plutonium used to generate the power are not renewable, so will eventually run out.
However, many still regard nuclear energy as clean and safe. They emphasise that, apart from the radioactive waste issue, it does not create air pollution or release greenhouse gases, and that the only by-product is steam, which is recycled into the atmosphere as clean water vapour.




