Synthetic Cubism – art form in which objects are flattened out into a 2D image with no depth, using simple shapes and bright colours
(Pronounced sin-thet-ik kyoo-biz-uhm)
Note: Analytical cubism breaks down an object from multiple viewpoints and recreates an image in fragmented and overlapping shapes.
Synthetic cubism was a stage of cubism from around 1912 to 1914 in which Picasso, Braque and Jean Gris composed their work, using collage materials.
To remember what synthetic cubism is, recall the following:
It was a sin not to consider the aesthetics of the cubes (synthetic cubism) – someone flattened them into two dimensions, and they looked like a collage.
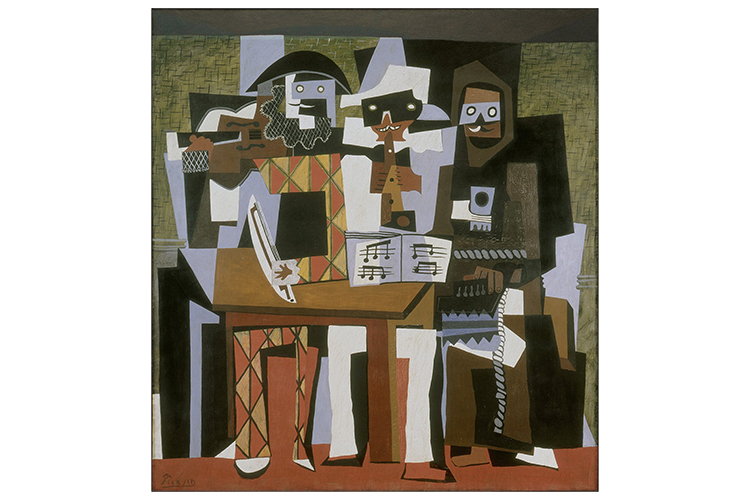


Pablo Picasso, Nous Autres Musiciens (Three Musicians), 1921
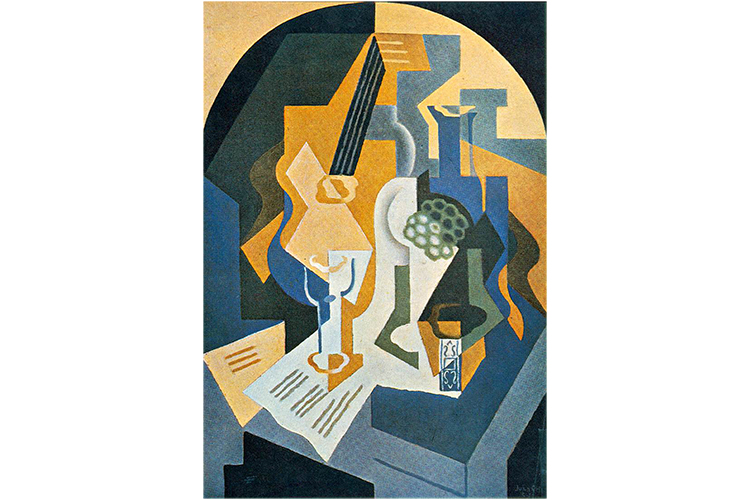

Juan Gris, Still Life with Fruit Dish and Mandolin, 1919
Synthetic Cubism Project
Creating a synthetic cubist-style artwork requires breaking forms down into their simplest forms, a two-dimensional shape.
Many cubist paintings were of still life arrangements. We will stick to this theme with our project but simplify it even more by using only one object.
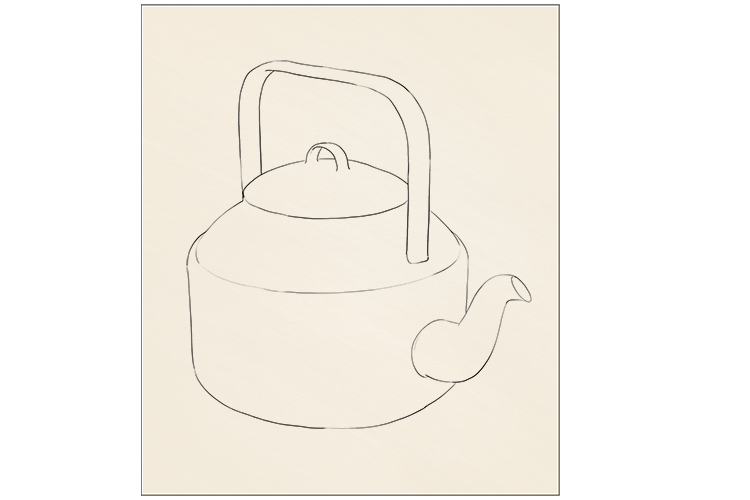
To start, decide on the object you want to draw. Try to think of an interesting yet simple form. We have chosen a teapot.
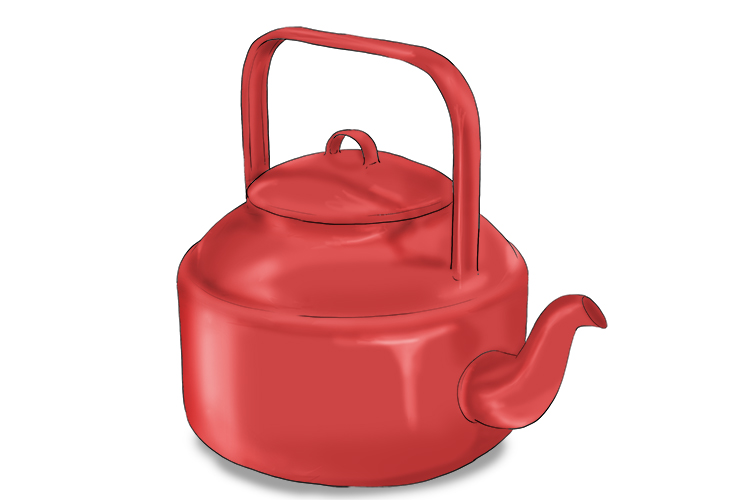

You only have to worry about the outline and any important lines on your object. Keep the image in the centre of the paper.
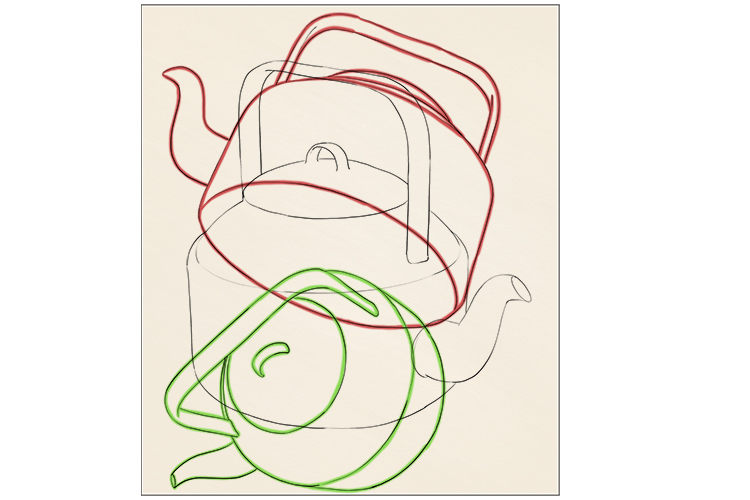
Overlapping your initial drawing, draw the object again from different angles (we have highlighted each one in a different colour so you can clearly see each outline).
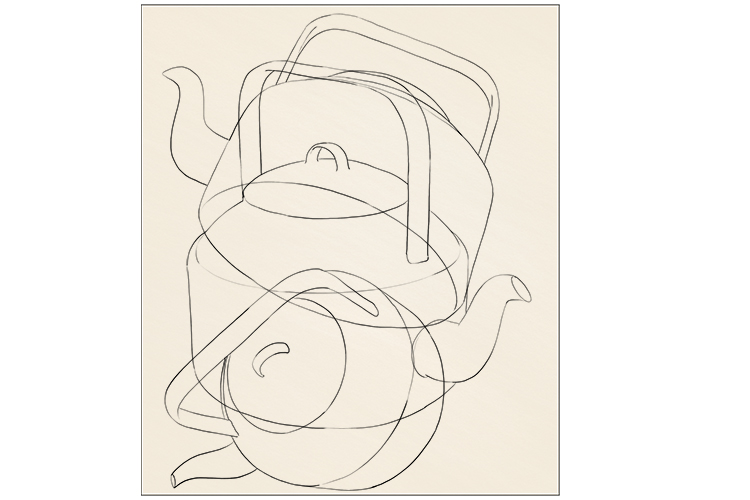
Now you have a drawing that is simply an assortment of different-shaped panels.
In some of the panels, draw in the outline of some simple geometric patterns or designs. Wood grain is used a lot.
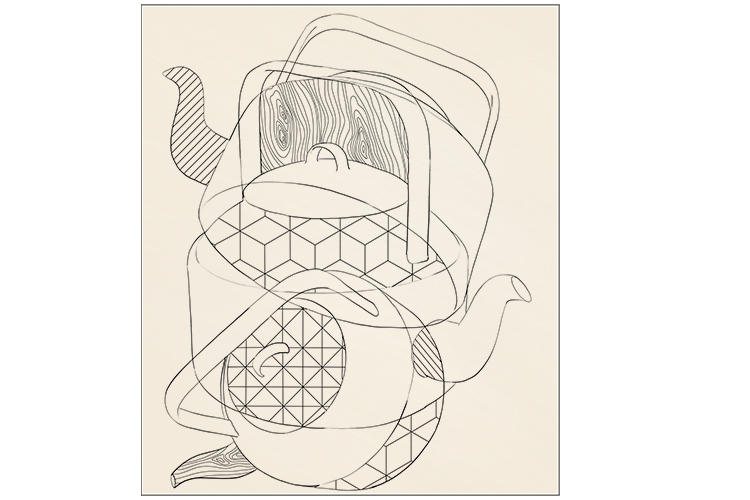
You can now colour your drawing with paint or pencil crayon. Try using complementary colours, as these opposing colours work well together and cubist artists used them a lot in their paintings.

Synthetic Cubism.




